KMP算法可以在O(n+m)的时间数量级上完成模式匹配,其做法在于:没当一次匹配过程中出现字符比较不等时,不需要回溯指针,而是利用已经得到的“部分匹配”的结果将模式向右“滑动”尽可能远的一段距离后,继续进行比较。
在KMP算法中主要是先得到子字符串的next数组,计算next数组方法如下:
(1)、next[1]=0,next[1]=1
(2)、后面求解每一位的next[j]值时,根据j的前一位进行比较,令k=next[j-1];
(3)、将s[j-1]于s[k]进行比较:
如果相等,则令该next[j]=k+1
如果不相等,令k=next[k],若k不等于0,跳到(3),否则,next[j]=1
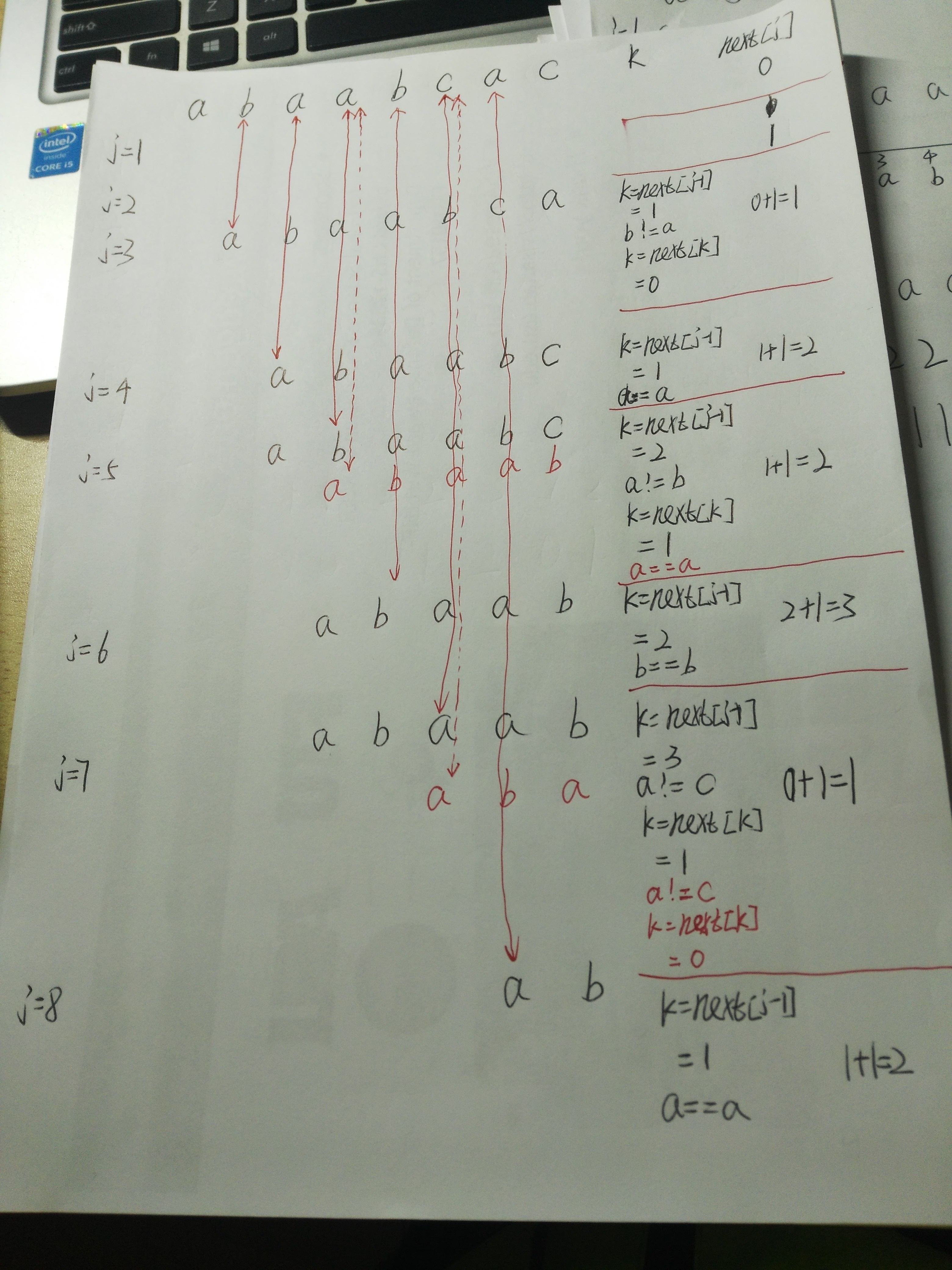
eg:
如下图j=4时,此时前面的next数组为0 1 1,所以k=next[3]=1 ,由于s[j-1]=s[3]=a、s[k]=s[1]=a,所以s[j]=s[4]=1+1=2
如下图j=5时,next={0,1,1,2},k=2,s[j-1]=a,s[k]=b,所以k=next[k]=next[2]=1,此时s[k]=s[1]=a,所以s[j]=s[5]=1+1=2
比如子字符串为:abaabcac,计算如下图
得到子字符串之后,在字符串匹配的时候,子字符串不再是移动1个字符串,而是移动next(j)个位置,代码如:(这里需要注意,next数组是从1开始的,没有0)
c++实现:

#include <iostream> #include <stdlib.h> #include <vector> using namespace std; //利用模版进行输出 template <typename T> void print(vector<T> a) { typename vector<T>::iterator it;//前面要加typename,要不会出错 for(it=++a.begin();it!=a.end();it++) { cout<<*it; } } vector<int> next_str={-1,0,1};//为了使下标从1开始,在前面添加一个-1 void next_list(vector<char> v,int n)//得到子字符串的next数组 { int j=3,k; while(j<=n) { k=next_str[j-1]; if(v[j-1]==v[k]) { k++; next_str.push_back(k); } else { k=next_str[k]; while(true) { if(k==0) { next_str.push_back(1); break; } if(v[j-1]==v[k]) { next_str.push_back(++k); break; } else { k=next_str[k]; } } } j++; } } int get_index(vector<char> l,vector<char> s,int n,int m) { int i=1,j=1; while(i<=n&&j<m) { if(j==0||l[i]==s[j]) { i++; j++; } else { j=next_str[j]; } } if(j==m) { return i-j+1; } else { return -1; } } int main() { int n; cin>>n; vector<char> longstr={'#'};//为了下标从1开始,添加一个’#‘ char c; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { cin>>c; longstr.push_back(c); } int m; cin>>m; vector<char> shortstr={'#'};//为了下标从1开始,添加一个’#‘ for(int i=0;i<m;i++) { cin>>c; shortstr.push_back(c); } // int n=20,m=8; // vector<char> longstr={'#','b','c','a','a','b','a','c','a','b','a','a','b','c','a','c','a','b','c','d','a'}; // vector<char> shortstr={'#','a','b','a','a','b','c','a','c'}; next_list(shortstr,m); print(next_str); cout<<endl; int index=get_index(longstr,shortstr,n,m); if(index>=0) { print(shortstr); cout<<"在"; print(longstr); cout<<"中,从位置"<<index<<"开始"<< endl; } else { print(shortstr); cout<<"不在"; print(longstr); cout<<"中endl"; } return 0; }
python实现:

#-*- coding:utf-8 -*- class KMP: def __init__(self,s_long,s_short): self.s_long=s_long self.s_short=s_short self.flag=0 def get_nextList(self): l=[0,1] for i in range(2,len(self.s_short)): l.append(self.get_num_1(self.s_short[0:i])) print l b=0 a=0 while True: if self.s_short[a]==self.s_long[b]: a+=1 b+=1 else: a=l[a]-1 if a==-1: a += 1 b += 1 if self.s_short==self.s_long[b:b+len(self.s_short)]: break if b==len(self.s_long): return 0 return b+1 ''' 功能(见图2、3):获得子字符串的next数组,和第一张图方法比一样,更容易理解 s:用于存储该字符前面所有的子字符串(注意子字符串是从这个字符串开始从后往前,长度慢慢增长) while循环:用于确定前面最长重复的字符串(注意,应该从长的开始匹配,且必须从第一个字符开始) 返回最长字符串长度+1 ''' def get_num_1(self,string): s=[] for i in range(1,len(string)): s.append(string[len(string)-i:len(string)]) while s: temp=s.pop() n=len(temp) if temp==string[0:n+0]: return len(temp)+1 return 1 long=raw_input() short=raw_input() print KMP(long,short).get_nextList()


