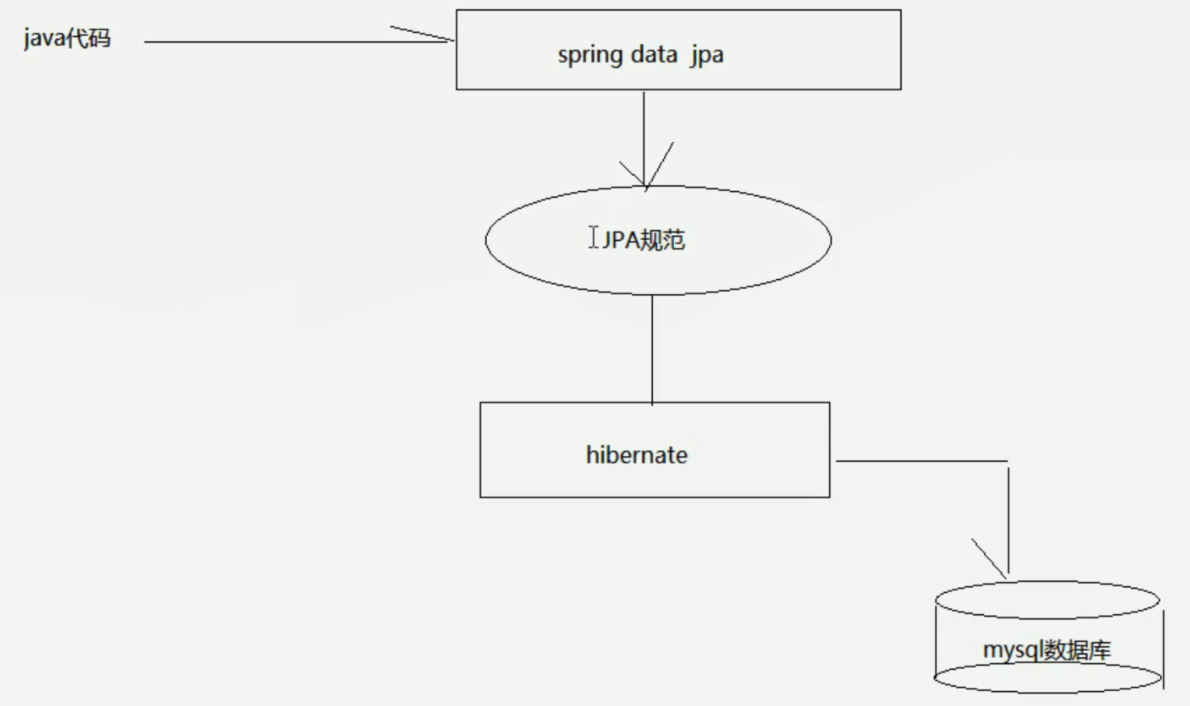
SpringDataJpaSpring Data JPA
让我们解脱了DA0层的操作,基本上所有CRUD都可以依赖于它来实现,在实际的工作工程中,推荐使用Spring Data JPA+ORM(如:hibernate)完成操作,这样在切换不同的ORM框架时提供了极大的方便,同时也使数据库层操作更加简单,方便解耦。
把JPA规范的代码封装起来,真正进行查询的还是hibernate或mybatis >>(封装了jdbc操作),然后进行查询或操作数据库。
SpringDataJpa入门操作(搭建环境)
创建工程,导入坐标

1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> 5 <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> 6 7 <groupId>cn.itcast</groupId> 8 <artifactId>jpa-day02</artifactId> 9 <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> 10 11 <properties> 12 <spring.version>5.0.2.RELEASE</spring.version> 13 <hibernate.version>5.0.7.Final</hibernate.version> 14 <s1f4j.version>1.6.6</s1f4j.version> 15 <log4j.version>1.2.12</log4j.version> 16 <c3pe.version>0.9.1.2</c3pe.version> 17 <mysql.version>5.1.6</mysql.version> 18 </properties> 19 20 <dependencies> 21 <!--junit单元测试--> 22 <dependency> 23 <groupId>junit</groupId> 24 <artifactId>junit</artifactId> 25 <version>4.9</version> 26 <scope>test</scope> 27 </dependency> 28 <!--spring beg--> 29 <dependency> 30 <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId> 31 <artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId> 32 <version>1.6.8</version> 33 </dependency> 34 <dependency> 35 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> 36 <artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId> 37 <version>${spring.version}</version> 38 </dependency> 39 <dependency> 40 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> 41 <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> 42 <version>${spring.version}</version> 43 </dependency> 44 <dependency> 45 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> 46 <artifactId>spring-context-support</artifactId> 47 <version>${spring.version}</version> 48 </dependency> 49 <!--spring对ORm框架的支持包--> 50 <dependency> 51 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> 52 <artifactId>spring-orm</artifactId> 53 <version>${spring.version}</version> 54 </dependency> 55 <dependency> 56 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> 57 <artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId> 58 <version>${spring.version}</version> 59 </dependency> 60 <dependency> 61 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> 62 <artifactId>spring-core</artifactId> 63 <version>${spring.version}</version> 64 </dependency> 65 66 <!--spring end--> 67 68 <!