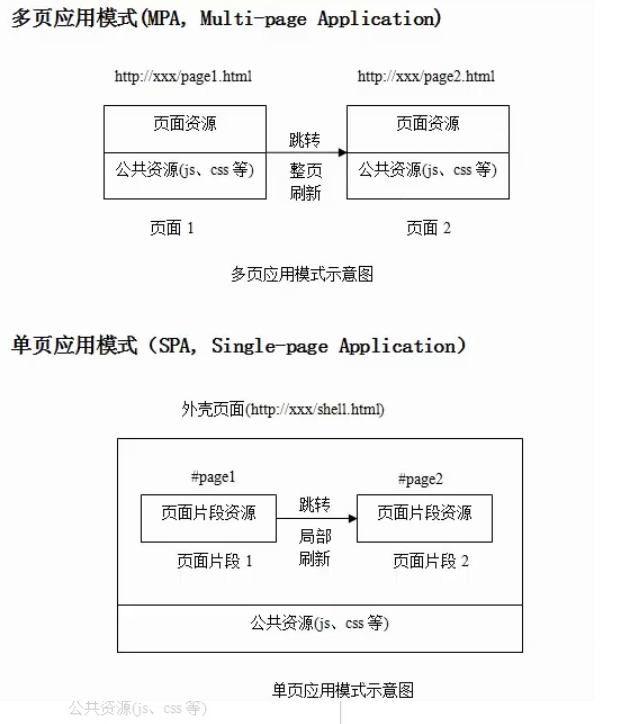
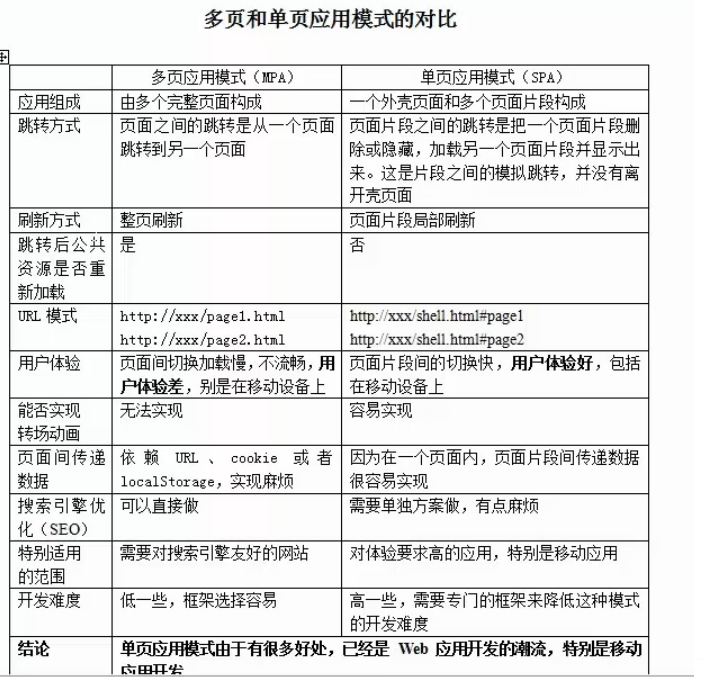
这样对比的话,单页面的优势确实很大,但当我自己去打开某宝,某东的移动端页面时,确实它们都是多页面应用。为什么?我能想到的就几点:
1.单页面使用的技术对低版本的浏览器不友好,大公司还得兼顾使用低版本浏览器的用户啊
2.功能模块开发来说,比如说单页面的业务公用组件,有时候你都不知道分给谁开发
3.seo优化吧(PS:既然是大应用应该很多人都知道,为什么还要做搜索引擎优化)
公司开发移动端使用的技术是vue,其实老大在要求使用多页面开发的时候,已经搭了一个vue多页面的脚手架供给我们去使用,但是我去看了看源码的时候写得很一般,所以决定自己重新去写过。
思路:
由于vue-cli已经写好了单页面的webpack文件,不去改动之前是它默认的一个页面引用打包的资源。既然是多页面,那么把webpack入口文件改成多个就好了啊。未改动时的webpack.base.conf.js(这个JS的功能主要在于全局配置,比如入口文件,出口文件,解析规则等)

// 把箭头部分的入口文件改为以下
entry: {
'index': '..../main.js' // 注意省略号是实际开发时的项目路径
'product': '..../main.js'
}
但是这样做效率得多低下,每增加一个新页面就要手动去添加新的入口,所以这里把入口文件封装为一个函数:
/**
* 获取多页面入口文件
* @globPath 文件路径
*/
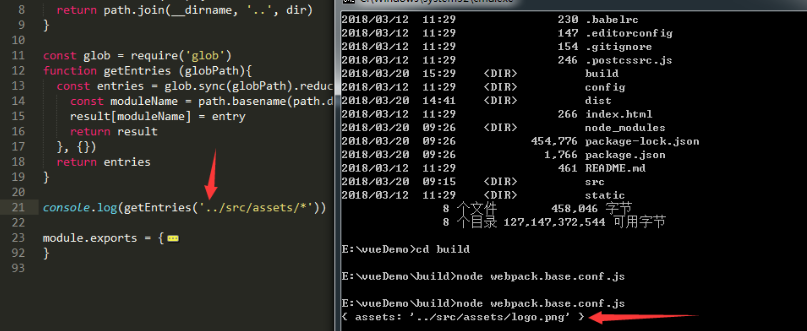
const glob = require('glob')
function getEntries(globPath) {
const entries = glob.sync(globPath).reduce((result, entry) => {
const moduleName = path.basename(path.dirname(entry)) // 获取模块名称
result[moduleName] = entry
return result
}, {})
return entries
}
注意在使用nodejs的glob模块之前,记得先下载依赖
测试一下这个函数
然后把webpack.base.config.js改为如下:
'use strict'
const path = require('path')
const utils = require('./utils')
const config = require('../config')
const vueLoaderConfig = require('./vue-loader.conf')
function resolve (dir) {
return path.join(__dirname, '..', dir)
}
const glob = require('glob')
function getEntries (globPath){
const entries = glob.sync(globPath).reduce((result, entry) => {
const moduleName = path.basename(path.dirname(entry)) // 获取模块名称
result[moduleName] = entry
return result
}, {})
return entries
}
const entries = getEntries('./src/modules/**/*.js')
module.exports = {
context: path.resolve(__dirname, '../'),
entry: entries, // 改动部分
output: {
path: config.build.assetsRoot,
filename: '[name].js',
publicPath: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production'
? config.build.assetsPublicPath
: config.dev.assetsPublicPath
},
resolve: {
extensions: ['.js', '.vue', '.json'],
alias: {
'vue$': 'vue/dist/vue.esm.js',
'@': resolve('src'),
}
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /.vue$/,
loader: 'vue-loader',
options: vueLoaderConfig
},
{
test: /.js$/,
loader: 'babel-loader',
include: [resolve('src'), resolve('test'), resolve('node_modules/webpack-dev-server/client')]
},
{
test: /.(png|jpe?g|gif|svg)(?.*)?$/,
loader: 'url-loader',
options: {
limit: 10000,
name: utils.assetsPath('img/[name].[hash:7].[ext]')
}
},
{
test: /.(mp4|webm|ogg|mp3|wav|flac|aac)(?.*)?$/,
loader: 'url-loader',
options: {
limit: 10000,
name: utils.assetsPath('media/[name].[hash:7].[ext]')
}
},
{
test: /.(woff2?|eot|ttf|otf)(?.*)?$/,
loader: 'url-loader',
options: {
limit: 10000,
name: utils.assetsPath('fonts/[name].[hash:7].[ext]')
}
}
]
},
node: {
// prevent webpack from injecting useless setImmediate polyfill because Vue
// source contains it (although only uses it if it's native).
