作者:桂。
时间:2018-05-20 12:04:24
链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/xingshansi/p/9063131.html
前言
相比DFT,CZT是完成频谱细化的一种思路,本文主要记录CZT的C代码实现。
一、代码实现
原理主要参考MATLAB接口:
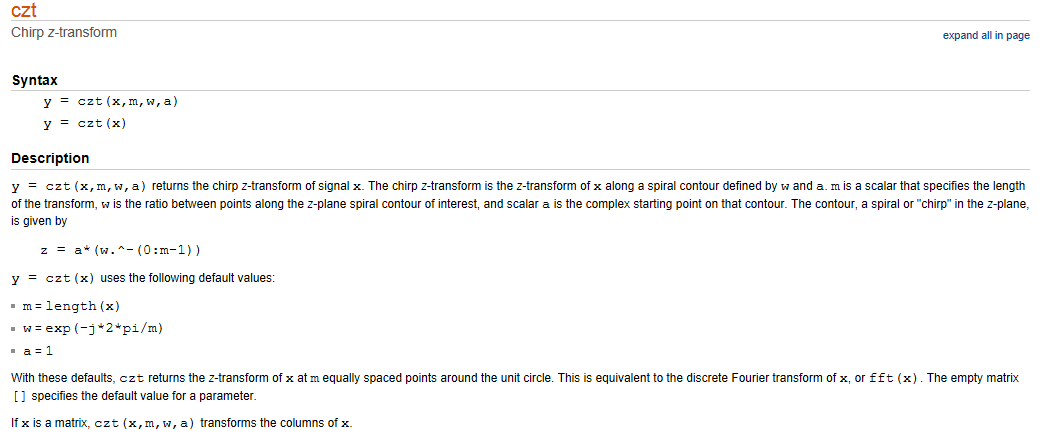
对应C代码实现:
Complex.c

/*============================= Chirp-Z Transform =============================*/ #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> #include "Complex.h" #include "FFT.h" void CZT(comp* x, int N, comp A, comp W, comp *xCZT, int M); void main() { int i; int N,M; double PI; double A0,Theta0; double W0,Phi0; comp* x; comp* xCZT; comp A,W; PI = 3.1415926; N = 5; //信号长度 M = 10; //chirp-z 变换输出长度 x = (comp *)calloc(N,sizeof(comp)); xCZT = (comp *)calloc(M,sizeof(comp)); for (i = 0;i < N; i++) { x[i].re=(float)(i-3); x[i].im = 0.0; } A0 = 1.0; //起始抽样点z0的矢量半径长度 Theta0 = 0.0; //起始抽样点z0的相角 A.re = (float)(A0*cos(Theta0)); A.im = (float)(A0*sin(Theta0)); Phi0 = 2.0*PI/M; //两相邻抽样点之间的角度差 W0 = 1.0; //螺线的伸展率 W.re = (float)(W0*cos(-Phi0)); W.im = (float)(W0*sin(-Phi0)); CZT(x,N,A,W,xCZT,M); printf("The Original Signal: "); for (i = 0; i<N; i++) { printf("%10.4f",x[i].re); printf("%10.4f ",x[i].im); } printf("The Chirp-Z Transfrom: "); for (i = 0 ;i<M ;i++) { printf("%10.4f",xCZT[i].re); printf("%10.4f ",xCZT[i].im); } } /*----------------函数说明---------------------- Name: CZT Function: Chirp-Z Transform Para: x[in][out]:待变换信号 N[in]:信号长度 A[in]: W[in]: M[in]:Chirp-Z变换输出长度 --------------------------------------------*/ void CZT(comp* x, int N, comp A, comp W, comp* xCZT, int M) { int i; int L; comp* h; comp* g; comp* pComp; comp tmp,tmp1,tmp2; i=1; do { i*=2; } while (i<N+M-1); L = i; h = (comp*)calloc(L,sizeof(comp)); g = (comp*)calloc(L,sizeof(comp)); pComp = (comp*)calloc(L,sizeof(comp)); for (i = 0; i<N; i++) { tmp1 = cpow(A,-i); tmp2 = cpow(W, i*i/2.0); tmp = cmul(tmp1,tmp2); g[i] = cmul(tmp,x[i]); } for (i = N;i<L; i++) { g[i] =czero(); } FFT(g,L,1); for (i = 0;i<=M-1;i++) { h[i] = cpow(W, -i*i/2.0); } for (i=M; i<=L-N;i++) { h[i] =czero(); } for (i = L-N+1; i<=L;i++) { h[i] = cpow(W,-(L-i)*(L-i)/2.0); } FFT(h,L,1); for (i = 0; i<L; i++) { pComp[i] = cmul(h[i],g[i]); } FFT(pComp,L,-1); //IDFT for (i = 0; i<M;i++) { tmp = cpow(W,i*i/2.0); xCZT[i] = cmul(tmp,pComp[i]); } }
Complex.h