--hibernate beg--> 69 <dependency> 70 <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId> 71 <artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId> 72 <version>${hibernate.version}</version> 73 </dependency> 74 <dependency> 75 <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId> 76 <artifactId>hibernate-entitymanager</artifactId> 77 <version>${hibernate.version}</version> 78 </dependency> 79 <dependency> 80 <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId> 81 <artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId> 82 <version>5.2.1.Final</version> 83 </dependency> 84 85 <!--hibernate end--> 86 87 <!--c3p0 beg--> 88 <dependency> 89 <groupId>c3p0</groupId> 90 <artifactId>c3p0</artifactId> 91 <version>0.9.1.2</version> 92 </dependency> 93 94 <!--log end--> 95 <dependency> 96 <groupId>log4j</groupId> 97 <artifactId>log4j</artifactId> 98 <version>1.2.17</version> 99 </dependency> 100 <dependency> 101 <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> 102 <artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId> 103 <version>1.7.25</version> 104 </dependency> 105 <dependency> 106 <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> 107 <artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId> 108 <version>1.6.6</version> 109 </dependency> 110 <!--log end--> 111 112 <dependency> 113 <groupId>mysq1</groupId> 114 <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> 115 <version>5.1.6</version> 116 </dependency> 117 <!-- spring data jpa 的坐标 --> 118 <dependency> 119 <groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId> 120 <artifactId>spring-data-jpa</artifactId> 121 <version>1.9.0.RELEASE</version> 122 </dependency> 123 <dependency> 124 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> 125 <artifactId>spring-test</artifactId> 126 <version>4.2.4.RELEASE</version> 127 </dependency> 128 129 <!--el beg 使用spring data jpa必须引入--> 130 <dependency> 131 <groupId>javax.el</groupId> 132 <artifactId>javax.el-api</artifactId> 133 <version>2.2.4</version> 134 </dependency> 135 <dependency> 136 <groupId>org.glassfish.web</groupId> 137 <artifactId>javax.el</artifactId> 138 <version>2.2.4</version> 139 </dependency> 140 <dependency> 141 <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> 142 <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> 143 <version>1.16.22</version> 144 </dependency> 145 </dependencies> 146 </project>
配置Spring的配置文件
1 <!--创建entityManagerFactory对象交给Spring容器管理--> 2 <bean id="entityManagerFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean"> (权限定位类名) 3 <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> (依赖注入) 4 <property name="packagesToScan " value="cn.itcast.domain"/> (配置的扫描的包,实体类所在的包) 5 <property name="persistenceProvider"> (JPA的实现厂家) 6 <bean class="org.hibernate.jpa.HibernatePersistenceProvider"/> 7 </property> 8 9 <!--jpa的供应商适配器--> 10 <property name="jpaVendorAdapter"> 11 <bean class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.vendor.HibernateJpaVendorAdapter"> 12 <!--配置是否自动创建数据库表--> 13 <property name="generateDdl" value="false"/> 14 <!--指定数据库类型--> 15 <property name="database" value="MYSQL"/> 16 <!--数据库方言:支持的特有语法(不同数据库有不同的语法)--> 17 <property name="databasePlatform" value="org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect"/> 18 <!--是否显示sql--> 19 <property name="showSql" value="true"/> 20 </bean> 21 </property> 22 23 <!--jpa的方言 :高级特性(配置了谁就拥有了谁的高级特性)--> 24 <property name="jpaDialect"> 25 <bean class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.vendor.HibernateJpaDialect"></bean> 26 </property> 27 </bean> 28 <!--2.创建数据库连接池--> 29 <bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"> 30 <property name="user" value="root"></property> 31 <property name="password" value="123456"></property> 32 <property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysq1:///jpa"></property> 33 <property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property> 34 </bean> 35 (以下的不需要特别记忆)>>> 36 <!--3.整合spring dataJpa--> 37 <jpa:repositories base-package="cn.itcast.dao" transaction-manager-ref="transactionManager" 38 entity-manager-factory-ref="entityManagerFactory"></jpa:repositories> 39 <!--4.配置事务管理器--> 40 <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager"> 41 <property name="entityManagerFactory" ref="entityManagerFactory"></property> 42 </bean> 43 <!--5.声明式事务--> 44 <!--6.配置 包扫描--> 45 <context:component-scan base-package="cn.itcast"></context:component-scan> 46 </beans>
编写符合SpringDataJpa规范的dao层接口
1 package cn.itcast.dao; 2 3 import cn.itcast.domain.Customer; 4 5 import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository; 6 import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaSpecificationExecutor; 7 /** 8 * 符合springDataJpa的dao层接口规范 9 * JpaRepository<操作的实体类类型,实体类中主键属性的类型) >>>封装了基本的CRUD操作 10 * JpaSpecificationExecutor<操作的实体类类型> >>>封装了复杂查询() 11 */ 12 public interface CustomerDao extends JpaRepository<Customer, Long>, JpaSpecificationExecutor<Customer> {}
完成客户的增删改查操作
