原文链接:http://www.yiidian.com/struts2/struts2-ognl.html
1 OGNL简介
OGNL 的全称是对象图导航语言( Object-Graph Navigation Language),它是一种功能强大的开源表达式语言,使用这种表达式语言,可以通过某种表达式语法,存储Java对象的任意属性,调用Java 对象的方法,同时能够自动实现必要的类型转换。如果把表达式看作是一种带有语义的字符串,那么 OGNL 无疑成为了这个语义字符串于Java对象之间的沟通桥梁。
2 OGNL数据结构
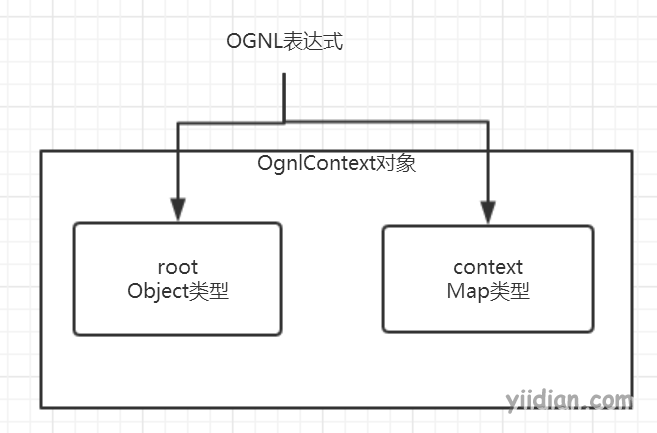
OGNL表达式,操作的是一个叫OgnlContext的对象。该对象包含两个属性:
- root:根对象,可以存入任何对象作为Root对象
- context:上下文对象,这是一个Map结构,可以往该Map存入任意key-value键值对
以上OgnlContext对象的两部分属性,我们都可以通过OGNL表达式进行数据存取。
3 OGNL表达式语法
Ognl表达式基本规则:
-
取root对象的值,只需要直接通过根对象属性即可
-
取context对象的值,必须通过指定的上下文容器中的#key.属性去取
3.1 环境准备
首先导入ognl包到项目
设计一个User类,用于存储数据
package com.yiidian.ognl;
/**
* @author 一点教程(yiidian.com)
*/
public class User {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public User() {
super();
}
public User(String name, Integer age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
3.2 基本取值
/**
* 基本取值
*/
@Test
// 取出root中的属性值
public void test1() throws Exception {
// 准备ONGLContext
// 准备Root
User rootUser = new User("tom", 18);
// 准备Context
Map<String, User> context = new HashMap<String, User>();
context.put("user1", new User("jack", 18));
context.put("user2", new User("rose", 22));
OgnlContext oc = new OgnlContext();
oc.setRoot(rootUser);
oc.setValues(context);
// ====使用OGNL表达式取出属性====
// 取出root中user对象的name属性
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("name", oc, oc.getRoot());
Integer age = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("age", oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(age);
// ---------------------------------------------------
// 取出context中键为user1对象的name属性
String name1 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user1.name", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name2 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user2.name", oc, oc.getRoot());
Integer age1 = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("#user2.age", oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(name1);
System.out.println(name2);
System.out.println(age1);
}
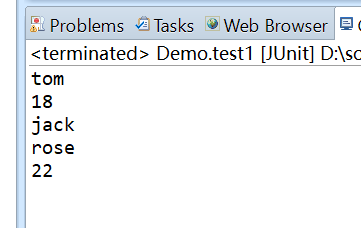
结果为:
3.3 赋值
/**
* 赋值
*/
@Test
public void test2() throws Exception {
// 准备ONGLContext
// 准备Root
User rootUser = new User("tom", 18);
// 准备Context
Map<String, User> context = new HashMap<String, User>();
context.put("user1", new User("jack", 18));
context.put("user2", new User("rose", 22));
OgnlContext oc = new OgnlContext();
oc.setRoot(rootUser);
oc.setValues(context);
// 编写OGNL表达式
// 将root中的user对象的name属性赋值
Ognl.getValue("name='jerry'", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("name", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name2 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user1.name='张三',#user1.name",oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(name2);
}
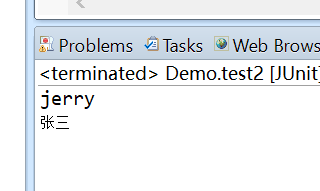
结果为:
3.4 调用方法
/**
* 调用方法
*/
@Test
public void test3() throws Exception {
// 准备ONGLContext
// 准备Root
User rootUser = new User("tom", 18);
// 准备Context
Map<String, User> context = new HashMap<String, User>();