/*=========================== Define comp as complex type cmplx c = (a,b) cmul c=a*b conjg c=a' cabs1 f=|a| cabs2 f=|a|**2 cadd c=a+b csub c=a-b czero c=(0.0,0.0) ===========================*/ #ifndef COMPLEX_H #define COMPLEX_H #include <math.h> typedef struct xy { float re; float im; }comp; comp cmplx(float a,float b); comp cmul(comp a,comp b); comp conjg(comp a); float cabs1(comp a); float cabs2(comp a); comp cadd(comp a,comp b); comp csub(comp a,comp b); comp czero(); comp cpow(comp a,double n); float arg(comp a); #endif
CZT.c

/*============================= Chirp-Z Transform =============================*/ #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> #include "Complex.h" #include "FFT.h" void CZT(comp* x, int N, comp A, comp W, comp *xCZT, int M); void main() { int i; int N,M; double PI; double A0,Theta0; double W0,Phi0; comp* x; comp* xCZT; comp A,W; PI = 3.1415926; N = 5; //信号长度 M = 10; //chirp-z 变换输出长度 x = (comp *)calloc(N,sizeof(comp)); xCZT = (comp *)calloc(M,sizeof(comp)); for (i = 0;i < N; i++) { x[i].re=(float)(i-3); x[i].im = 0.0; } A0 = 1.0; //起始抽样点z0的矢量半径长度 Theta0 = 0.0; //起始抽样点z0的相角 A.re = (float)(A0*cos(Theta0)); A.im = (float)(A0*sin(Theta0)); Phi0 = 2.0*PI/M; //两相邻抽样点之间的角度差 W0 = 1.0; //螺线的伸展率 W.re = (float)(W0*cos(-Phi0)); W.im = (float)(W0*sin(-Phi0)); CZT(x,N,A,W,xCZT,M); printf("The Original Signal: "); for (i = 0; i<N; i++) { printf("%10.4f",x[i].re); printf("%10.4f ",x[i].im); } printf("The Chirp-Z Transfrom: "); for (i = 0 ;i<M ;i++) { printf("%10.4f",xCZT[i].re); printf("%10.4f ",xCZT[i].im); } } /*----------------函数说明---------------------- Name: CZT Function: Chirp-Z Transform Para: x[in][out]:待变换信号 N[in]:信号长度 A[in]: W[in]: M[in]:Chirp-Z变换输出长度 --------------------------------------------*/ void CZT(comp* x, int N, comp A, comp W, comp* xCZT, int M) { int i; int L; comp* h; comp* g; comp* pComp; comp tmp,tmp1,tmp2; i=1; do { i*=2; } while (i<N+M-1); L = i; h = (comp*)calloc(L,sizeof(comp)); g = (comp*)calloc(L,sizeof(comp)); pComp = (comp*)calloc(L,sizeof(comp)); for (i = 0; i<N; i++) { tmp1 = cpow(A,-i); tmp2 = cpow(W, i*i/2.0); tmp = cmul(tmp1,tmp2); g[i] = cmul(tmp,x[i]); } for (i = N;i<L; i++) { g[i] =czero(); } FFT(g,L,1); for (i = 0;i<=M-1;i++) { h[i] = cpow(W, -i*i/2.0); } for (i=M; i<=L-N;i++) { h[i] =czero(); } for (i = L-N+1; i<=L;i++) { h[i] = cpow(W,-(L-i)*(L-i)/2.0); } FFT(h,L,1); for (i = 0; i<L; i++) { pComp[i] = cmul(h[i],g[i]); } FFT(pComp,L,-1); //IDFT for (i = 0; i<M;i++) { tmp = cpow(W,i*i/2.0); xCZT[i] = cmul(tmp,pComp[i]); } }
FFT.c

#include "FFT.h" void FFT(comp *data,int FFTn,int inverse) { comp u,w,t; double temp1,temp2; double pi; int i,j,k,l,ip; int le,le1,m; pi=3.1415926f; m=0; while(FFTn != (0x0001<<m)) m++; for(i=0,j=0; i<FFTn-1; i++) { if(i<j) { t=data[j]; data[j]=data[i]; data[i]=t; } k=FFTn/2; while(k<=j) { j-=k; k/=2; } j+=k; } le=1; for(l=0; l<m; l++ ) { le*=2; le1=le/2; u.re=(float)1.0; u.im=(float)0.0; w.re=(float)cos(pi/le1); w.im=(float)(inverse*sin(pi/le1)); for(j=0; j<le1; j++) { for(i=j; i<FFTn; i+=le) { ip=i+le1; t.re=data[ip].re*u.re-data[ip].im*u.im; t.im=data[ip].re*u.im+data[ip].im*u.re; data[ip].re=data[i].re-t.re; data[ip].im=data[i].im-t.im; data[i].re+=t.re; data[i].im+=t.im; } temp1=u.re; temp2=u.im; u.re=(float)(temp1*w.re-temp2*w.im); u.im=(float)(temp1*w.im+temp2*w.re); } } if(inverse>0) return; for(i=0; i<FFTn; i++) { data[i].re/=FFTn; data[i].im/=FFTn; } return; }
FFT.h

#ifndef _FFT1_H_ #define _FFT1_H_ #include "Complex.h" //======================================== //功能: 实现FFT //输入: data[in][out]: 数据指针; FFTn[in]:FFT点数; // inverse[in]:正反FFT标志位:1,正FFT;-1,逆FFT void FFT(comp *data,int FFTn,int inverse); #endif
二、仿真测试
参数设置:

结果对比:
- matlab

- C
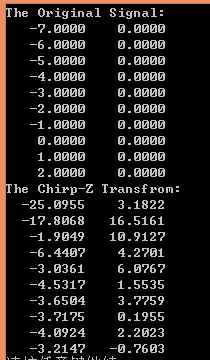
利用CZT对信号进行频率估计:
频率细化直接查找:
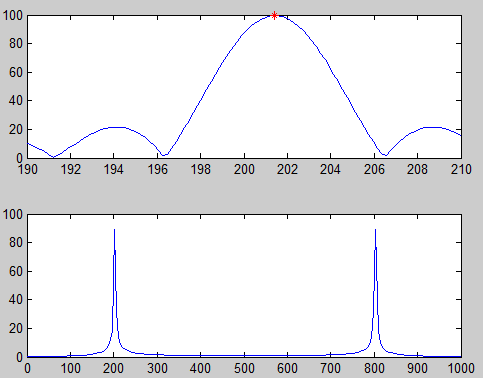
仿真code:
clc;clear all;close all;
fs = 1000;
f0 = 201.3;
t = [0:199]/fs;
sig = (sin(2*pi*t*f0));
% %存入txt
% fp=fopen('data.txt','a');%'A.txt'为文件名;'a'为打开方式:在打开的文件末端添加数据,若文件不存在则创建。
% fprintf(fp,'%f ',sig);%fp为文件句柄,指定要写入数据的文件。注意:%d后有空格。
% fclose(fp);%关闭文件。
f1 = 190;
f2 = 210;
m = 100;
w = exp(-1j*2*pi*(f2-f1)/(m*fs));
a = exp(1j*2*pi*f1/fs);
y = czt(sig,m,w,a);
[val,pos] = max(abs(y));
fre_est = (pos-1)*(f2-f1)/m+f1;
y1 = fft(sig);
figure()
subplot 211
plot(linspace(f1,f2,length(y)),abs(y));
hold on;
scatter(fre_est,abs(y(pos)),'r*');
subplot 212
plot(t/max(t)*fs,abs(y1))
C读取txt数据:
// #include <stdio.h> int n,r; double d; FILE *f; void main() { f=fopen("data.txt","r"); n=0; while (1) { r=fscanf(f,"%lf",&d); if (1==r) { n++; printf("[%d]==%lg ",n,d); } else if (0==r) { fscanf(f,"%*c"); } else break; } fclose(f); system("pause"); }
C语言仿真:
/*============================= Chirp-Z Transform =============================*/ #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> #include "Complex.h" #include "FFT.h" #define Size 100 //信号长度 void CZT(comp* x, int N, comp A, comp W, comp *xCZT, int M); double max_ab(double x,double y);//求最大值 void main() { int i; int r; int N,M; float da; double fre_est; FILE *f; double PI; double A0,Theta0; double W0,Phi0; int pos; double maxdata; double maxcache; float fs; float fstart; float fend; comp* x; double absx[Size];//存储绝对值 comp* xCZT; comp A,W; fs = 1000.0;//frequency sample fstart = 200.0; fend = 215.0; PI = 3.1415926; f=fopen("data.txt","r"); N = Size; //信号长度 M = Size; //chirp-z 变换输出长度 x = (comp *)calloc(N,sizeof(comp)); xCZT = (comp *)calloc(M,sizeof(comp)); for (i = 0; i<N; i++) { r=fscanf(f,"%f",&da); //读取数据 x[i].re = da; x[i].im = 0.0; printf("n = %f ",x[i].re ); } fclose(f); // A0 = 1.0; //起始抽样点z0的矢量半径长度 Theta0 = 2.0*PI*fstart/fs; //起始抽样点z0的相角 A.re = (float)(A0*cos(Theta0)); A.im = (float)(A0*sin(Theta0)); Phi0 = (fend-fstart)*2.0*PI/M/fs; //两相邻抽样点之间的角度差 W0 = 1.0; //螺线的伸展率 W.re = (float)(W0*cos(-Phi0)); W.im = (float)(W0*sin(-Phi0)); CZT(x,N,A,W,xCZT,M); printf("The Original Signal: "); for (i = 0; i<N; i++) { absx[i] = sqrt(xCZT[i].re*xCZT[i].re + xCZT[i].im*xCZT[i].im);//频谱 printf("%10.4f",x[i].re); printf("%10.4f ",x[i].im); } printf("The Chirp-Z Transfrom: "); for (i = 0 ;i<M ;i++) { printf("%10.4f",xCZT[i].re); printf("%10.4f ",xCZT[i].im); } printf("The Chirp-Z Transfrom square: "); for (i = 0 ;i<M ;i++) { printf("%lf ",absx[i]); } //找出频谱峰值 maxcache = 0; pos = 0; for (i = 0 ;i<M ;i++) { maxdata = max_ab(maxcache,absx[i]); if (maxdata == absx[i]) pos++; maxcache = maxdata; } //频率估计 fre_est = fstart + (pos-1.0)*(fend-fstart)/M; printf("frequency estiamton: %lf",fre_est); //绘制频谱 // system("pause"); } /* Function: max */ double max_ab(double x,double y) { return(x>y?x:y); } /*----------------函数说明---------------------- Name: CZT Function: Chirp-Z Transform Para: x[in][out]:待变换信号 N[in]:信号长度 A[in]: W[in]: M[in]:Chirp-Z变换输出长度 --------------------------------------------*/ void CZT(comp* x, int N, comp A, comp W, comp* xCZT, int M) { int i; int L; comp* h; comp* g; comp* pComp; comp tmp,tmp1,tmp2; i=1; do { i*=2; } while (i<N+M-1); L = i; h = (comp*)calloc(L,sizeof(comp)); g = (comp*)calloc(L,sizeof(comp)); pComp = (comp*)calloc(L,sizeof(comp)); for (i = 0; i<N; i++) { tmp1 = cpow(A,-i); tmp2 = cpow(W, i*i/2.0); tmp = cmul(tmp1,tmp2); g[i] = cmul(tmp,x[i]); } for (i = N;i<L; i++) { g[i] =czero(); } FFT(g,L,1); for (i = 0;i<=M-1;i++) { h[i] = cpow(W, -i*i/2.0); } for (i=M; i<=L-N;i++) { h[i] =czero(); } for (i = L-N+1; i<=L;i++) { h[i] = cpow(W,-(L-i)*(L-i)/2.0); } FFT(h,L,1); for (i = 0; i<L; i++) { pComp[i] = cmul(h[i],g[i]); } FFT(pComp,L,-1); //IDFT for (i = 0; i<M;i++) { tmp = cpow(W,i*i/2.0); xCZT[i] = cmul(tmp,pComp[i]); } }
原始数据:

