摘要:概述、script的编写、test命令、[]判断符号、默认变量($1...)、if...then条件判断式、
一、概述
【什么是shell script】
针对shell所写的脚本,将多个命令汇整起来一起执行
可以进行类似程序的编写,并且不需要经过编译就能够执行
利用shell的功能所写的一个“程序”,这个程序是使用纯文本文件,将一些shell的语法与命令写在里面,搭配正则表达式、管道命令与数据流重定向等功能,以达到我们所想要的处理目的。
【用途】
简化我们日常的工作管理
一些服务的启动都是通过shell script进行的
二、编写第一个Hello world程序
【预处理】
新建一个script文件:vi helloworld.sh
【代码】

1 #!bin/bash 2 # Program: 3 # This is my first script. 4 # History: 5 # 2017-9-30 liuyu First release 6 7 echo "Hello World!" 8 exit 0
说明:
#!bin/bash:声明这个script使用的shell名称
声明这个文件内是使用bash的语法,即这个程序被执行时,它就能够加载bash的相关环境配置文件(一般来说就是non-login shell的~/.bashrc),并且执行bash使我们下面的命名能够执行。
exit 0:告知执行结果
我们可以利用exit这个命令来让程序中断,并且回传一个数值给系统。如“exit 0”代表离开script并且回传一个0给系统,即我们执行完这个script后,若接着执行echo $?则可得到0的值。
【执行script程序】
bash 文件名
三、简单的shell script练习
1. 交互式脚本:变量内容由用户决定
题目:请你以read命令的用途,编写一个script,它可以让用户输入firstname与lastname,最后并且在屏幕上显示“Your full name is: ”的内容。

1 #!bin/bash 2 # Program: 3 # an easy interactive program 4 # History: 5 # 2017-9-30 liuyu First release 6 7 8 read -p "Please input your firstname: " firstname 9 read -p "please input your lastname: " lastname 10 echo "Your full name is $firstname $lastname!"
2. 把日期作文件名:利用日期进行文件的创建
题目:我希望将每天的数据备份在不同的文件里,所以就需要以每天的日期作为文件名。关键是日期怎么来!假设我要创建3个空的文件,文件名最开头由用户决定(我们假设是filename),那今天的日期是2017/9/30,我想以前天、昨天、今天的日期来创建这些文件,即filename20170928, filename20170929, dilename20170930,该如何是好?

1 #!bin/bash 2 # Program: 3 # filename is created by user's input. 4 # History: 5 # 2017-9-30 liuyu First release 6 7 echo "I will use 'touch' to create three files." 8 read -p "Please input your filename: " fileuser 9 10 #开始判断有否配置文件名,防止用户随意按[Enter],我们默认开头为filename 11 filename=${fileuser:-"filename"} 12 13 date1=$(date --date='2 days ago' +%Y%m%d) #前两天的日期 14 date2=$(date --date='1 days ago' +%Y%m%d) 15 date3=$(date +%Y%m%d) #今天的日期 16 file1=${filename}${date1} #追加的方式配置文件名 17 file2=${filename}${date2} 18 file3=${filename}${date3} 19 20 touch "$file1" #防止有空格 21 touch "$file2" 22 touch "$file3"
说明:此程序运用了许多bash中的变量知识,所以学好shell才能轻松地编写script!
3. 数值运算:简单的加减乘除
题目:让用户输入两个整数,然后计算出这两个数相乘的结果。