根据id查询
- findOne
em.find() 立即加载
- getOne
@Transactional:保证getOne正常运行
em.getReference() 延迟加载 >>返回的是一个客户的动态代理对象,什么时候用、什么时候查询
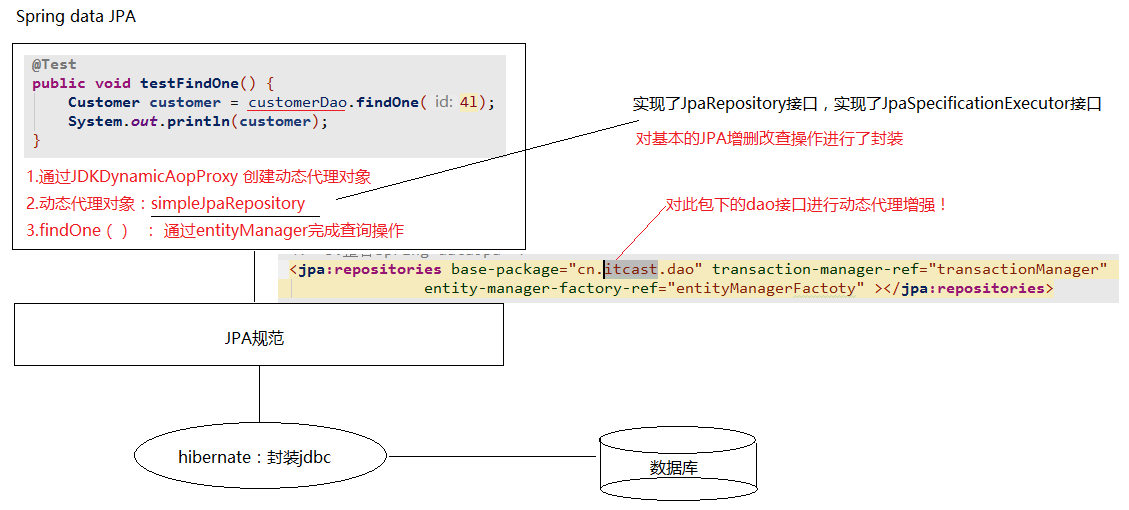
1 @Test 2 public void testFindOne() { 3 Customer customer = customerDao.findOne(3l); 4 System.out.println(customer); 5 }
保存和更新(sava)
- 如果没有id主键属性:>> 保存
1 @Test 2 public void testSave() { 3 Customer customer = new Customer(); 4 customer.setCustname("黑马程序员"); 5 customer.setCustaddress("北京"); 6 customer.setCustindustry("IT教育"); 7 customerDao.save(customer); 8 }
- 存在id主键属性: >> 根据id查询数据,更新数据
1 @Test 2 public void testUpdate() { 3 Customer customer = new Customer(); 4 customer.setCustid(1l); 5 customer.setCustname("播客"); 6 customer.setCustindustry("黑马程序员很厉害"); 7 customerDao.save(customer); 8 }
根据id删除(delete)
1 @Test 2 public void testDelete() { 3 Customer customer = new Customer(); 4 customerDao.delete(1l); 5 }
查询所有客户(findAll)
1 @Test 2 public void findAll(){ 3 List<Customer> list = customerDao.findAll(); 4 for (Customer customer : list) { 5 System.out.println(customer); 6 }
SpringDataJpa的运行过程和原理剖析
1. 通过JdkDynamicAopProxy的 invoke 方法创建了一个动态代理对象
2. simpleJpaRepository当中封装了 JPA的操作(借助JPA的api完成数据库的CRUD)
3. 通过 hibernate完成数据库操作(封装了jdbc)
复杂查询
-
借助接口中的定义好的方法完成查询
findone(id):根据id查询
测试统计查询:查询客户的总数量
1 @Test 2 public void testdount() { 3 long count = customerDao.count();//查询全部的客户数量System.out.println(count); 4 System.out.println(count); 5 }
测试:判断id为3的客户是否存在
- 可以查询以下id为3的客户
如果值为空,代表不存在,如果不为空,代表存在
- 判断数据库中id为3的客户的数量
如果数量为0,代表不存在(false),如果大于0,代表存在(true)
1 @Test 2 public void testExists() { 3 boolean exists = customerDao.exists(3l); 4 System.out.println(exists); 5 }
-
jpql的查询方式♦♦
jpql:jpa query language( jpq查询语言 )
特点:语法或关键字和sql语句类似
查询的是类和类中的属性
需要将JPQL语句配置到接口方法上
1 .特有的查询:需要在dao接口上配置方法
2. 在新添加的方法上,使用注解的形式配置jpql查询语句
3. 注解:@Query
案例:根据客户名称查询名称 >> 使用Jpql的形式查询
CustomerDao
1 public interface CustomerDao extends JpaRepository<Customer, Long>, JpaSpecificationExecutor<Customer> { 2 /** 3 * 案例:根据客户名称查询名称 4 * 使用Jpql的形式查询 5 * jpql: from Customer where custName = ? 6 */ 7 @Query(value = "from Customer where custname = ?") 8 public Customer findJpql(String custname); 9 }
JpqlTest
1 @Test 2 public void testFindJpql(){ 3 Customer customer = customerDao.findJpql("传智"); 4 System.out.println(customer); 5 }
案例:根据客户名称和客户id查询客户 >> 使用Jpql的形式查询
- 对于多个占位符参数: 赋值的时候,默认的情况下,占位符的位置需要和方法参数中的位置保持一致 [ custName >> String name custId >> Long id ]
@Query(value="from Customer where custName=? and custId=?")
