说到统计词频数,python比cuda要好用多了,首先是python有相关的库供我们使用,
还有python调用相关的函数,省去我们在cuda中需要写很多的函数。汉语的词频统计
和英语有些不同,汉语需要用到jiba库。
英文词频统计的思路:1.首先我们将文中的特殊字符,替换为空格;
2.进行词语分割;
3.遍历文中的词语,计算出现的次数。
汉语词频统计思路:整体的思路和英文是一样的,但是汉语的词语分割会出现一些
我们不需要的目标词语,所以我们需要将这些词语排除掉。
代码如下:

#CalHamletV1.py def getText(): txt = open("hamlet.txt", "r").read() txt = txt.lower() for ch in '!"#$%&()*+,-./:;<=>?@[\]^_‘{|}~': txt = txt.replace(ch, " ") #将文本中特殊字符替换为空格 return txt hamletTxt = getText() words = hamletTxt.split() counts = {} for word in words: counts[word] = counts.get(word,0) + 1 items = list(counts.items()) items.sort(key=lambda x:x[1], reverse=True) for i in range(10): word, count = items[i] print ("{0:<10}{1:>5}".format(word, count))

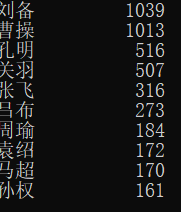
#CalThreeKingdomsV2.py import jieba excludes = {"将军","却说","荆州","二人","不可","不能","如此","商议","军士","如何","军马","主公","左右", "天下","次日"} txt = open("三国演义.txt", "r", encoding='utf-8').read() words = jieba.lcut(txt) counts = {} for word in words: if len(word) == 1: continue elif word == "诸葛亮" or word == "孔明曰": rword = "孔明" elif word == "关公" or word == "云长": rword = "关羽" elif word == "玄德" or word == "玄德曰": rword = "刘备" elif word == "孟德" or word == "丞相": rword = "曹操" else: rword = word counts[rword] = counts.get(rword,0) + 1 for word in excludes: del counts[word] items = list(counts.items()) items.sort(key=lambda x:x[1], reverse=True) for i in range(10): word, count = items[i] print ("{0:<10}{1:>5}".format(word, count))
运行结果: