1、可以使用Python的字典实现,对于一个特定的字符串,使用for循环遍历其中的字符,并保存成字典形式。字典的key为字符,value为字符在整个字符串中出现的次数。
2、拓展:如果题目为比较两个字符串是否相似,例如字符串str1 = "abcdefd"与字符串str2 = "bcadef"为相似的,因为字符串中出现的字符的次数是相同的。对于字符串str1以及字符串str2可以得到两个字典dict1以及dict2。此时可以使用模块operator中的方法对dict1以及dict2进行比较,即可得出是否为相似的字符串。
3、前导知识:
(1)关于Python的字典:dict1 = {'a':2, 'b':3, 'c':8, 'd':4}
- 分别取字典的键、值:print(dict1.values(), dict1.keys())。结果:dict_values([4, 2, 8, 3]) dict_keys(['d', 'a', 'c', 'b']) 注意返回的是列表的形式。
- 同时取字典的键、值:print(dict1.items())或者print(dict1)
- 排序sorted()函数:
对键正向排序(默认形式):
1 dict1={'a':2,'e':3,'f':8,'d':4} 2 dict2 = sorted(dict1) 3 print(dict2)
输出:
1 ['a', 'd', 'e', 'f']
对键反向排序:
1 dict1={'a':2,'e':3,'f':8,'d':4} 2 dict2 = sorted(dict1,reverse=True) 3 print(dict2) 4 结果:['f', 'e', 'd', 'a']
对值排序:
1 dict1={'a':2, 'e':3, 'f':8, 'd':4} 2 list1= sorted(dict1.values()) 3 print(list1) #结果:[2, 3, 4, 8]
设值reverse=True 进行反向排序
也可以用dict1.items(),得到包含键,值的元组
由于迭代对象是元组,返回值自然是元组组成的列表
