C++11中引入了一个用于多线程操作的thread类,下面进行简单演示如何使用,以及如果进行多线程同步。
-
thread简单示例
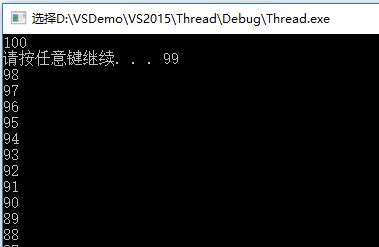
#include <iostream> #include <thread> #include <Windows.h> using namespace std; void thread01() { for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { cout << "Thread 01 is working !" << endl; Sleep(100); } } void thread02() { for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { cout << "Thread 02 is working !" << endl; Sleep(200); } } int main() { thread task01(thread01); thread task02(thread02); task01.join(); task02.join(); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { cout << "Main thread is working !" << endl; Sleep(200); } system("pause"); }
输出:
-
thread detach不阻塞主线程
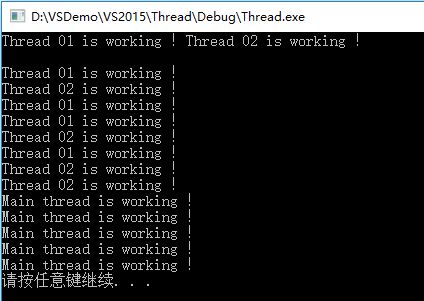
两个子线程并行执行,join函数会阻塞主流程,所以子线程都执行完成之后才继续执行主线程。可以使用detach将子线程从主流程中分离,独立运行,不会阻塞主线程:
#include <iostream> #include <thread> #include <Windows.h> using namespace std; void thread01() { for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { cout << "Thread 01 is working !" << endl; Sleep(100); } } void thread02() { for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { cout << "Thread 02 is working !" << endl; Sleep(200); } } int main() { thread task01(thread01); thread task02(thread02); task01.detach(); task02.detach(); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { cout << "Main thread is working !" << endl; Sleep(200); } system("pause"); }
输出:
使用detach的主线程和两个子线程并行执行。
-
thread带参数子线程
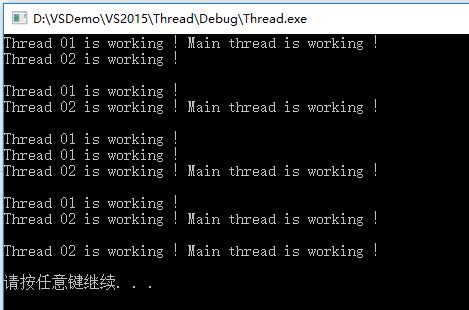
在绑定的时候也可以同时给带参数的线程传入参数:
#include <iostream> #include <thread> #include <Windows.h> using namespace std; //定义带参数子线程 void thread01(int num) { for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) { cout << "Thread 01 is working !" << endl; Sleep(100); } } void thread02(int num) { for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) { cout << "Thread 02 is working !" << endl; Sleep(200); } } int main() { thread task01(thread01, 5); //带参数子线程 thread task02(thread02, 5); task01.detach(); task02.detach(); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { cout << "Main thread is working !" << endl; Sleep(200); } system("pause"); }
输出:
-
多线程同步mutex
多个线程同时对同一变量进行操作的时候,如果不对变量做一些保护处理,有可能导致处理结果异常:
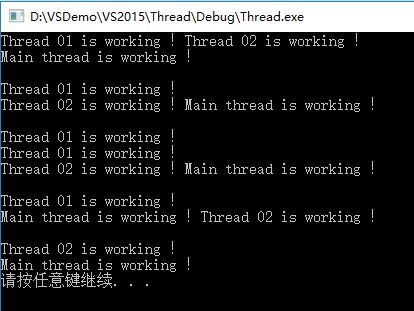
#include <iostream> #include <thread> #include <Windows.h> using namespace std; int totalNum = 100; void thread01() { while (totalNum > 0) { cout << totalNum << endl; totalNum--; Sleep(100); } } void thread02() { while (totalNum > 0) { cout << totalNum << endl; totalNum--; Sleep(100); } } int main() { thread task01(thread01); thread task02(thread02); task01.detach(); task02.detach(); system("pause"); }
部分输出结果:
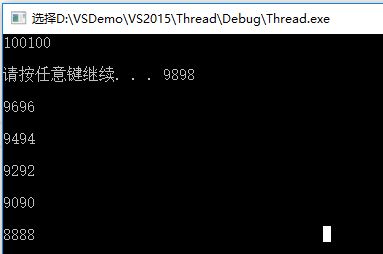
有两个问题,一是有很多变量被重复输出了,而有的变量没有被输出;二是正常情况下每个线程输出的数据后应该紧跟一个换行符,但这里大部分却是另一个线程的输出。
这是由于第一个线程对变量操作的过程中,第二个线程也对同一个变量进行各操作,导致第一个线程处理完后的输出有可能是线程二操作的结果。针对这种数据竞争的情况,可以使用线程互斥对象mutex保持数据同步。mutex类的使用需要包含头文件mutex。
#include <iostream> #include <thread> #include <Windows.h> #include <mutex> using namespace std; mutex mu; //线程互斥对象 int totalNum = 100; void thread01() { while (totalNum > 0) { mu.lock(); //同步数据锁 cout << totalNum << endl; totalNum--; Sleep(100); mu.unlock(); //解除锁定 } } void thread02() { while (totalNum > 0) { mu.lock(); cout << totalNum << endl; totalNum--; Sleep(100); mu.unlock(); } } int main() { thread task01(thread01); thread task02(thread02); task01.detach(); task02.detach(); system("pause"); }
多线程中加入mutex互斥对象之后输出正常: