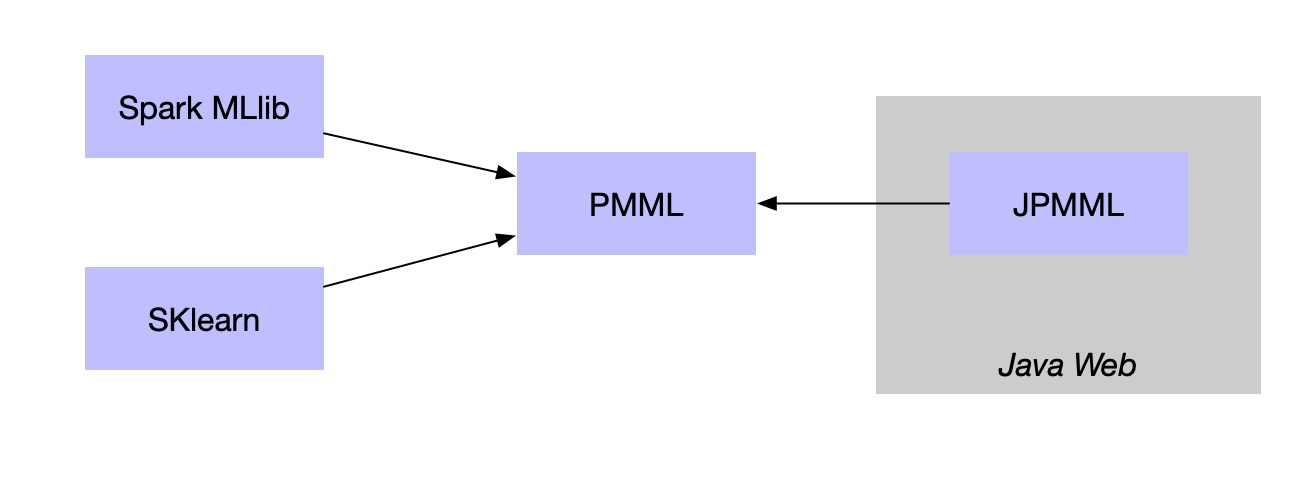
PMML是一种通用的配置文件,只要遵循标准的配置文件,就可以在Spark中训练机器学习模型,然后再web接口端去使用。目前应用最广的就是基于Jpmml来加载模型在javaweb中应用,这样就可以实现跨平台的机器学习应用了。
训练模型
首先在spark MLlib中使用mllib包下的逻辑回归训练模型:
import org.apache.spark.mllib.classification.{LogisticRegressionModel, LogisticRegressionWithLBFGS}
import org.apache.spark.mllib.evaluation.MulticlassMetrics
import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.LabeledPoint
import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils
val training = spark.sparkContext
.parallelize(Seq("0,1 2 3 1", "1,2 4 1 5", "0,7 8 3 6", "1,2 5 6 9").map( line => LabeledPoint.parse(line)))
// Run training algorithm to build the model
val model = new LogisticRegressionWithLBFGS()
.setNumClasses(2)
.run(training)
val test = spark.sparkContext
.parallelize(Seq("0,1 2 3 1").map( line => LabeledPoint.parse(line)))
// Compute raw scores on the test set.
val predictionAndLabels = test.map { case LabeledPoint(label, features) =>
val prediction = model.predict(features)
(prediction, label)
}
// Get evaluation metrics.
