接URL匹配那一节。
在book中的urls.py
from django.urls import path from . import views urlpatterns = [ path('', views.index), path('web/', views.web), path('19/0425/<html>',views.trans), ]
在book中的views.py
from django.http import HttpResponse
#html参数用来接收urls.py中的<html> def trans(request,html): return HttpResponse("<h1>{}</h1>".format(html))
启动服务后,我们在浏览器中输入http://127.0.0.1:8000/19/0425/transform
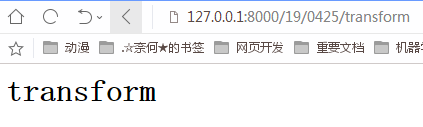
即urls.py中的html参数为transform,成功的显示在了前端界面中。
一般有五种方式:
(1)str--匹配的第一个非空字符,除去‘/’,默认使用的是这种方式;
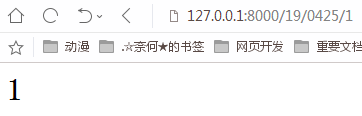
(2)int--匹配0或正整数;

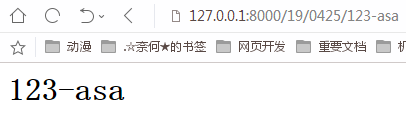
(3)slug--由ASCII字母或数字组成,通过'-'连接的字符串;
(4)uuid--uuid格式的字符串;

(5)path--匹配的一个非空字符串,包括‘/’;

from django.urls import path from . import views urlpatterns = [ path('', views.index), path('web/', views.web), path('19/0425/<str:html>',views.trans), path('19/0425/<int:page>',views.trans2), path('19/0425/<int:numa>/<int:numb>',views.trans3), path('19/0425/<slug:slugStr>',views.trans4), path('19/0425/<uuid:uu>',views.trans5), path('19/0425/<path:home>',views.trans6), ]
from django.http import HttpResponse #157f572e-ebbc-4914-a5b2-6e3ed0bb9c8c # Create your views here. def index(request): html="<h1 style='color:red'>hello world</h1>" return HttpResponse(html) def web(request): html="<h1>Djang Web</h1>" return HttpResponse(html) def trans(request,html): return HttpResponse("<h1>{}</h1>".format(html)) def trans2(request,page): return HttpResponse("<h1>{}</h1>".format(page)) def trans3(request,numa,numb): return HttpResponse("<h1>{}</h1>".format(numa+numb)) def trans4(request,slugStr): return HttpResponse("<h1>{}</h1>".format(slugStr)) def trans5(request,uu): return HttpResponse("<h1>{}</h1>".format(uu)) def trans6(request,home): return HttpResponse("<h1>{}</h1>".format(home))