setImmediate: false,
// prevent webpack from injecting mocks to Node native modules
// that does not make sense for the client
dgram: 'empty',
fs: 'empty',
net: 'empty',
tls: 'empty',
child_process: 'empty'
}
}
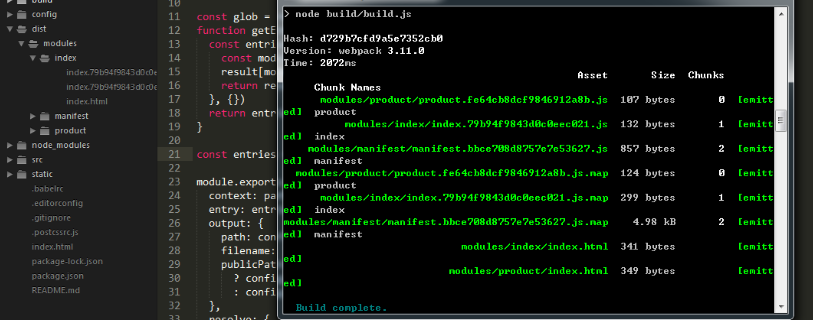
注意我的多页面目录:

公共配置搞完之后是打包文件:webpack.prod.conf.js,打包文件的修改主要是输出文件的配置,因为要对应入口文件的文件夹,还有就是一个页面对应一个htmlwebpackplugin配置,这个配置是加在文件的plugins里面的,按照上面的消除手动加入配置的思路这里也加入htmlwebpackplugin的配置函数
/**
* 页面打包
* @entries 打包文件
* @config 参数配置
* @module 使用的主体
*/
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin')
function pack (entries, module) {
for (const path in entries) {
const conf = {
filename: `modules/${path}/index.html`,
template: entries[path], // 模板路径
inject: true,
chunks: ['manifest', 'vendor', path] // 必须先引入公共依赖
}
module.plugins.push(new HtmlWebpackPlugin(conf))
}
}
最终打包文件改为如下
'use strict'
const path = require('path')
const utils = require('./utils')
const webpack = require('webpack')
const config = require('../config')
const merge = require('webpack-merge')
const baseWebpackConfig = require('./webpack.base.conf')
const CopyWebpackPlugin = require('copy-webpack-plugin')
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin')
const ExtractTextPlugin = require('extract-text-webpack-plugin')
const OptimizeCSSPlugin = require('optimize-css-assets-webpack-plugin')
const UglifyJsPlugin = require('uglifyjs-webpack-plugin')
const env = require('../config/prod.env')
const glob = require('glob')
function getEntries (globPath){
const entries = glob.sync(globPath).reduce((result, entry) => {
const moduleName = path.basename(path.dirname(entry)) // 获取模块名称
result[moduleName] = entry
return result
}, {})
return entries
}
const entries = getEntries('./src/modules/**/*.html') // 获取多页面所有入口文件
const webpackConfig = merge(baseWebpackConfig, {
module: {
rules: utils.styleLoaders({
sourceMap: config.build.productionSourceMap,
extract: true,
usePostCSS: true
})
},
devtool: config.build.productionSourceMap ? config.build.devtool : false,
output: {
path: config.build.assetsRoot,
filename: 'modules/[name]/[name].[chunkhash].js',
// publicPath: '/' // 改为相对路径
// chunkFilename: utils.assetsPath('js/[id].[chunkhash].js')
},
plugins: [
// http://vuejs.github.io/vue-loader/en/workflow/production.html
new webpack.DefinePlugin({
'process.env': env
}),
new UglifyJsPlugin({
uglifyOptions: {
compress: {
warnings: false
}
},
sourceMap: config.build.productionSourceMap,
parallel: true
}),
// extract css into its own file
new ExtractTextPlugin({
filename: utils.assetsPath('css/[name].[contenthash].css'),
// Setting the following option to `false` will not extract CSS from codesplit chunks.
// Their CSS will instead be inserted dynamically with style-loader when the codesplit chunk has been loaded by webpack.
