主要内容:
一、模板方法模式定义
| 模板方法模式定义: |
| defines the skeleton of an algorithm in a method, deferring some steps to subclasses. Template Method lets subclasses redefine certain steps of an algorithm without changing the algorithm's structure. |
| 定义一个方法操作算法的框架(骨架结构),而将一些步骤延迟到子类中。模板方法使子类可以在不改变一个算法的结构的情况下,就可以重定义该算法的某些特定步骤。 |
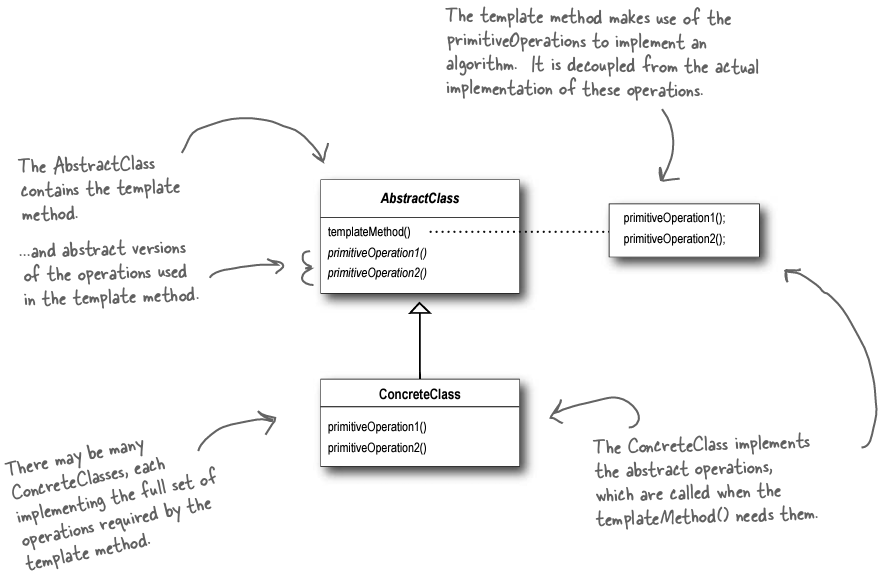
如上图所示(截取自《Head First Design Patterns》一书),具体各个部分有什么作用见上图,这里就不啰嗦了。
二、模板方法模式优势
|
封装不变部分,扩展可变部分。把不变部分的算法封装到父类实现,而可变部分的根据子类的具体需要,则可以通过继承来扩展。 |
| 提取公共部分,构成一个“模板”,模板的作用在于对算法或者流程的一个结构化、规范化,子类不能修改“模板方法”的整个算法骨架或者流程的顺序等,只能根据自身的不同,对模板方法中算法的某一步进行扩展。 |
|
行为由父类控制,子类实现。子类可以通过扩展的方法增加相应的功能,符合开闭原则。 |
三、模板方法模式在Android源码中的应用
在Android源码中,View中的Draw()方法就是一个“模板方法”。它定义了一系列“Draw”过程,主要包括这几个步骤(截取自源代码):
/*
* Draw traversal performs several drawing steps which must be executed
* in the appropriate order:
*
* 1. Draw the background
* 2. If necessary, save the canvas' layers to prepare for fading
* 3. Draw view's content
* 4. Draw children
* 5. If necessary, draw the fading edges and restore layers
* 6. Draw decorations (scrollbars for instance)
*/
具体函数代码如下所示:
 View Code
View Code
/** * Manually render this view (and all of its children) to the given Canvas. * The view must have already done a full layout before this function is * called. When implementing a view, implement * {@link #onDraw(android.graphics.Canvas)} instead of overriding this method. * If you do need to override this method, call the superclass version. * * @param canvas The Canvas to which the View is rendered. */ public void draw(Canvas canvas) { if (ViewDebug.TRACE_HIERARCHY) { ViewDebug.trace(this, ViewDebug.HierarchyTraceType.DRAW); } final int privateFlags = mPrivateFlags; final boolean dirtyOpaque = (privateFlags & DIRTY_MASK) == DIRTY_OPAQUE && (mAttachInfo == null || !mAttachInfo.mIgnoreDirtyState); mPrivateFlags = (privateFlags & ~DIRTY_MASK) | DRAWN; /* * Draw traversal performs several drawing steps which must be executed * in the appropriate order: * * 1. Draw the background * 2. If necessary, save the canvas' layers to prepare for fading * 3. Draw view's content * 4. Draw children * 5. If necessary, draw the fading edges and restore layers * 6. Draw decorations (scrollbars for instance) */ // Step 1, draw the background, if needed int saveCount; if (!dirtyOpaque) { final Drawable background = mBGDrawable; if (background != null) { final int scrollX = mScrollX; final int scrollY = mScrollY; if (mBackgroundSizeChanged) { background.setBounds(0, 0, mRight - mLeft, mBottom - mTop); mBackgroundSizeChanged = false; } if ((scrollX | scrollY) == 0) { background.draw(canvas); } else { canvas.translate(scrollX, scrollY); background.draw(canvas); canvas.translate(-scrollX, -scrollY); } } } // skip step 2 & 5 if possible (common case) final int viewFlags = mViewFlags; boolean horizontalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_HORIZONTAL) != 0; boolean verticalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_VERTICAL) != 0; if (!verticalEdges && !horizontalEdges) { // Step 3, draw the content if (!dirtyOpaque) onDraw(canvas); // Step 4, draw the children dispatchDraw(canvas); // Step 6, draw decorations (scrollbars) onDrawScrollBars(canvas); // we're done... return; } /* * Here we do the full