独立的集合bean

在多个bean之间可共享该独立bean。
示例:
<bean id="car1" class="com.entity.Car"> <property name="brand" value="BMW"/> <property name="color" value="白色"/> </bean> <bean id="car2" class="com.entity.Car"> <property name="brand" value="BENZ"/> <property name="color" value="红色"/> </bean> <bean id="car3" class="com.entity.Car"> <property name="brand" value="AUDI"/> <property name="color" value="黑色"/> </bean>
<util:list id="mycars">
<ref bean="car1"/>
<ref bean="car2"/>
<ref bean="car3"/>
</util:list>
在其他bean中即可共享该mycars--bean。
<bean name="stu,s1,s2" class="com.entity.Students">
<property name="cars">
<ref bean="mycars"/>
</property>
</bean>
P名空间

使用p命名空间时需要先声明使用对应的命名空间,即在beans元素上加入:
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
使用p命名空间的好处是简化配置信息。
示例:
<bean id="car1" class="com.entity.Car" p:brand="BMW" p:color="白色"/> <bean id="car2" class="com.entity.Car" p:brand="BENZ" p:color="红色"/> <bean id="car3" class="com.entity.Car" p:brand="AUDI" p:color="黑色"/>
静态工厂注入

使用的是工厂中的静态方法。
在service层引用的dao,1.可以使用原始的方式注入,2.也可以使用静态工厂注入,自己编写一个工厂类,里面静态方法返回一个dao的实现类对象。
静态工厂BinessDAOFactory:
package com.factory; import com.dao.CarDAO; import com.dao.StudentsDAO; import com.dao.impl.CarDAOImpl; import com.dao.impl.StudentsDAOImpl; public class BinessDAOFactory { //获得学生的DAO实例 public static StudentsDAO getStudentsDAOImplInstance(){ return new StudentsDAOImpl(); } //获得汽车的DAO实例、 public static CarDAO getCarDAOImplInstance(){ return new CarDAOImpl(); } //获得用户的DAO实例 /*public static UsersDAO getUsersDAOImplInstance(){ return new UsersDAOImpl(); }*/ }
applicationContext.xml:
<!-- 一个学生bean -->
<bean id="s" class="com.entity.Students" p:sid="s0001" p:name="金泰妍" p:gender="女" p:birthday="1989-03-09" p:address="韩国"/>
<!-- 学生dao bean -->
<bean id="sDao" class="com.factory.BinessDAOFactory"
factory-method="getStudentsDAOImplInstance">//静态方法
</bean>
<!-- 学生service bean -->
<bean id="sService" class="com.service.impl.StudentsServiceImpl">
<property name="studentsDAO" ref="sDao"></property>
</bean>
测试:
@Test public void fun1(){ ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); Students s=(Students) ctx.getBean("s"); //System.out.println(s); StudentsServiceImpl sService=(StudentsServiceImpl) ctx.getBean("sService"); sService.add(s); }
实例工厂注入

工厂:
public class BinessDAOFactory { //获得学生的DAO实例 public StudentsDAO getStudentsDAOImplInstance(){ return new StudentsDAOImpl(); } }
applicationContext.xml:
<!-- 工厂bean的注入 -->
<bean id="businessFactory" class="com.factory.BinessDAOFactory"></bean>
<!-- 实例工厂注入--得到dao的bean -->
<bean id="sDao1" factory-bean="businessFactory" factory-method="getStudentsDAOImplInstance">
</bean>
<!-- 学生service bean -->
<bean id="sService" class="com.service.impl.StudentsServiceImpl">
<property name="studentsDAO" ref="sDao1"></property>
</bean>
测试:
public class StudentServiceImplTest { @Test public void fun1(){ ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); Students s=(Students) ctx.getBean("s"); //System.out.println(s); StudentsServiceImpl sService=(StudentsServiceImpl) ctx.getBean("sService"); sService.add(s); } }
bean之间的依赖关系