val metrics = new MulticlassMetrics(predictionAndLabels)
val accuracy = metrics.accuracy
println(s"Accuracy = $accuracy")
// Save and load model
// model.save(spark.sparkContext, "target/tmp/scalaLogisticRegressionWithLBFGSModel")
// val sameModel = LogisticRegressionModel.load(spark.sparkContext,"target/tmp/scalaLogisticRegressionWithLBFGSModel")
model.toPMML(spark.sparkContext, "/tmp/xhl/data/test2")
训练得到的模型保存到hdfs。
PMML模型文件
模型下载到本地,重新命名为xml。
可以看到默认四个特征分别叫做feild_0,field_1...目标为target
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<PMML version="4.2" xmlns="http://www.dmg.org/PMML-4_2">
<Header description="logistic regression">
<Application name="Apache Spark MLlib" version="2.2.0"/>
<Timestamp>2018-11-15T10:22:25</Timestamp>
</Header>
<DataDictionary numberOfFields="5">
<DataField name="field_0" optype="continuous" dataType="double"/>
<DataField name="field_1" optype="continuous" dataType="double"/>
<DataField name="field_2" optype="continuous" dataType="double"/>
<DataField name="field_3" optype="continuous" dataType="double"/>
<DataField name="target" optype="categorical" dataType="string"/>
</DataDictionary>
<RegressionModel modelName="logistic regression" functionName="classification" normalizationMethod="logit">
<MiningSchema>
<MiningField name="field_0" usageType="active"/>
<MiningField name="field_1" usageType="active"/>
<MiningField name="field_2" usageType="active"/>
<MiningField name="field_3" usageType="active"/>
<MiningField name="target" usageType="target"/>
</MiningSchema>
<RegressionTable intercept="0.0" targetCategory="1">
<NumericPredictor name="field_0" coefficient="-5.552297758753701"/>
<NumericPredictor name="field_1" coefficient="-1.4863480719075117"/>
<NumericPredictor name="field_2" coefficient="-5.7232298850417855"/>
<NumericPredictor name="field_3" coefficient="8.134075057437393"/>
</RegressionTable>
<RegressionTable intercept="-0.0" targetCategory="0"/>
</RegressionModel>
</PMML>
接口使用
在接口的web工程中引入maven jar:
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.jpmml/pmml-evaluator -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jpmml</groupId>
<artifactId>pmml-evaluator</artifactId>
<version>1.4.3</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.jpmml/pmml-evaluator-extension -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jpmml</groupId>
<artifactId>pmml-evaluator-extension</artifactId>
<version>1.4.3</version>
</dependency>
接口代码中直接读取pmml,使用模型进行预测:
package soundsystem;
import org.dmg.pmml.FieldName;
import org.dmg.pmml.PMML;
import org.jpmml.evaluator.*;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class PMMLDemo2 {
private Evaluator loadPmml(){
PMML pmml = new PMML();
try(InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("/Users/xingoo/Desktop/test2.xml")){
pmml = org.jpmml.model.PMMLUtil.unmarshal(inputStream);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
ModelEvaluatorFactory modelEvaluatorFactory = ModelEvaluatorFactory.newInstance();
return modelEvaluatorFactory.newModelEvaluator(pmml);
}
private Object predict(Evaluator evaluator,int a, int b, int c, int d) {
Map<String, Integer> data = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
data.put("field_0", a);
data.put("field_1", b);
data.put("field_2", c);
data.put("field_3", d);
List<InputField> inputFields = evaluator.getInputFields();
//过模型的原始特征,从画像中获取数据,作为模型输入
Map<FieldName, FieldValue> arguments = new LinkedHashMap<FieldName, FieldValue>();
for (InputField inputField : inputFields) {
FieldName inputFieldName = inputField.getName();
Object rawValue = data.get(inputFieldName.getValue());
FieldValue inputFieldValue = inputField.prepare(rawValue);
arguments.put(inputFieldName, inputFieldValue);
}
Map<FieldName, ?> results = evaluator.evaluate(arguments);
List<TargetField> targetFields = evaluator.getTargetFields();
TargetField targetField = targetFields.get(0);
FieldName targetFieldName = targetField.getName();
ProbabilityDistribution target = (ProbabilityDistribution) results.get(targetFieldName);
System.out.println(a + " " + b + " " + c + " " + d + ":" + target);
return target;
}
public static void main(String args[]){
PMMLDemo2 demo = new PMMLDemo2();
Evaluator model = demo.loadPmml();
demo.predict(model,2,5,6,8);
demo.predict(model,7,9,3,6);
demo.predict(model,1,2,3,1);
demo.predict(model,2,4,1,5);
}
}
得到输出内容:
2 5 6 8:ProbabilityDistribution{result=1, probability_entries=[1=0.9999949538769296, 0=5.046123070395758E-6]}
7 9 3 6:ProbabilityDistribution{result=0, probability_entries=[1=1.1216598160542013E-9, 0=0.9999999988783402]}
1 2 3 1:ProbabilityDistribution{result=0, probability_entries=[1=2.363331367481431E-8, 0=0.9999999763666864]}
2 4 1 5:ProbabilityDistribution{result=1, probability_entries=[1=0.9999999831203591, 0=1.6879640907241367E-8]}
其中result为LR最终的结果,概率为二分类的概率。
参考资料
- 官方文档:https://openscoring.io/
- JPMML官方文档:https://github.com/jpmml/jpmml-evaluator
- jpmml-sklearn:https://github.com/jpmml/jpmml-sklearn
- jpmml-sparkml:https://github.com/jpmml/jpmml-sparkml/tree/master
- 用PMML实现机器学习模型的跨平台上线:http://www.cnblogs.com/pinard/p/9220199.html
- PMML模型文件在机器学习的实践经验:https://blog.csdn.net/hopeztm/article/details/78321700