fledged routine... * (this is an uncommon case where speed matters less, * this is why we repeat some of the tests that have been * done above) */ boolean drawTop = false; boolean drawBottom = false; boolean drawLeft = false; boolean drawRight = false; float topFadeStrength = 0.0f; float bottomFadeStrength = 0.0f; float leftFadeStrength = 0.0f; float rightFadeStrength = 0.0f; // Step 2, save the canvas' layers int paddingLeft = mPaddingLeft; final boolean offsetRequired = isPaddingOffsetRequired(); if (offsetRequired) { paddingLeft += getLeftPaddingOffset(); } int left = mScrollX + paddingLeft; int right = left + mRight - mLeft - mPaddingRight - paddingLeft; int top = mScrollY + getFadeTop(offsetRequired); int bottom = top + getFadeHeight(offsetRequired); if (offsetRequired) { right += getRightPaddingOffset(); bottom += getBottomPaddingOffset(); } final ScrollabilityCache scrollabilityCache = mScrollCache; final float fadeHeight = scrollabilityCache.fadingEdgeLength; int length = (int) fadeHeight; // clip the fade length if top and bottom fades overlap // overlapping fades produce odd-looking artifacts if (verticalEdges && (top + length > bottom - length)) { length = (bottom - top) / 2; } // also clip horizontal fades if necessary if (horizontalEdges && (left + length > right - length)) { length = (right - left) / 2; } if (verticalEdges) { topFadeStrength = Math.max(0.0f, Math.min(1.0f, getTopFadingEdgeStrength())); drawTop = topFadeStrength * fadeHeight > 1.0f; bottomFadeStrength = Math.max(0.0f, Math.min(1.0f, getBottomFadingEdgeStrength())); drawBottom = bottomFadeStrength * fadeHeight > 1.0f; } if (horizontalEdges) { leftFadeStrength = Math.max(0.0f, Math.min(1.0f, getLeftFadingEdgeStrength())); drawLeft = leftFadeStrength * fadeHeight > 1.0f; rightFadeStrength = Math.max(0.0f, Math.min(1.0f, getRightFadingEdgeStrength())); drawRight = rightFadeStrength * fadeHeight > 1.0f; } saveCount = canvas.getSaveCount(); int solidColor = getSolidColor(); if (solidColor == 0) { final int flags = Canvas.HAS_ALPHA_LAYER_SAVE_FLAG; if (drawTop) { canvas.saveLayer(left, top, right, top + length, null, flags); } if (drawBottom) { canvas.saveLayer(left, bottom - length, right, bottom, null, flags); } if (drawLeft) { canvas.saveLayer(left, top, left + length, bottom, null, flags); } if (drawRight) { canvas.saveLayer(right - length, top, right, bottom, null, flags); } } else { scrollabilityCache.setFadeColor(solidColor); } // Step 3, draw the content if (!dirtyOpaque) onDraw(canvas); // Step 4, draw the children dispatchDraw(canvas); // Step 5, draw the fade effect and restore layers final Paint p = scrollabilityCache.paint; final Matrix matrix = scrollabilityCache.matrix; final Shader fade = scrollabilityCache.shader; if (drawTop) { matrix.setScale(1, fadeHeight * topFadeStrength); matrix.postTranslate(left, top); fade.setLocalMatrix(matrix); canvas.drawRect(left, top, right, top + length, p); } if (drawBottom) { matrix.setScale(1, fadeHeight * bottomFadeStrength); matrix.postRotate(180); matrix.postTranslate(left, bottom); fade.setLocalMatrix(matrix); canvas.drawRect(left, bottom - length, right, bottom, p); } if (drawLeft) { matrix.setScale(1, fadeHeight * leftFadeStrength); matrix.postRotate(-90); matrix.postTranslate(left, top); fade.setLocalMatrix(matrix); canvas.drawRect(left, top, left + length, bottom, p); } if (drawRight) { matrix.setScale(1, fadeHeight * rightFadeStrength); matrix.postRotate(90); matrix.postTranslate(right, top); fade.setLocalMatrix(matrix); canvas.drawRect(right - length, top, right, bottom, p); } canvas.restoreToCount(saveCount); // Step 6, draw decorations (scrollbars) onDrawScrollBars(canvas); }
其中第三步( Step 3)Draw view's content函数:
/** * Implement this to do your drawing. * * @param canvas the canvas on which the background will be drawn */ protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { }
第四步( Step 4) draw children
/** * Called by draw to draw the child views. This may be overridden * by derived classes to gain control just before its children are drawn * (but after its own view has been drawn). * @param canvas the canvas on which to draw the view */ protected void dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas) { }
从上面的Draw()“模板方法”可以看出,当继承View子类中,如果要重写或者扩展这个方法时,整个方法流程和基本内容不能够修改,子类只能通过扩展onDraw(Canvas canvas)和dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas)两个函数,使子类自己的View显示效果和别的具体子类的不同。现在来看看继承自View类的具体子类如何扩展Draw()模板方法显示自己的与众不同:
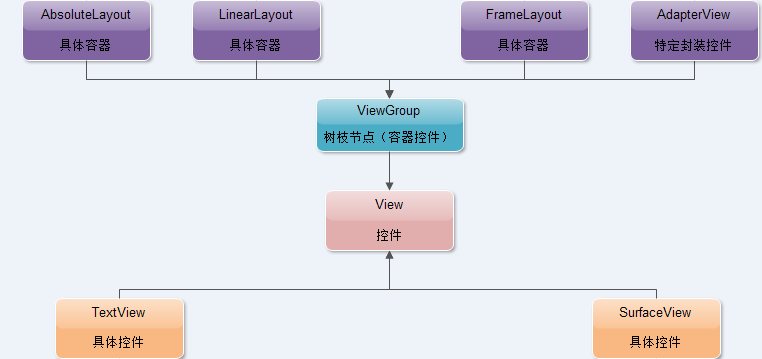
1、TextView类中重写了OnDraw函数
@Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { if (mPreDrawState == PREDRAW_DONE) { final ViewTreeObserver observer = getViewTreeObserver(); observer.removeOnPreDrawListener(this); mPreDrawState = PREDRAW_NOT_REGISTERED; } if (mCurrentAlpha <= ViewConfiguration.ALPHA_THRESHOLD_INT) return; restartMarqueeIfNeeded(); // Draw the background for this view super.onDraw(canvas); final int compoundPaddingLeft = getCompoundPaddingLeft(); final int compoundPaddingTop = getCompoundPaddingTop(); final int compoundPaddingRight = getCompoundPaddingRight(); final int compoundPaddingBottom = getCompoundPaddingBottom(); final int scrollX = mScrollX; final int scrollY = mScrollY; final int right = mRight; final int left = mLeft; final int bottom = mBottom; final int top = mTop; final Drawables dr = mDrawables; if (dr != null) { /* * Compound, not extended, because the icon is not clipped * if the text height is smaller. 。。。 }
2、SurfaceView重写了dispatchDraw()函数:
@Override protected void dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas) { if (mWindowType != WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_APPLICATION_PANEL) { // if SKIP_DRAW is cleared, draw() has already punched a hole if ((mPrivateFlags & SKIP_DRAW) == SKIP_DRAW) { // punch a whole in the view-hierarchy below us canvas.drawColor(0, PorterDuff.Mode.CLEAR); } } super.dispatchDraw(canvas); }
3、ViewGroup类重写了dispatchDraw()函数:
@Override protected void dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas) { final int count = mChildrenCount; final View[] children = mChildren; int flags = mGroupFlags; if ((flags & FLAG_RUN_ANIMATION) != 0 && canAnimate()) { final boolean cache = (mGroupFlags & FLAG_ANIMATION_CACHE) == FLAG_ANIMATION_CACHE; final boolean buildCache = !isHardwareAccelerated(); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { final View child = children[i]; if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE) { final LayoutParams params = child.getLayoutParams(); attachLayoutAnimationParameters(child, params, i, count); bindLayoutAnimation(child); if (cache) { child.setDrawingCacheEnabled(true); if (buildCache) { child.buildDrawingCache(true); } } } } final LayoutAnimationController controller = mLayoutAnimationController; if (controller.willOverlap()) { mGroupFlags |= FLAG_OPTIMIZE_INVALIDATE; } controller.start(); mGroupFlags &= ~FLAG_RUN_ANIMATION; mGroupFlags &= ~FLAG_ANIMATION_DONE; if (cache) { mGroupFlags |= FLAG_CHILDREN_DRAWN_WITH_CACHE; } if (mAnimationListener != null) { mAnimationListener.onAnimationStart(controller.getAnimation()); } } int saveCount = 0; final boolean clipToPadding = (flags & CLIP_TO_PADDING_MASK) == CLIP_TO_PADDING_MASK; if (clipToPadding) { saveCount = canvas.save(); canvas.clipRect(mScrollX + mPaddingLeft, mScrollY + mPaddingTop, mScrollX + mRight - mLeft - mPaddingRight, mScrollY + mBottom - mTop - mPaddingBottom); } // We will draw our child's animation, let's reset the flag mPrivateFlags &= ~DRAW_ANIMATION; mGroupFlags &= ~FLAG_INVALIDATE_REQUIRED; boolean more = false; final long drawingTime = getDrawingTime(); if ((flags & FLAG_USE_CHILD_DRAWING_ORDER) == 0) { for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { final View child = children[i]; if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE || child.getAnimation() != null) { more |= drawChild(canvas, child, drawingTime); } } } else { for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { final View child = children[getChildDrawingOrder(count, i)]; if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE || child.getAnimation() != null) { more |= drawChild(canvas, child, drawingTime); } } } // Draw any disappearing views that have animations if (mDisappearingChildren != null) { final ArrayList<View> disappearingChildren = mDisappearingChildren; final int disappearingCount = disappearingChildren.size() - 1; // Go backwards -- we may delete as animations finish for (int i = disappearingCount; i >= 0; i--) { final View child = disappearingChildren.get(i); more |= drawChild(canvas, child, drawingTime); } } if (clipToPadding) { canvas.restoreToCount(saveCount); } // mGroupFlags might have been updated by drawChild() flags = mGroupFlags; if ((flags & FLAG_INVALIDATE_REQUIRED) == FLAG_INVALIDATE_REQUIRED) { invalidate(true); } if ((flags & FLAG_ANIMATION_DONE) == 0 && (flags & FLAG_NOTIFY_ANIMATION_LISTENER) == 0 && mLayoutAnimationController.isDone() && !more) { // We want to erase the drawing cache and notify the listener after the // next frame is drawn because one extra invalidate() is caused by // drawChild() after the animation is over mGroupFlags |= FLAG_NOTIFY_ANIMATION_LISTENER; final Runnable end = new Runnable() { public void run() { notifyAnimationListener(); } }; post(end); } }
总之,首先在View.Draw()“模板方法”函数将设计界面分成6个步骤,合并不变部分,然后将可变部分提取、独立出来,让子类TextView等扩展修改成自己“独特”的界面效果。在我们自己的实际开发中,如果要设计自己的界面效果大部分的时候,我们都是覆盖重写onDraw(Canvas canvas)函数。
此外:根据模版方法中的方法,可以分为两大类:模版方法(Template Method)和基本方法(Primitive Method)。其中我们这里的例子Draw()函数就是一个“模板方法”。
而基本方法又可以分为三种:抽象方法(Abstract Method)、具体方法(Concrete Method)和钩子方法(Hook Method):
抽象方法:一个抽象方法由抽象类声明,由具体子类实现。
具体方法:一个具体方法由抽象类声明并实现,而子类并不实现或置换。
钩子方法:一个钩子方法由抽象类声明并实现,而子类会加以扩展。我们这里的onDraw()函数就是一个钩子方法。
最后记住:

本人能力和时间有限(缺少“模式使用”内容,以后会添加),写的很粗糙,恭候大家的批评指正,谢谢~~~
