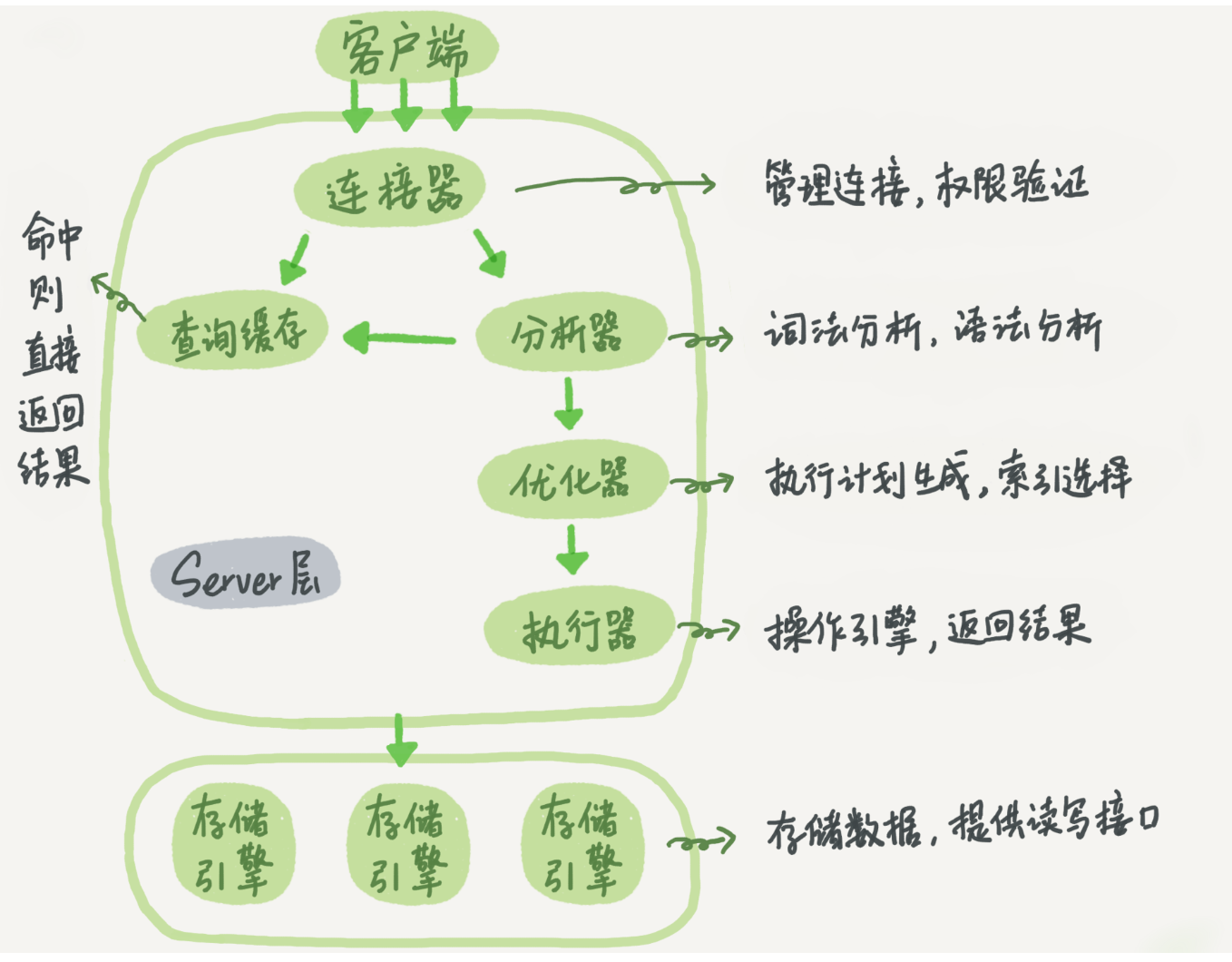
mysql架构示意图:
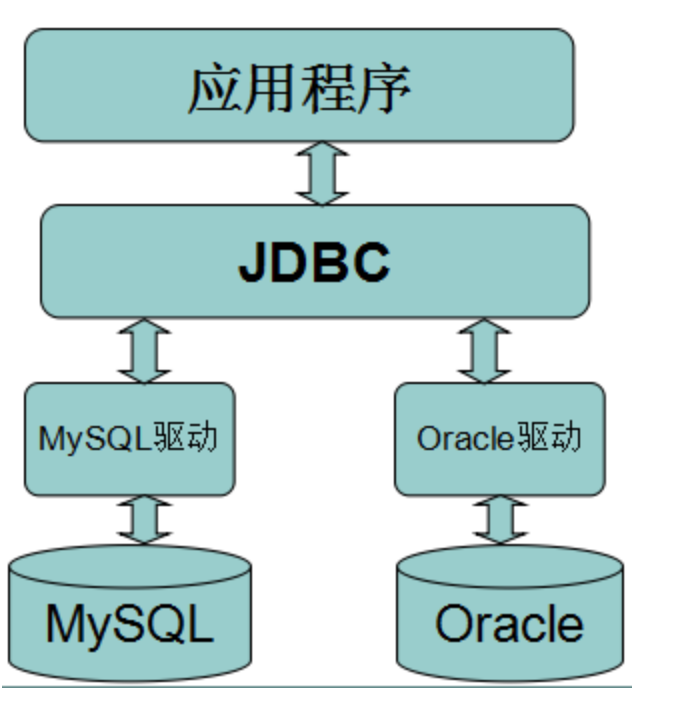
最原始的JDBC实现(mysql-connctor-java): 加载JDBC驱动程序 → 建立数据库连接Connection → 创建执行SQL的语句Statement(preparedStatement) → 处理执行结果ResultSet → 释放资源
DataSource->Connection->Statement
DataSource的核心方法:
public interface DataSource extends CommonDataSource,Wrapper {
Connection getConnection() throws SQLException;
Connection getConnection(String username, String password)
throws SQLException;
}
Connection核心api:
public interface Connection extends Wrapper, AutoCloseable {
Statement createStatement() throws SQLException;
PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql) throws SQLException;
CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql) throws SQLException;
void setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit) throws SQLException;
boolean getAutoCommit() throws SQLException;
void commit() throws SQLException;
void rollback() throws SQLException;
void close() throws SQLException;
boolean isClosed() throws SQLException;
}
Statement核心API定义,执行静态的sql:
public interface Statement extends Wrapper, AutoCloseable {
ResultSet executeQuery(String sql) throws SQLException;
int executeUpdate(String sql) throws SQLException;
void close() throws SQLException;
boolean execute(String sql, String columnNames[]) throws SQLException;
boolean isClosed() throws SQLException;
public boolean isCloseOnCompletion() throws SQLException;
}
ibatis的核心应该是重写statement
sharding-jdbc核心应该也是对statement
druid核心应该是Connection
各个中间件通过Statement的execute向下递归调用