// It's currently set to `true` because we are seeing that sourcemaps are included in the codesplit bundle as well when it's `false`,
// increasing file size: https://github.com/vuejs-templates/webpack/issues/1110
allChunks: true,
}),
// Compress extracted CSS. We are using this plugin so that possible
// duplicated CSS from different components can be deduped.
new OptimizeCSSPlugin({
cssProcessorOptions: config.build.productionSourceMap
? { safe: true, map: { inline: false } }
: { safe: true }
}),
// generate dist index.html with correct asset hash for caching.
// you can customize output by editing /index.html
// see https://github.com/ampedandwired/html-webpack-plugin
// keep module.id stable when vendor modules does not change
new webpack.HashedModuleIdsPlugin(),
// enable scope hoisting
new webpack.optimize.ModuleConcatenationPlugin(),
// split vendor js into its own file
new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({
name: 'vendor',
minChunks (module) {
// any required modules inside node_modules are extracted to vendor
return (
module.resource &&
/.js$/.test(module.resource) &&
module.resource.indexOf(
path.join(__dirname, '../node_modules')
) === 0
)
}
}),
// extract webpack runtime and module manifest to its own file in order to
// prevent vendor hash from being updated whenever app bundle is updated
new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({
name: 'manifest',
minChunks: Infinity
}),
// This instance extracts shared chunks from code splitted chunks and bundles them
// in a separate chunk, similar to the vendor chunk
// see: https://webpack.js.org/plugins/commons-chunk-plugin/#extra-async-commons-chunk
new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({
name: 'app',
async: 'vendor-async',
children: true,
minChunks: 3
}),
// copy custom static assets
new CopyWebpackPlugin([
{
from: path.resolve(__dirname, '../static'),
to: config.build.assetsSubDirectory,
ignore: ['.*']
}
])
]
})
if (config.build.productionGzip) {
const CompressionWebpackPlugin = require('compression-webpack-plugin')
webpackConfig.plugins.push(
new CompressionWebpackPlugin({
asset: '[path].gz[query]',
algorithm: 'gzip',
test: new RegExp(
'\.(' +
config.build.productionGzipExtensions.join('|') +
')$'
),
threshold: 10240,
minRatio: 0.8
})
)
}
if (config.build.bundleAnalyzerReport) {
const BundleAnalyzerPlugin = require('webpack-bundle-analyzer').BundleAnalyzerPlugin
webpackConfig.plugins.push(new BundleAnalyzerPlugin())
}
function pack (entries, module) {
for (const path in entries) {
const conf = {
filename: `modules/${path}/index.html`,
template: entries[path], // 模板路径
inject: true,
chunks: ['manifest', 'vendor', path] // 必须先引入公共依赖
}
module.plugins.push(new HtmlWebpackPlugin(conf))
}
}
pack(entries, webpackConfig)
module.exports = webpackConfig
然后启动npm run build尝试打包文件