ArrayList是一种以数组实现的List,与数组相比,它具有动态扩展的能力,因此也可称之为动态数组。
那么我们可以看看实现:
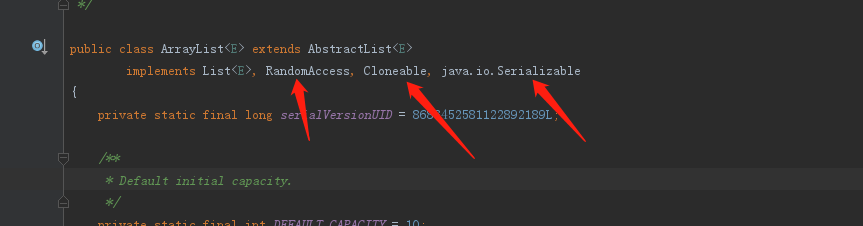
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
可以看出ArrayList实现了list,randomaccess,clonable接口,
其中 randomaccess,clonable接口,是没有响应的方法,只是一种标识接口,第一个randomaccess接口标识代表,arraylist支持快速访问,cloneable接口标识表示可以arraylist可以被克隆,序列化,表示可以用于传输,
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L; //默认初始化容量 private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; //空数组如果传入的容量为0时使用 private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; //空数组,传传入容量时使用,添加第一个元素的时候会重新初始为默认容量大小 private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; //存储数据的缓冲区,使用关键字transient不适用序列化 transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access /** * The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains). * * @serial */
//集合中的元素
private int size;
(1)DEFAULT_CAPACITY
默认容量为10,也就是通过new ArrayList()创建时的默认容量。
(2)EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
空的数组,这种是通过new ArrayList(0)创建时用的是这个空数组。
(3)DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
也是空数组,这种是通过new ArrayList()创建时用的是这个空数组,与EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA的区别是在添加第一个元素时使用这个空数组的会初始化为DEFAULT_CAPACITY(10)个元素。
(4)elementData
真正存放元素的地方,使用transient是为了不序列化这个字段。
至于没有使用private修饰,后面注释是写的“为了简化嵌套类的访问”,但是楼主实测加了private嵌套类一样可以访问。
private表示是类私有的属性,只要是在这个类内部都可以访问,嵌套类或者内部类也是在类的内部,所以也可以访问类的私有成员。
(5)size
真正存储元素的个数,而不是elementData数组的长度。
构造方法:
//初始化容量的构造方法
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { if (initialCapacity > 0) { this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; } else if (initialCapacity == 0) { this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ initialCapacity); } } //空餐构造方法 不传初始容量,初始化为DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA空数组,会在添加第一个元素的时候扩容为默认的大小,即10。 public ArrayList() { this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } //传入元素的构造方法 ,将集合中的元素传入ArrayList中 public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) { elementData = c.toArray(); if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) { // c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652) if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
//将传入集合的元素传入到集合中 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class); } else { // replace with empty array. this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } }
那么我们在使用arraylist的使用该怎么用呢,最好是初始化容量,避免在动态扩容的时候消耗性能的,终所周知的是,arraylist是一个线程不安全的,那么我们在项目中为什么还使用呢,.由于我们使用的是局部使用,并没有作为一个共享变量来使用,所以是安全的,也是
在独立的线程中使用,
再看增加方法:
public boolean add(E e) {
//检查是否需要扩容 ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
//在末尾加上数据 elementData[size++] = e; return true; }
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
//如果是空数据组,那么就初始化最小容量
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
//扩容
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
//扩容方法
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
(1)检查是否需要扩容;
(2)如果elementData等于DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA则初始化容量大小为DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
(3)新容量是老容量的1.5倍(oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1)),如果加了这么多容量发现比需要的容量还小,则以需要的容量为准;
(4)创建新容量的数组并把老数组拷贝到新数组;
删除方法:
//删除指定元素的方法索引下数据的方法
public E remove(int index) {
//检查是否越界 rangeCheck(index); //表示被修改的次数 modCount++; E oldValue = elementData(index); //如果不是最后一位,将索引位置后的数据前移
//具体操作是这样:调用操作系统的方法 将数组中的数据拷贝,将到指定的位置 int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work return oldValue; }
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
/*
Copies an array from the specified source array, beginning at the
* specified position, to the specified position of the destination array.
* A subsequence of array components are copied from the source
* array referenced by <code>src</code> to the destination array
* referenced by <code>dest</code>. The number of components copied is
* equal to the <code>length</code> argument. The components at
* positions <code>srcPos</code> through
/public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,
Object dest, int destPos,
int length);
(1)检查索引是否越界;
(2)获取指定索引位置的元素;
(3)如果删除的不是最后一位,则其它元素往前移一位;
(4)将最后一位置为null,方便GC回收;
(5)返回删除的元素。
可以看到,ArrayList删除元素的时候并没有缩容。
ArrayList中只有扩容方法,并没减少容量的方法
快速移除的方法:
private void fastRemove(int index) { modCount++; int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work }
移除指定元素:
public boolean remove(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (elementData[index] == null) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } else { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } return false; }
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew); size += numNew; return numNew != 0; }
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount int numMoved = size - index; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew, numMoved); System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew); size += numNew; return numNew != 0; }
ArrayList里面最核心的方法:
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved);
public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,
Object dest, int destPos,
int length);
* @param src the source array.
* @param srcPos starting position in the source array.
* @param dest the destination array.
* @param destPos starting position in the destination data.
* @param length the number of array elements to be copied.
从指定数组中将从index索引位置,拷贝到目标数组中指定索引位置,.length为拷贝数的长度.