估计结果:

与MATLAB结果一致:
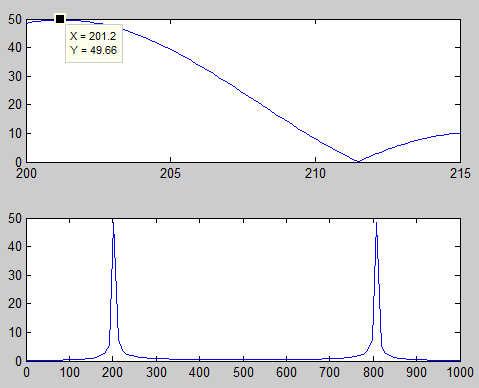
如果存在两个信号呢?
MATLAB
clc;clear all;close all;
fs = 256;
% f0 = 202;
% f1 = 208;
t = [0:625]/fs;
sig = single(2*cos(2*pi*102*t)+5*cos(2*pi*105*t));
%存入txt
fp=fopen('data.txt','a');%'A.txt'为文件名;'a'为打开方式:在打开的文件末端添加数据,若文件不存在则创建。
fprintf(fp,'%f
',sig);%fp为文件句柄,指定要写入数据的文件。注意:%d后有空格。
fclose(fp);%关闭文件。
f1 = 100;
f2 = 108;
m = 625;
w = exp(-1j*2*pi*(f2-f1)/(m*fs));
a = exp(1j*2*pi*f1/fs);
y = czt(sig,m,w,a);
data_cache = diff(abs(y));
vals = abs(y);
dataall = [];
posall = [];
flag = 0;
for i = 1:length(y)-2
if ((data_cache(1,i)*data_cache(1,i+1))<0)
flag = flag + 1;
dataall = [ dataall vals(i)];
posall = [posall,i];
end
end
[val,pos] = sort(dataall,'descend');
pos = posall(pos);
fre_est = (pos-1)*(f2-f1)/m+f1;
figure()
y1 = fft(sig);
subplot 211
plot(linspace(f1,f2,length(y)),abs(y));
axis([95,110,0,1500]);
hold on;
scatter(fre_est(1:2),ones(1,2),'r*');
hold on;
% scatter(fre_est,abs(y(pos)),'r*');
subplot 212
plot(t/max(t)*fs,abs(y1))
axis([95,110,0,1500]);
C:
运行中如果报错:

需要将fopen的data.txt添加绝对路径,注意:\而不是。

/*============================= Chirp-Z Transform =============================*/ #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> #include "Complex.h" #include "FFT.h" #define Size 626 //信号长度 void CZT(comp* x, int N, comp A, comp W, comp *xCZT, int M); double max_ab(double x,double y);//求最大值 void main() { int i; int r; int flag = 0; int N,M; float da; double fre_est1, fre_est2; FILE *f; double datall[Size] = {0};//新建足够大的数据 int posall[Size] = {0}; double diffdata [Size-1]; double PI; double A0,Theta0; double W0,Phi0; int pos1,pos2; double maxdata; double maxcache; float fs; float fstart; float fend; comp* x; double absx[Size];//存储绝对值 comp* xCZT; comp A,W; fs = 256.0;//frequency sample fstart = 100.0; fend = 108.0; PI = 3.1415926; f=fopen("data.txt","r"); N = Size; //信号长度 M = Size; //chirp-z 变换输出长度 x = (comp *)calloc(N,sizeof(comp)); xCZT = (comp *)calloc(M,sizeof(comp)); for (i = 0; i<N; i++) { r=fscanf(f,"%f",&da); //读取数据 x[i].re = da; x[i].im = 0.0; printf("n = %f ",x[i].re ); } fclose(f); // A0 = 1.0; //起始抽样点z0的矢量半径长度 Theta0 = 2.0*PI*fstart/fs; //起始抽样点z0的相角 A.re = (float)(A0*cos(Theta0)); A.im = (float)(A0*sin(Theta0)); Phi0 = (fend-fstart)*2.0*PI/M/fs; //两相邻抽样点之间的角度差 W0 = 1.0; //螺线的伸展率 W.re = (float)(W0*cos(-Phi0)); W.im = (float)(W0*sin(-Phi0)); CZT(x,N,A,W,xCZT,M); printf("The Original Signal: "); for (i = 0; i<N; i++) { absx[i] = sqrt(xCZT[i].re*xCZT[i].re + xCZT[i].im*xCZT[i].im);//频谱 printf("%10.4f",x[i].re); printf("%10.4f ",x[i].im); } printf("The Chirp-Z Transfrom: "); for (i = 0 ;i<M ;i++) { printf("%10.4f",xCZT[i].re); printf("%10.4f ",xCZT[i].im); } printf("The Chirp-Z Transfrom square: "); //for (i = 0 ;i<M ;i++) //{ // printf("%lf ",absx[i]); //} //找出频谱峰值 //maxcache = 0; //pos = 0; //for (i = 0 ;i<M ;i++) // { // maxdata = max_ab(maxcache,absx[i]); // if (maxdata == absx[i]) pos++; // maxcache = maxdata; // } ////频率估计 //fre_est = fstart + (pos-1.0)*(fend-fstart)/M; //printf("frequency estiamton: %lf",fre_est); //找第二个频率分量 for (i = 0 ;i < M-1 ;i++) { diffdata[i] = absx[i+1]-absx[i]; } for (i = 0;i < M-2 ;i++) { if((diffdata[i]*diffdata[i+1])<0.0) { datall[flag] = absx[i]; posall[flag] = i; flag ++; } } maxcache = -1; pos1 = 0; for (i = 0 ;i<flag ;i++) { maxdata = max_ab(maxcache,datall[i]); if (maxdata == datall[i]) pos1 = i; maxcache = maxdata; } datall[pos1] = 0; maxcache = -1; pos2 = 0; for (i = 0 ;i<flag ;i++) { maxdata = max_ab(maxcache,datall[i]); if (maxdata == datall[i]) pos2 = i; maxcache = maxdata; } fre_est1 = fstart + (posall[pos1]-1.0)*(fend-fstart)/M; fre_est2 = fstart + (posall[pos2]-1.0)*(fend-fstart)/M; printf("frequency estiamton: %lf and %lf",fre_est1,fre_est2); //绘制频谱 // system("pause"); } /* Function: max */ double max_ab(double x,double y) { return(x>y?x:y); } /*----------------函数说明---------------------- Name: CZT Function: Chirp-Z Transform Para: x[in][out]:待变换信号 N[in]:信号长度 A[in]: W[in]: M[in]:Chirp-Z变换输出长度 --------------------------------------------*/ void CZT(comp* x, int N, comp A, comp W, comp* xCZT, int M) { int i; int L; comp* h; comp* g; comp* pComp; comp tmp,tmp1,tmp2; i=1; do { i*=2; } while (i<N+M-1); L = i; h = (comp*)calloc(L,sizeof(comp)); g = (comp*)calloc(L,sizeof(comp)); pComp = (comp*)calloc(L,sizeof(comp)); for (i = 0; i<N; i++) { tmp1 = cpow(A,-i); tmp2 = cpow(W, i*i/2.0); tmp = cmul(tmp1,tmp2); g[i] = cmul(tmp,x[i]); } for (i = N;i<L; i++) { g[i] =czero(); } FFT(g,L,1); for (i = 0;i<=M-1;i++) { h[i] = cpow(W, -i*i/2.0); } for (i=M; i<=L-N;i++) { h[i] =czero(); } for (i = L-N+1; i<=L;i++) { h[i] = cpow(W,-(L-i)*(L-i)/2.0); } FFT(h,L,1); for (i = 0; i<L; i++) { pComp[i] = cmul(h[i],g[i]); } FFT(pComp,L,-1); //IDFT for (i = 0; i<M;i++) { tmp = cpow(W,i*i/2.0); xCZT[i] = cmul(tmp,pComp[i]); } }
另外:quantusII有对应的DSP builder,Vivado/ISE是否有类似工具,直接代码转HDL? HLS算是一个,其他呢?有时间可以将*.c转成*.v试验。
一个基本应用,频率精确测量:一种卫星信号载波频率精确估计算法.pdf
