This 和super都是Java中的关键字,this表示当前对象,可以调用方法、属性、指向对象本身。super表示父类,可以调用父类的方法、属性、对象。This在Java中使用有三种:
第一,指向当前对象
1 package day03; 2 3 4 5 public class Fruit { 6 7 int i = 0; 8 9 10 11 Fruit eatFruit() { 12 13 i++; 14 15 return this; 16 17 } 18 19 20 21 public static void main(String[] args) { 22 23 Fruit fruit = new Fruit(); 24 25 fruit.eatFruit().eatFruit(); 26 27 } 28 29 }
通过return this,哪个对象调用eatFruit就能返回对象自身。
第二,修饰属性
1 package day03; 2 3 4 5 public class Orange { 6 7 private int num; 8 9 10 11 public Orange(int num) { 12 13 this.num = num; 14 15 } 16 17 18 19 public static void main(String[] args) { 20 21 new Orange(100); 22 23 } 24 25 }
Main方法中传递了一个int值为100的参数,表示橘子的数量,并且这个数量赋值给了全局变量num。所以num现在的值是100.
第三,This和构造函数一起用,充当全局关键字效果
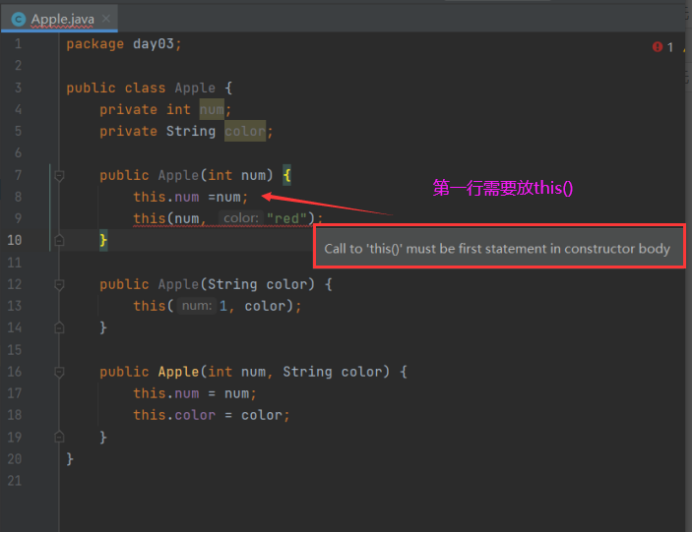
1 package day03; 2 3 4 5 public class Apple { 6 7 private int num; 8 9 private String color; 10 11 12 13 public Apple(int num) { 14 15 this(num, "red"); 16 17 } 18 19 20 21 public Apple(String color) { 22 23 this(1, color); 24 25 } 26 27 28 29 public Apple(int num, String color) { 30 31 this.num = num; 32 33 this.color = color; 34 35 } 36 37 }
可以看到this关键字参数相当于调用了其他构造方法,然后传递参数进去,需要注意this()必须放在构造方法第一行,否则编译不通过。
this和super特点对照表:
|
关键字 |
this |
super |
|
调用方式 |
调用本类中的属性、构造函数、方法 |
调用父类中的属性、构造函数、方法 |
|
调用位置 |
构造函数第一行,其他可自行指定 |
构造函数第一行,其他可自行指定 |
|
调用次数 |
一个构造函数只能调用一次 |
一个构造函数只能调用一次 |
eg1:
【Lemon.java】
1 package day03; 2 3 4 5 public class Lemon extends Fruit { 6 7 int i = 0; 8 9 10 11 Fruit eatFruit() { 12 13 i++; 14 15 return super.eatFruit(); 16 17 } 18 19 }
【Fruit.java】
1 package day03; 2 3 4 5 public class Fruit { 6 7 int i = 0; 8 9 10 11 Fruit eatFruit() { 12 13 i++; 14 15 return this; 16 17 } 18 19 20 21 public static void main(String[] args) { 22 23 Fruit fruit = new Fruit(); 24 25 fruit.eatFruit().eatFruit(); 26 27 } 28 29 }
eg2:
【Fruit.java】
1 package day04; 2 3 4 5 public class Fruit { 6 7 int num; 8 9 String color; 10 11 12 13 public Fruit() { 14 15 } 16 17 18 19 public void eat() { 20 21 System.out.println("吃水果"); 22 23 } 24 25 26 27 public Fruit(int num) { 28 29 this(num, "red"); 30 31 } 32 33 34 35 36 37 public Fruit(int num, String color) { 38 39 this.num = num; 40 41 this.color = color; 42 43 } 44 45 }
【Banana.java】
1 package day04; 2 3 4 5 public class Banana extends Fruit{ 6 7 private int num; 8 9 private String color; 10 11 12 13 public Banana(int num) { 14 15 super(); 16 17 } 18 19 20 21 public static void main(String[] args) { 22 23 new Fruit(100); 24 25 } 26 27 }
eg3:
【Fruit .java】
1 package day04; 2 3 4 5 public class Fruit { 6 7 int num; 8 9 String color; 10 11 12 13 public void eat() { 14 15 System.out.println("吃水果"); 16 17 } 18 19 20 21 public Fruit(int num) { 22 23 this(num, "red"); 24 25 } 26 27 28 29 public Fruit(String color) { 30 31 this(1, color); 32 33 } 34 35 36 37 public Fruit(int num, String color) { 38 39 this.num = num; 40 41 this.color = color; 42 43 } 44 45 }
【Apple.java】
1 package day04; 2 3 4 5 public class Apple extends Fruit { 6 7 public Apple(int num) { 8 9 super(num); 10 11 } 12 13 14 15 public Apple(String color) { 16 17 super(color); 18 19 } 20 21 22 23 public Apple(int num, String color) { 24 25 super(num, color); 26 27 } 28 29 30 31 @Override 32 33 public void eat() { 34 35 super.num = 1; 36 37 System.out.println("吃了" + num + "个苹果"); 38 39 } 40 41 }