这里对排序的规则进行了定义,x指元组,x[1]是值,x[0]是键
dict1={'a':2,'e':3,'f':8,'d':4}
list1= sorted(dict1.items(),key=lambda x:x[1])
print(list1)
结果:
[('a', 2), ('e', 3), ('d', 4), ('f', 8)]
对键进行排序:
dict1={'a':2,'e':3,'f':8,'d':4}
list1= sorted(dict1.items(),key=lambda x:x[0])
print(list1)
结果:
[('a', 2), ('d', 4), ('e', 3), ('f', 8)]
(2)Python 字典(Dictionary) cmp()方法(python2.X)
Python 字典的 cmp() 函数用于比较两个字典元素。
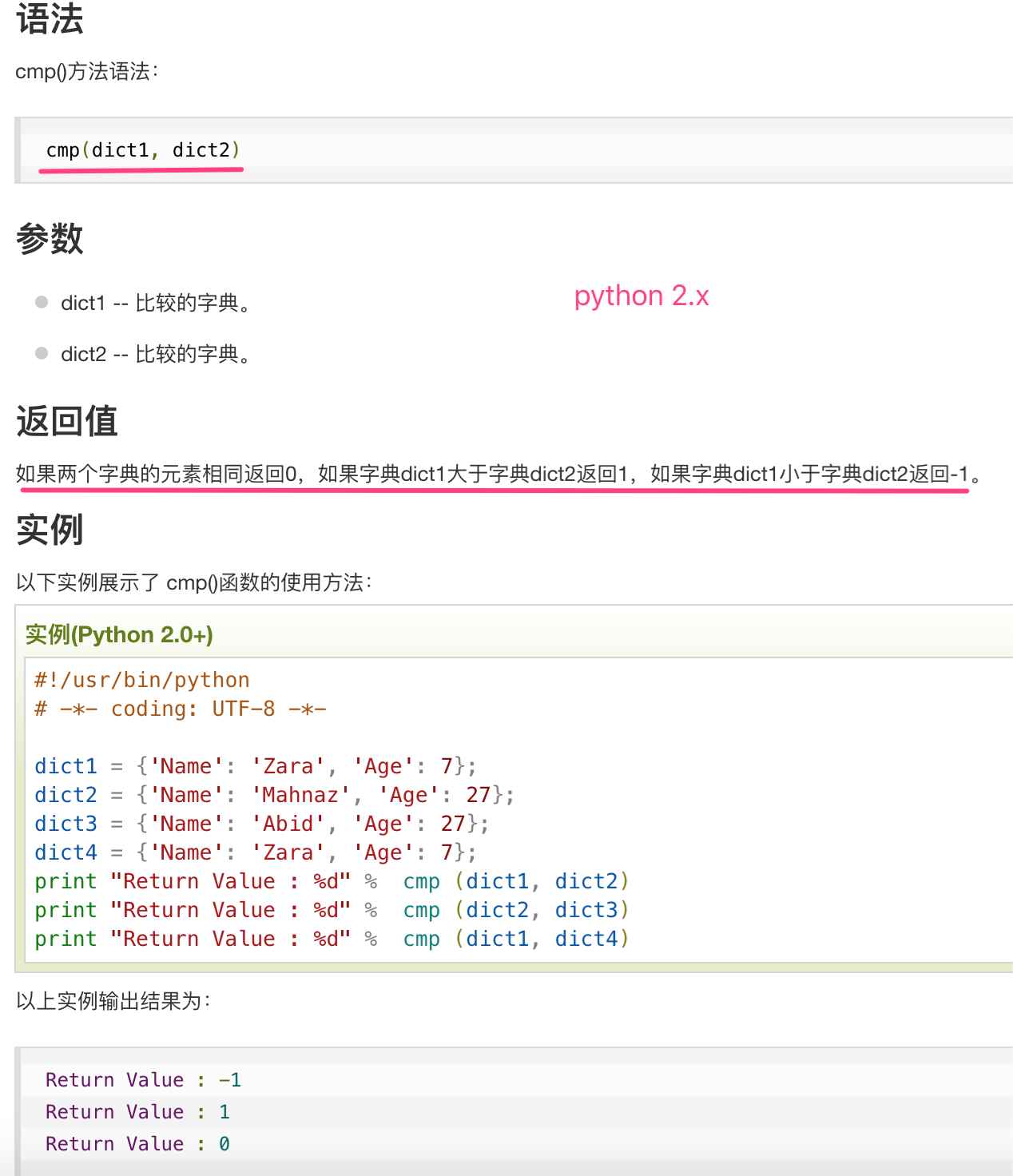
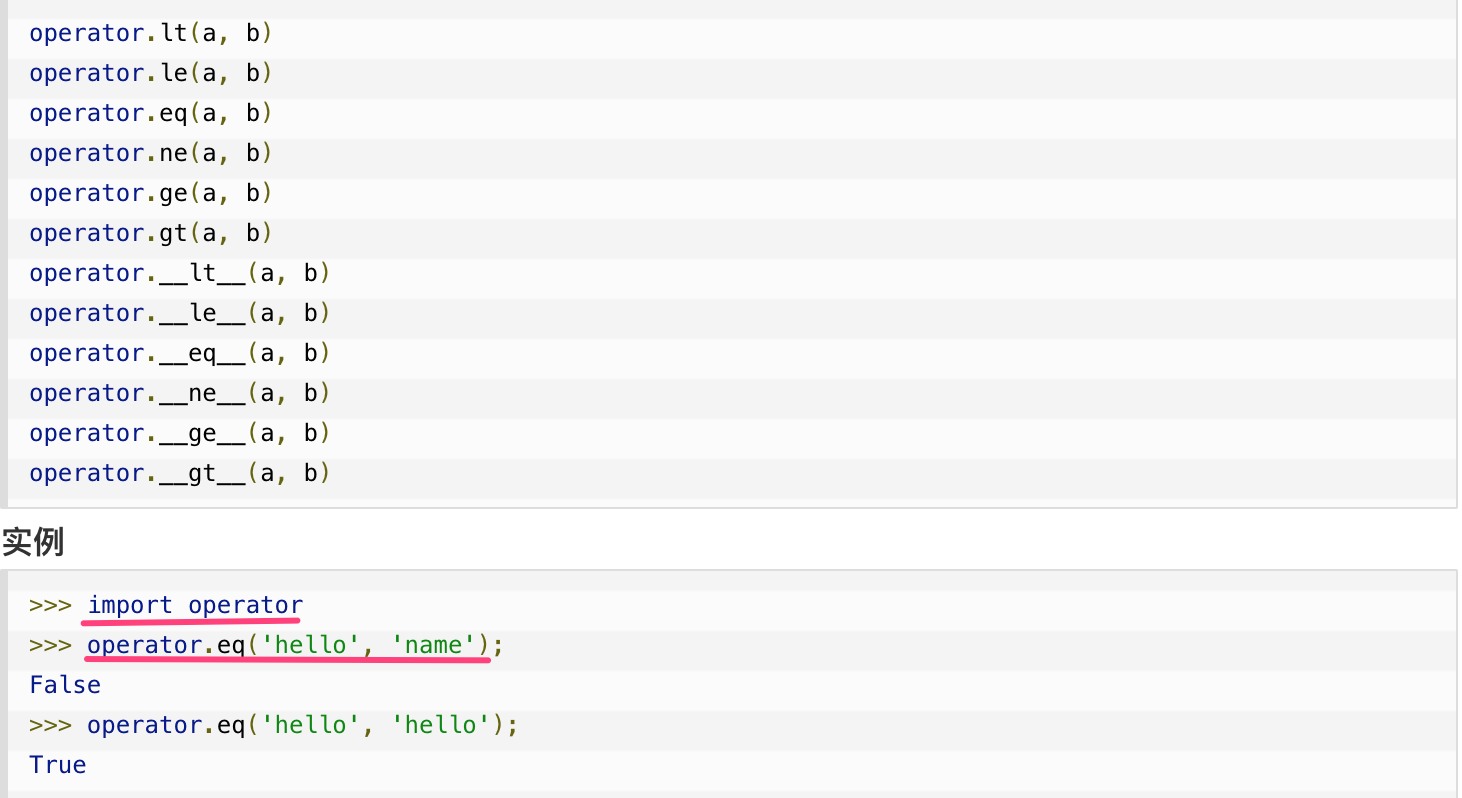
Python 3.X 的版本中已经没有 cmp 函数,如果你需要实现比较功能,需要引入 operator 模块,适合任何对象,包含的方法有:
4、面试题:字符串str1 = "abcdefd"与字符串str2 = "bcadef"为相似。
代码实现:
1 # author by xuelisheng 2 import operator 3 4 str1 = 'abcdefgaaa' # 给出字符串 5 str2 = 'abcdefg' # 给出字符串 6 7 d1 = {} # 给出字典 8 d2 = {} # 给出字典 9 10 for x in str1: 11 if x in d1: 12 d1[x] = d1[x] + 1 13 else: 14 d1[x] = 1 15 16 for x in str2: 17 if x in d2: 18 d2[x] = d2[x] + 1 19 else: 20 d2[x] = 1 21 22 print(operator.eq(d1, d2))