在Students类中加上Car car这个属性字段。
<!-- 一个学生bean -->
<bean id="s" class="com.entity.Students" p:sid="s0001" p:name="金泰妍" p:gender="女" p:birthday="1989-03-09" p:address="韩国" p:car-ref="c" depends-on="c"/>
<bean id="c" class="com.entity.Car" p:brand="BWM" p:color="白色"/>
学生bean依赖汽车bean,在初始化的时候会先初始化Car。
bean的生命周期
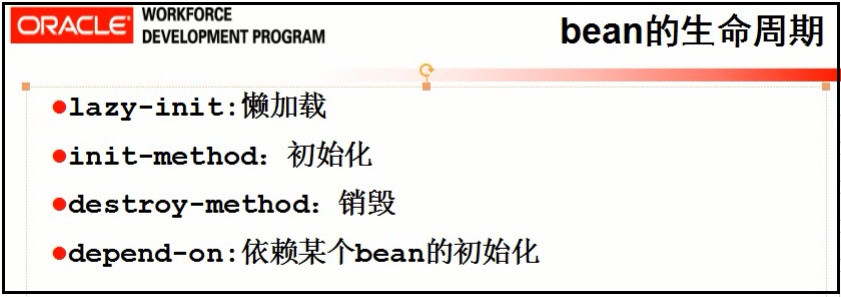
1.懒加载,在用到该bean的时候,才会去初始化它,加载它。
Students.java:
package com.entity; import java.io.Serializable; import java.text.ParseException; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Date; import java.util.List; import javax.annotation.PostConstruct; import javax.annotation.Resource; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; //加注解注入,起一个别名s1 @Component("haha") public class Students implements Serializable { private String sid;// 学号 private String name;// 姓名 private String gender;// 性别 private Date birthday;// 生日 private String address;// 住址 private Car car;// 学生拥有的车的引用 // private List<Car> cars; //初始化方法,在构造方法之后调用 public void initStudents(){ System.out.println("执行学生的initStudents()方法"); } //在ApplicationContext对象被销毁的时候执行 public void destroyStudents(){ System.out.println("执行学生的destroyStudents()方法"); } public Students(String sid, String name, String gender, Date birthday, String address) { super(); this.sid = sid; this.name = name; this.gender = gender; this.birthday = birthday; this.address = address; } public Students(String sid, String name, String gender, Date birthday, String address, Car car) { super(); this.sid = sid; this.name = name; this.gender = gender; this.birthday = birthday; this.address = address; this.car = car; } public Car getCar() { return car; } public void setCar(Car car) { this.car = car; } public Students(String sid, String name, String gender, String address) { this.sid = sid; this.name = name; this.gender = gender; this.address = address; } /*//解决方法1: //在构造方法之后执行一些初始化的操作 @PostConstruct public void init(){ //在调用完构造函数之后,birthday还为null,然后使用这个直接赋值 try { this.setBirthday(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd").parse("2000-05-17")); } catch (ParseException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } }*/ public Students() { System.out.println("一个学生创建啦..."); } public String getSid() { return sid; } // @Value("s0006") public void setSid(String sid) { this.sid = sid; } public String getName() { return name; } // @Value("IU") public void setName(String name) { System.out.println("执行了setName()方法"); this.name = name; } public String getGender() { return gender; } // @Value("女") public void setGender(String gender) { this.gender = gender; } public Date getBirthday() { return birthday; } // @Value("1998-07-15") public void setBirthday(Date birthday) { this.birthday = birthday; } public String getAddress() { return address; } // @Value("韩国首尔") public void setAddress(String address) { this.address = address; } @Override public String toString() { return "Students [sid=" + sid + ", name=" + name + ", gender=" + gender + ", birthday=" + birthday + ", address=" + address + ", car=" + car + "]"; } }
applicationContext.xml:
<!-- 一个学生bean -->
<bean id="s" class="com.entity.Students" p:sid="s0001" p:name="金泰妍" p:gender="女" p:birthday="1989-03-09" p:address="韩国" p:car-ref="c" depends-on="c" lazy-init="true" init-method="initStudents" destroy-method="destroyStudents" scope="prototype"/>
<bean id="c" class="com.entity.Car" p:brand="BWM" p:color="白色"/>
测试:
public class StudentServiceImplTest { @Test public void fun1(){ ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); Students s=(Students) ctx.getBean("s"); Students ss=(Students) ctx.getBean("s"); System.out.println(s==ss);//单例:true prototype:false //System.out.println(s); StudentsServiceImpl sService=(StudentsServiceImpl) ctx.getBean("sService"); sService.add(s); ((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext)ctx).close(); } }
使用注解配置:
Students.java:
package com.entity; import java.io.Serializable; import java.text.ParseException; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Date; import java.util.List; import javax.annotation.PostConstruct; import javax.annotation.PreDestroy; import javax.annotation.Resource; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.DependsOn; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; //加注解注入,起一个别名s1 @Component("s") @DependsOn(value="car")//依赖关系 @Scope("prototype")//得到的bean对象是否为单例的singleton,prototype public class Students implements Serializable { private String sid;// 学号 private String name;// 姓名 private String gender;// 性别 private Date birthday;// 生日 private String address;// 住址 private Car car;// 学生拥有的车的引用 // private List<Car> cars; //初始化方法,在构造方法之后调用 @PostConstruct//初始化方法 public void initStudents(){ System.out.println("执行学生的initStudents()方法"); } //在ApplicationContext对象被销毁的时候执行 @PreDestroy//销毁方法 public void