1 #!bin/bash 2 # Program: 3 # multiply two integer. 4 # History: 5 # liuyu 2017-9-30 First release 6 7 echo "You should input 2 integers,i will cross them!" 8 read -p "first number: " firnum 9 read -p "second number: " secnum 10 total=$(($firnum*$secnum)) 11 echo "The result of $firnum*$secnum is $total."
四、test命令的测试功能
1. 功能
检测系统上面某些文件、测试文件的相关属性。
2. 常用命令
| 命令 | 意义 |
| test -e filename | 该文件名是否存在 |
| test -f filename | 该文件名是否存在且为文件 |
| test -e filename | 该文件名是否存在且为目录 |
| test -S filename | 该文件名是否存在且为一个Socket文件 |
| test -L filename | 该文件名是否存在且为一个连接文件 |
| test -r filename | 该文件名是否存在且具有“可读”的权限 |
| test -w filename | 该文件名是否存在且具有“可写”的权限 |
| test -x filename | 该文件名是否存在且具有“可执行”的权限 |
| test file1 -nt file2 | 判断file1是否比file2新 |
| test file1 -ef file2 | 判断file1与file2是否为同一个文件,主要用于hard link |
| test n1 -eq n2 | 两数值相等 |
| test n1 -gt n2 | n1大于n2 |
| test n1 -lt n2 | n1小于n2 |
| test n1 -ge n2 | n1大于等于n2 |
| test n1 -le n2 | n1小于等于n2 |
| test -z string | 判断是否为空字符串,若是,返回true |
| test str1=str2 | 判断str1是否等于str2 |
| -a | 两个条件同时成立,如test -r file -a -x file,则file同时具有r与x权限时,才回传true |
| -o | 任何一个条件成立,如test -r file -o -x file,则file具有r或x权限时,就可回传true |
| ! | 反向状态,如test ! -x file,当file不具有x时,才回传true |
3. 示例
题目:写一个script,让用户输入一个文件名,要求进行下面的判断:
这个文件是否存在,若不存在则给予一个“Filename does not exist”的信息,并中断程序;
若这个文件存在,则判断它是个目录或文件,结果输出“Filename is regular file”或“Filename is directory”;
判断一下,执行者的身份对这个文件或目录所拥有的权限,并输出权限数据。

1 #!bin/bash 2 # Program: 3 # A script which covers the using of test. 4 # History: 5 # 2017-9-30 liuyu First release 6 7 echo "Please input a filename, I will check the filename's type and permission." 8 read -p "Input a filename: " filename 9 test -z $filename && echo "You must input a filename." && exit 0 10 11 test ! -e $filename && echo "The filename '$filename' DO NOT exist" && exit 0 12 13 test -f $filename && filetype="regular file" 14 test -d $filename && filetype="directory" 15 test -r $filename && perm="readable" 16 test -w $filename && perm="writable" 17 test -x $filename && perm="executable" 18 19 echo "The filename: $filename is a $filetype" 20 echo "And the permissions are : $perm"
五、判断符号[]的使用
1. 功能
数据的判断、字符串判别
2. 用法
| 命令 | 意义 |
| [ -z "$HOME" ] | 判断HOME变量是否为空 |
| [ "$HOME" == "$var" ] | 判断两个变量是否相等 |
| [ "$HOME" == "string" ] | 判断变量的内容是否为string |
3. 示例
题目:写一个script,要求如下:
当执行一个程序的时候,这个程序会让用户选择Y或N;
如果用户输入Y或y时,就显示“OK, continue”;
如果用户输入N或n时,就显示“Oh, interrupt!”;
如果不是Y/y/N/n之内的其他字符,就显示“I don't know what your choice is”。

1 #!/bin/bash 2 # Program: 3 # A practice with []. 4 # History: 5 # 2017-9-30 liuyu First release 6 7 read -p "Please input (Y/N): " yn 8 [ "$yn" == "Y" -o "$yn" == "y" ] && echo "OK, continue" && exit 0 9 [ "$yn" == "N" -o "$yn" == "n" ] && echo "Oh, interrupt!" && exit 0 10 echo "I don't know what your choice is." && exit 0
六、默认变量($0,$1...)
1. 概述
我们知道命令可以带有参数,而我们还需要知道的是shell script也可以在脚本文件名后面带有参数。(注意!一定是script文件喔!)
2. 示例
题目:重新启动系统注册表文件
命令:/etc/init.d/syslog restart
评讲:此命令可以重新启动/etc/init.d/syslog这个程序
题目:承上,关闭该服务
命令:/etc/init.d/syslog stop
3. 用法
文件名 opt1 opt2 opt3 opt4
$0 $1 $2 $3 $4
解释:执行的脚本文件名为$0这个变量,第一个接的参数就是$1。
补充:只要我们在script里面善用$1的话,就可以很简单地立即执行某些命令功能了!
补充:除了这些数字的变量之外,我们还有一些较为特殊的变量可以在script内使用来调用这些参数。
$#:代表后接的参数“个数”
$@:代表"$1"、"$2"、"$3"、"$4"之意,每个变量是独立的(用双引号括起来)
$*:代表“"$1c$2c$3c$4"”,其中c为分隔字符,默认为空格键,所以本例中代表“"$1 $2 $3 $4"”之意
4. 练习
题目:假设你要执行一个可以带参数的script,执行该脚本后屏幕会显示如下的数据。
程序的文件名
共有几个参数
若参数的个数小于2则告知用户参数数量太少
全部的参数内容
第一个参数
第二个参数

