一、Python 2.7.x 和 3.x 版本的区别小结
- print函数
1、python2
1 import platform 2 3 print ‘Python’, platform.python_version() 4 print ‘Hello, World!’ 5 print(“Hello,World!’) 6 print "text", ; print 'print more text on the same line'
输出结果:
1 Python 2.7.6 2 Hello, World! 3 Hello, World! 4 text print more text on the same line
2、python3
1 import platform 2 3 print('Python', platform.python_version()) 4 print('Hello, World!') 5 6 print("some text,", end="") 7 print(' print more text on the same line')
结果输出: 1 Python 3.5.1 2 Hello, World! 3 some text, print more text on the same line
1 >>> print 'Hello,World!' 2 File "<stdin>", line 1 3 print 'Hello,World!' 4 ^ 5 SyntaxError: Missing parentheses in call to 'print'
注意:
在Python 2中使用额外的括号也是可以的。但反过来在Python 3中想以Python2的形式不带括号调用print函数时,会触发SyntaxError。
- 整数除法
1、python2
1 print '3 / 2 =', 3 / 2 2 print '3 // 2 =', 3 // 2 3 print '3 / 2.0 =', 3 / 2.0 4 print '3 // 2.0 =', 3 // 2.0
结果输出:
1 3 / 2 = 1 2 3 // 2 = 1 3 3 / 2.0 = 1.5 4 3 // 2.0 = 1.0
2、python3
1 print('3 / 2 =', 3 / 2) 2 print('3 // 2 =', 3 // 2) 3 print('3 / 2.0 =', 3 / 2.0) 4 print('3 // 2.0 =', 3 // 2.0)
结果输出:
1 3 / 2 = 1.5 2 3 // 2 = 1 3 3 / 2.0 = 1.5 4 3 // 2.0 = 1.0
- 触发异常
1、python2
Python 2支持新旧两种异常触发语法,而Python 3只接受带括号的的语法(不然会触发SyntaxError):
1 >>> raise IOError, "file error" 2 Traceback (most recent call last): 3 File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> 4 IOError: file error
1 >>> raise IOError("file error") 2 Traceback (most recent call last): 3 File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> 4 IOError: file error
2、python3
1 >>> raise IOError, "file error" 2 File "<stdin>", line 1 3 raise IOError, "file error" 4 ^ 5 SyntaxError: invalid syntax
1 >>> raise IOError("file error") 2 Traceback (most recent call last): 3 File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> 4 OSError: file error
- 异常处理
1、python2
1 try: 2 let_us_cause_a_NameError 3 except NameError, err: 4 print err, '--> our error message'
结果输出:
1 name 'let_us_cause_a_NameError' is not defined --> our error message
2、python3
1 try: 2 let_us_cause_a_NameError 3 except NameError as err: 4 print(err, '--> our error message')
结果输出:
1 name 'let_us_cause_a_NameError' is not defined --> our error message
Python 3中的异常处理也发生了一点变化。在Python 3中必须使用“as”关键字。
-
input()解析用户的输入
Python 3改进了input()函数,这样该函数就会总是将用户的输入存储为str对象。在Python 2中,为了避免读取非字符串类型会发生的一些危险行为,不得不使用raw_input()代替input()。
1、python2
1 >>> my_input = input('enter a number: ') 2 3 enter a number: 123 4 5 >>> type(my_input) 6 <type 'int'> 7 8 >>> my_input = raw_input('enter a number: ') 9 10 enter a number: 123 11 12 >>> type(my_input) 13 <type 'str'>
2、python3
1 >>> my_input = input('enter a number: ') 2 enter a number: 123 3 >>> type(my_input) 4 <class 'str'>
-
返回可迭代对象
1、python2
1 print range(3) 2 print type(range(3))
结果输出:
1 [0, 1, 2] 2 <type 'list'>
2、python3
1 print(range(3)) 2 print(type(range(3))) 3 print(list(range(3)))
结果输出:
1 range(0, 3) 2 <class 'range'> 3 [0, 1, 2]
二、用户输入
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 4 # 将用户输入的内容赋值给 name 变量 5 name = raw_input("请输入用户名:") 6 7 # 打印输入的内容 8 print name
结果输出:
1 >>> name = raw_input("请输入用户名:") 2 请输入用户名:yinjia 3 >>> print name 4 yinjia
输入密码时,如果想要不可见,需要利用getpass 模块中的 getpass方法,即:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 4 import getpass 5 6 # 将用户输入的内容赋值给 name 变量 7 pwd = getpass.getpass("请输入密码:") 8 9 # 打印输入的内容 10 print pwd
结果输出:
1 >>> import getpass 2 >>> pwd = getpass.getpass("请输入密码:") 3 请输入密码: 4 >>> print pwd 5 123456
三、while循环
- 基本循环
Python 编程中 while 语句用于循环执行程序,即在某条件下,循环执行某段程序,以处理需要重复处理的相同任务。其基本形式为:
while 判断条件: 执行语句……
执行语句可以是单个语句或语句块。判断条件可以是任何表达式,任何非零、或非空(null)的值均为true。
当判断条件假false时,循环结束。
执行流程图如下:
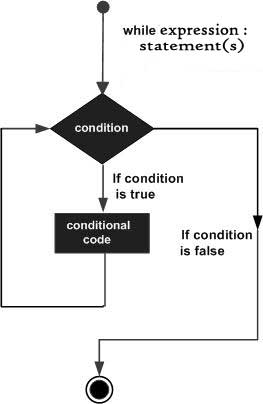
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 3 count = 0 4 while (count < 9): 5 print 'The count is:', count 6 count = count + 1 7 8 print "Good bye!"
结果输出:
1 The count is: 0 2 The count is: 1 3 The count is: 2 4 The count is: 3 5 The count is: 4 6 The count is: 5 7 The count is: 6 8 The count is: 7 9 The count is: 8 10 Good bye!
- break
break用于退出所有循环
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 3 sum = 0 4 number = 0 5 6 while number < 20: 7 number += 1 8 sum += number 9 if sum >= 100: 10 break 11 print("The number is", number) 12 print("The sum is", sum)
结果输出:
1 The number is 14 2 The sum is 105
- continue
continue用于退出当前循环,继续下一次循环。
1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 3 sum = 0 4 number = 0 5 6 while number < 20: 7 number += 1 8 if number == 10 or number == 11: 9 continue 10 sum += number 11 print("The sum is", sum)
结果输出:
1 The sum is 189