context.put("user1", new User("jack", 18));
context.put("user2", new User("rose", 22));
OgnlContext oc = new OgnlContext();
oc.setRoot(rootUser);
oc.setValues(context);
// 编写OGNL表达式
// 调用root中user对象的setName方法
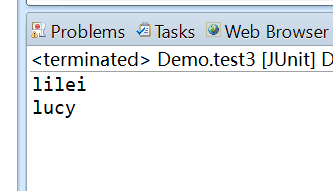
Ognl.getValue("setName('lilei')", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("getName()", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name2 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user1.setName('lucy'),#user1.getName()", oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(name2);
}
结果为:
3.5 调用静态方法
1)设计一个OgnlUtil类,里面有个sayHello的静态方法
package com.yiidian.ognl;
/**
* @author 一点教程(yiidian.com)
*/
public class OgnlUtil {
public static String sayHello(String name){
return "你好,"+name;
}
}
使用Ognl表达式调用sayHello静态方法
/**
* 调用静态方法
*/
@Test
public void test4() throws Exception {
// 准备ONGLContext
// 准备Root
User rootUser = new User("tom", 18);
// 准备Context
Map<String, User> context = new HashMap<String, User>();
context.put("user1", new User("jack", 18));
context.put("user2", new User("rose", 22));
OgnlContext oc = new OgnlContext();
oc.setRoot(rootUser);
oc.setValues(context);
// 编写OGNL表达式
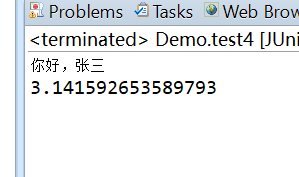
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("@com.yiidian.ognl.OgnlUtil@sayHello('张三')", oc,oc.getRoot());
Double pi = (Double) Ognl.getValue("@@PI", oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(pi);
}
3.6 创建对象(List、Map)
/**
* 创建对象(List、Map)
*/
@Test
public void test5() throws Exception {
// 准备ONGLContext
// 准备Root
User rootUser = new User("tom", 18);
// 准备Context
Map<String, User> context = new HashMap<String, User>();
context.put("user1", new User("jack", 18));
context.put("user2", new User("rose", 22));
OgnlContext oc = new OgnlContext();
oc.setRoot(rootUser);
oc.setValues(context);
// 编写OGNL表达式
// 创建list对象
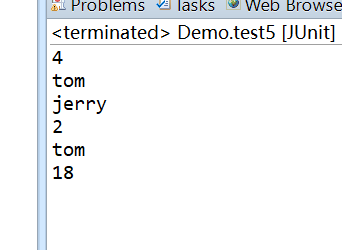
Integer size = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("{'tom','jerry','jack','rose'}.size()", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("{'tom','jerry','jack','rose'}[0]", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name2 = (String) Ognl.getValue("{'tom','jerry','jack','rose'}.get(1)", oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(size);
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(name2);
// 创建Map对象
Integer size2 = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("#{'name':'tom','age':18}.size()", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name3 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#{'name':'tom','age':18}['name']", oc, oc.getRoot());
Integer age = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("#{'name':'tom','age':18}.get('age')", oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(size2);
System.out.println(name3);
System.out.println(age);
}
结果为:
源码下载:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1lD59FmfQLsG1h1Yvx55WUg
欢迎关注我的公众号::一点教程。获得独家整理的学习资源和日常干货推送。
如果您对我的系列教程感兴趣,也可以关注我的网站:yiidian.com