destroyStudents(){ System.out.println("执行学生的destroyStudents()方法"); } public Students(String sid, String name, String gender, Date birthday, String address) { super(); this.sid = sid; this.name = name; this.gender = gender; this.birthday = birthday; this.address = address; } public Students(String sid, String name, String gender, Date birthday, String address, Car car) { super(); this.sid = sid; this.name = name; this.gender = gender; this.birthday = birthday; this.address = address; this.car = car; } public Car getCar() { return car; } @Resource(name="car") public void setCar(Car car) { this.car = car; } public Students(String sid, String name, String gender, String address) { this.sid = sid; this.name = name; this.gender = gender; this.address = address; } /*//解决方法1: //在构造方法之后执行一些初始化的操作 @PostConstruct public void init(){ //在调用完构造函数之后,birthday还为null,然后使用这个直接赋值 try { this.setBirthday(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd").parse("2000-05-17")); } catch (ParseException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } }*/ public Students() { System.out.println("一个学生创建啦..."); } public String getSid() { return sid; } @Value("s0006") public void setSid(String sid) { this.sid = sid; } public String getName() { return name; } @Value("IU") public void setName(String name) { System.out.println("执行了setName()方法"); this.name = name; } public String getGender() { return gender; } @Value("女") public void setGender(String gender) { this.gender = gender; } public Date getBirthday() { return birthday; } @Value("1998-07-15") public void setBirthday(Date birthday) { this.birthday = birthday; } public String getAddress() { return address; } @Value("韩国首尔") public void setAddress(String address) { this.address = address; } @Override public String toString() { return "Students [sid=" + sid + ", name=" + name + ", gender=" + gender + ", birthday=" + birthday + ", address=" + address + ", car=" + car + "]"; } }
Car.java:
package com.entity; import java.io.Serializable; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; //注解注入,,之后的实例名称叫car @Component("car") public class Car implements Serializable{ private String brand;// 品牌 private String color;// 颜色 public Car() { System.out.println("一辆汽车诞生啦..."); } public Car(String brand, String color) { super(); this.brand = brand; this.color = color; } public String getBrand() { return brand; } @Value("BMW") public void setBrand(String brand) { this.brand = brand; } public String getColor() { return color; } @Value("黑色") public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } @Override public String toString() { return "Car [brand=" + brand + ", color=" + color + "]"; } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util" xmlns:cache="http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache/spring-cache-4.0.xsd"> <!-- 表示使用注解 --> <context:annotation-config/> <!-- 扫描带注解的包 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.entity"/> <!-- 实现类型转换的bean --> <!-- id的名字必须是这个 --> <bean id="customEditorConfigurer" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.CustomEditorConfigurer"> <property name="propertyEditorRegistrars"> <list> <bean class="com.convert.MyCustomDateEditorRegister"> <property name="format" value="yyyy-MM-dd"></property> </bean> </list> </property> </bean> <bean id="dateFormat" class="java.text.SimpleDateFormat"> <constructor-arg value="yyyy-MM-dd"/> </bean> <!-- 一个学生bean --> <!-- <bean id="s" class="com.entity.Students" p:sid="s0001" p:name="金泰妍" p:gender="女" p:birthday="1989-03-09" p:address="韩国" p:car-ref="c" depends-on="c" lazy-init="true" init-method="initStudents" destroy-method="destroyStudents" scope="prototype"/> <bean id="c" class="com.entity.Car" p:brand="BWM" p:color="白色"/> --> <!-- 静态工厂注入 学生dao bean --> <!-- <bean id="sDao" class="com.factory.BinessDAOFactory" factory-method="getStudentsDAOImplInstance"> </bean> --> <!-- 工厂bean的注入 --> <bean id="businessFactory" class="com.factory.BinessDAOFactory"></bean> <!-- 实例工厂注入##得到dao的bean --> <bean id="sDao1" factory-bean="businessFactory" factory-method="getStudentsDAOImplInstance"> </bean> <!-- 学生service bean --> <bean id="sService" class="com.service.impl.StudentsServiceImpl"> <property name="studentsDAO" ref="sDao1"></property> </bean> </beans>
测试:
package com.service.impl; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.entity.Students; public class StudentServiceImplTest { @Test public void fun1(){ ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); Students s=(Students) ctx.getBean("s"); Students ss=(Students) ctx.getBean("s"); System.out.println(s==ss);//单例:true prototype:false //System.out.println(s); StudentsServiceImpl sService=(StudentsServiceImpl) ctx.getBean("sService"); sService.add(s); ((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext)ctx).close(); } }