1 #!/bin/bash 2 # Program: 3 # Default variable of shell script. 4 # History: 5 # 2017-10-1 liuyu First release 6 7 echo "The script name is ==> $0" 8 echo "Total parameter number is ==> $#" 9 [ "$#" -lt 2 ] && echo "The number of parameter is less than 2. Stop here." && exit 0 10 echo "Your whole parameter is ==> '$@'" 11 echo "The 1st parameter ==> $1" 12 echo "The 2nd parameter ==> $2"
注意:参数个数就是你执行该文件时在该文件后加的参数个数,即,若你执行“bash sh07.sh”,则参数个数为0。
5. shift:造成参数变量号码偏移
我们要知道的是——脚本后面所接的变量能够进行偏移。
我们通过一个例子来说明偏移是什么。
题目:我们将上个文件中的内容稍作变化,用来显示每次偏移后参数的变化情况。

1 #!/bin/bash 2 # Program: 3 # Default variable of shell script. 4 # History: 5 # 2017-10-1 liuyu First release 6 7 echo "Total parameter number is ==> $#" 8 echo "Your whole parameter is ==> '$@'" 9 shift #进行第一次“一个变量的shift” 10 echo "Total parameter number is ==> $#" 11 echo "Your whole parameter is ==> '$@'" 12 shift 3 #进行第二次“三个变量的shift” 13 echo "Total parameter number is ==> $#" 14 echo "Your whole parameter is ==> '$@'"
如果我们执行“bash sh08.sh one two three four five six”,我们会看到如下显示:
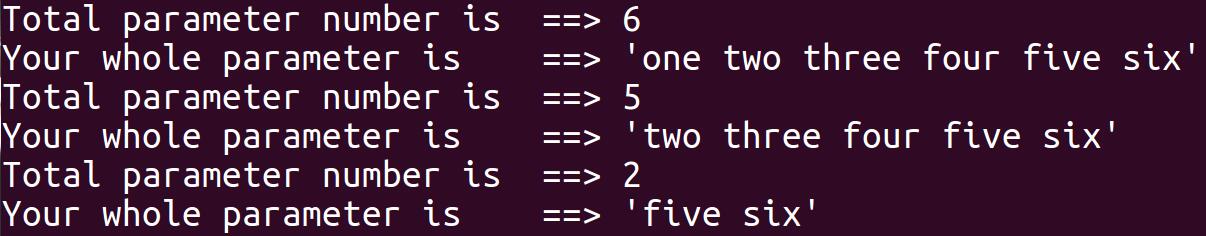
分析:通过这个结果,我们知道shift会移动变量,而且shift后面可以接数字,代表拿掉最前面的几个参数的意思。
注:“七/八/九”都属于条件判断式下的子内容。
七、条件判断式——if...then
1. 单层判断
【命令】
if [ 条件判断式 ]; then
当条件判断式成立时,可以进行的命令工作内容;
fi
【条件判断式】
当有多个条件要判别时,除了可以将多个条件写入一个中括号内的情况之外,还可以使用多个中括号,而此时每个中括号内只写入一个判断式。
即[ "$yn" == "Y" -o "$yn" == "y" ] 可以被替换为 [ "$yn" == "Y" ] || [ "$yn" == "y" ]
【示例】
题目:将sh06.sh这个脚本修改成为if...then的样式

1 #!/bin/bash 2 # Program: 3 # A practice with []. 4 # History: 5 # 2017-9-30 liuyu First release 6 7 read -p "Please input (Y/N): " yn 8 if [ "$yn" == "Y" ] || [ "$yn" == "y" ]; then 9 echo "OK, continue" 10 exit 0 11 fi 12 if [ "$yn" == "N" ] || [ "$yn" == "n" ]; then 13 echo "oh, interrupt!" 14 exit 0 15 fi 16 echo "I don't know what your choice is." && exit 0
2. 多层判断
【命令1】
if [ 条件判断式 ]; then
当条件判断式成立时,可以进行的命令工作内容;
else
当条件判断式不成立时,可以进行的命令工作内容;
fi
【命令2】
if [ 条件判断式一 ]; then
当条件判断式一成立时,可以进行的命令工作内容;
elif [ 条件判断式二 ]; then
当条件判断式二成立时,可以进行的命令工作内容;
else
当条件判断式一与二均不成立时,可以进行的命令工作内容;
fi
【示例】
题目:将sh06-2.sh这个脚本修改成为if...elif...else的样式

1 #!/bin/bash 2 # Program: 3 # A practice with []. 4 # History: 5 # 2017-9-30 liuyu First release 6 7 read -p "Please input (Y/N): " yn 8 if [ "$yn" == "Y" ] || [ "$yn" == "y" ]; then 9 echo "OK, continue" 10 elif [ "$yn" == "N" ] || [ "$yn" == "n" ]; then 11 echo "oh, interrupt!" 12 else 13 echo "I don't know what your choice is." 14 fi
【练习】
题目:一般来说,如果你不希望用户由键盘输入额外的数据时,可以使用上一节提到的参数功能($1)!让用户在执行命令时就将参数代进去。现在我们想让用户输入“hello”这个关键字时,利用参数的方法可以这样依序设计:①判断$1是否为hello,如果是的话,就显示“Hello,how are you?”;②如果没有加任何参数,就提示用户必须要使用的参数;③而如果加入的参数不是hello,就提醒用户仅能使用hello为参数。

1 #!/bin/bash 2 # Program: 3 # Check $1 is equal to "hello" 4 # History: 5 # 2017-10-1 liuyu FIrst release 6 7 if [ "$1" == "hello" ]; then 8 echo "Hello,how are you?" 9 elif [ "$1" == "" ]; then 10 echo "You must input parameters,ex> {$0 someword}" 11 else 12 echo "The only parameter is 'hello',ex> {$0 hello}" 13 fi
评讲:我们在$1的位置分别输入hello、没有输入、随意输入,就可以看到不同的输出。
八、利用case...esac判断
九、利用函数功能
十、循环(loop)
1. 条件循环
【while do done】
while [ condition ] //中括号内的状态就是判断式
do //循环的开始
程序段落
done //循环的结束
解释:当 condition 条件成立时,就进行循环,直到 condition 的条件不成立才停止。
【until do done】
until [ condition ]
do
程序段落
done
解释:当 condition 条件成立时,就终止循环,否则就持续进行循环的程序段。
【练习】
题目1:假设我要让用户输入yes或者是YES才结束程序的执行,否则就一直进行告知用户输入字符串。

1 #!/bin/bash 2 # Program: 3 # while:Repeat question until user input correct answer. 4 # History: 5 # 2017-10-1 liuyu First release 6 7 while [ "$yn" != "yes" -a "$yn" != "YES" ] 8 do 9 read -p "Please input yes/YES to stop this program: " yn 10 done 11 echo "OK! you input the correct answer."

1 #!/bin/bash 2 # Program: 3 # until:Repeat question until user input correct answer. 4 # History: 5 # 2017-10-1 liuyu First release 6 7 until [ "$yn" == "yes" -o "$yn" == "YES" ] 8 do 9 read -p "Please input yes/YES to stop this program: " yn 10 done 11 echo "OK! you input the correct answer."
题目2:计算1+2+3+...+100这个数据。

1 #!/bin/bash 2 # Program: 3 # Use loop to calculate "1+2+3+...+100" result. 4 # History: 5 # 2017-10-1 liuyu First release 6 7 ans=0 # 这是累加的数值变量 8 i=0 # 这是累计的数值,亦即是1,2,3... 9 while [ "$i" != "100" ] 10 do 11 i=$(($i+1)) 12 ans=$(($ans+$i)) 13 done 14 echo "The result of '1+2+3+...+100' is ==> $ans"
题目3:让用户自行输入一个数字,让程序由1+2+...直到用户输入的数字为止。

1 #!/bin/bash 2 # Program: 3 # practice of until of page 394. 4 # History: 5 # 2017-10-1 liuyu First release 6 7 ans=0 8 i=0 9 read -p "Please input a integer: " n 10 if [ "$n" -le "0" ]; then 11 echo "Sorry, you input a integer which isn't bigger than one!" 12 exit 0; 13 else 14 until [ "$i" -eq "$n" ] 15 do 16 i=$(($i+1)) 17 ans=$(($ans+$i)) 18 done 19 echo "The result of '1+2+3+...+$n' is ==> $ans" 20 fi
2. 固定循环
【for do done】
for var in con1 con2 con3 ...
do
程序段
done
解释:变量var的内容在第 i 次循环时为coni
【练习】
题目1:假设我有三种动物,分别是 dog, cat, elephant 三种,我想每一行都输出这样:“There are dogs...”之类的字样。

1 #!/bin/bash 2 # Program: 3 # Using for...loop to print 3 animals 4 # History: 5 # 2017-10-1 liuyu First release 6 7 for animal in dog cat elephant 8 do 9 echo "There are ${animal}s..." 10 done
题目2:系统上的账号都是写在/etc/passwd内的第一个字段,你能不能通过管道命令 cut 找出单纯的账号名称后,以 id 及 finger 分别检查用户的标识符与特殊参数呢?

1 #!/bin/bash 2 # Program: 3 # Use id,finger command to check system account's information. 4 # History: 5 # 2017-10-1 liuyu First release 6 7 users=$(cut -d ':' -f1 /etc/passwd) 8 for username in $users 9 do 10 id $username 11 finger $username 12 done
评讲:执行此脚本后,我们的系统账号就会被获取出来检查。
补充:这个操作还可以用在每个账号的删除/更改上面呢!
题目3:我现在需要一连串的数字来进行循环。如我想要利用 ping 这个可以判断网络状态的命令。来进行网络状态的实际检测时,我想要检测的域是本机所在的192.168.1.1~192.168.1.100,由于有100台主机,故我不想在 for 后面输入1到100。

1 #!/bin/bash 2 # Program: 3 # Use ping command to check the network's PC state. 4 # History: 5 # 2017-10-1 liuyu First release 6 7 network="192.168.1" #先定义一个域的前面部分 8 for sitenu in $(seq 1 100) #seq为sequence(连续)的缩写之意 9 do 10 #下面的语句取得ping的回传值是正确的还是失败的 11 ping -c l -w l ${network}.${sitenu} &> /dev/null && result=0 || result=1 12 #开始回显结果是正确的启动(UP)还是错误的没有连通(DOWN) 13 if [ "$result" == 0 ]; then 14 echo "Sever ${network}.${sitenu} is UP." 15 else 16 echo "Sever ${network}.${sitenu} is DOWN." 17 fi 18 done
评讲:上面这一串命令执行之后就可以显示出192.168.1.1~192.168.1.100共100部主机目前是否能与你的机器连通!如果你的域与我们所在的位置不同,则直接修改上面那个network的变量内容即可!
题目4:让用户输入某个目录文件名,然后找出某目录内的文件名的权限。

1 #!/bin/bash 2 # Program: 3 # User input dir name, I find the permission of files. 4 # History: 5 # 2017-10-1 liuyu First release 6 7 # 1.先看看这个目录是否存在 8 read -p "Please input a directory: " dir 9 if [ "$dir" == "" -o ! -d "$dir" ]; then 10 echo "The $dir is NOT exist in your system." 11 exit 1; 12 fi 13 14 # 2. 开始测试文件 15 filelist=$(ls $dir) # 列出所有在该目录下的文件名 16 for filename in $filelist 17 do 18 perm="" 19 test -r "$dir/$filename" && perm="$perm readable" 20 test -w "$dir/$filename" && perm="$perm writable" 21 test -x "$dir/$filename" && perm="$perm executable" 22 echo "The file $dir/$filenam's permission is $perm." 23 done
评讲:此题涉及判断式与循环的综合。
【另一种使用方式——适合于数值运算中】
for ( ( 初始值; 限制值; 执行步长 ) )
do
程序段
done
解释:初始值为某个变量在循环当中的初始值(直接以类似i=1设置好);限制值为当变量的值在这个限制值的范围内,就继续进行循环,例如i<=100;执行步长为每做一次循环时变量的变化量,如i=i+1。
题目:进行1累加到用户输入的循环

1 #!/bin/bash 2 # Program: 3 # Use for to calculate "1+2+...+${your_input}". 4 # History: 5 # 2017-10-1 liuyu release 6 7 read -p "Please input a number, I will count for 1+2+...+your_input: " n 8 9 ans=0 10 for ((i=1; i<=$n; i=i+1)) 11 do 12 ans=$(($ans+$i)) 13 done 14 echo "The result of '1+2+3+...+$n' is ==> $ans."
十一、shell script的追踪与调试
1. 概述
script在执行之前,最怕出现语法错误的问题了!那么我们如何调试呢?
我们有没有办法不需要通过直接执行该 script 就可以来判断是否有问题呢?
有的,而且很简单,只要在执行该script的命令中加上相关参数即可。
2. 用法
bash [-nx] 文件名 //-n为不执行script,仅查询语法的问题;-x为将使用到的script内容显示到屏幕上(执行过程显示出来,很重要)