public Customer findCustNameAndId (String name , Long id );
- 也可以指定占位符参数的位置 : ?索引的方式,指定此占位的取值来源
@Query (value=" from Customer where custName = ?2 and custId = ?1 ")
public Customer findCustNameAndId ( Long id , String name );
CustomerDao
1 @Query(value = "from Customer where custname = ? and custid = ?") 2 public Customer findCustNameAndId(String custname, long id);
JpqlTest
1 @Test 2 public void testCustNameAndId(){ 3 Customer customer = customerDao.findCustNameAndId("黑马",2l); 4 System.out.println(customer); 5 }
使用jpql完成更新操作案例:根据id更新更新2号客户的名称,将名称改为“黑马程序员”
CustomerDao
1 @Query(value = " update Customer set custname = ?2 where custid = ?1 ") //代表的是进行查询 2 @Modifying //当前执行的是一个更新操作 3 //更新不需要返回值 选择void 4 public void UpdateCustomer( long custid,String custname);
JpqlTest
1 @Test 2 @Transactional //添加对事务的支持 3 @Rollback(value = false) //设置是否自动回滚 4 public void testUpdateCustomer(){ 5 customerDao.UpdateCustomer(2l,"黑马程序员"); 6 }
执行结束后,默认回滚事务,可以通过@Rollback 设置是否自动回滚 >> false | true
-
SQL查询方式.
1 .特有的查询:需要在dao接口上配置方法
2. 在新添加的方法上,使用注解的形式配置sql查询语句
3. 注解:@Query
value: jsql | sql
nativeQuery : fals(使用jpql查询) l true(使用本地查询:sql查询)
CustomerDao
1 @Query(value = "select * from cst_customer",nativeQuery = true) 2 public List<Object[]>findSql();
JpqlTest
1 @Test 2 public void testfindSql(){ 3 List<Object[]> list = customerDao.findSql(); 4 for (Object[] obj : list) { 5 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(obj));//每一个里面都还是object数组,所以需要借助Arrays.toString()方法打印数组 6 }
-
方法命名规则查询
>> 1: findBy +属性名(首字母大写)
public Customer findByCustname(String custname);
1 @Test 2 public void testNaming(){ 3 Customer customer = customerDao.findByCustname("传智"); 4 System.out.println(customer); 5 }
>> 2: findBy + 属性名(首字母大写)+ “查询方式”
public List<Customer> findByCustnameLike(String custname);
1 @Test 2 public void testfindByCustnameLike(){ 3 List<Customer> list = customerDao.findByCustnameLike("黑马%"); 4 for (Customer customer : list) { 5 System.out.println(customer); 6 } }
>> 3: findBy + 属性名(首字母大写)+ “查询方式” + “多条件的连接符(and | or)” + 属性名 + “查询方式”
使用客户名称模糊匹配和客户所属行业精准匹配的查询
public List<Customer> findByCustnameLikeAndCustindustry(String custname, String custindustry); //结果可能是一个或多个,所以选择List<Customer>
1 @Test 2 public void testFindByCustnameLikeAndCustindustry(){ 3 List<Customer> list = customerDao.findByCustnameLikeAndCustindustry("黑马%","it教育"); 4 for (Customer customer : list) { 5 System.out.println(customer); 6 } }
Specifications动态查询
- root :查询的根对象(查询的任何属性都可以从根对象中获取)
- cirteriaQuery:顶层查询对象,自定义查询方式(了解,一般不用)
- cirteriaBuilder:查询的构造器,封装了很多查询条件
public Predicate toPredicate(Root<Customer> root , CriteriaQuery<?> query , CriteriaBuilder cb) { } //封装查询条件
查询客户名为 “传智” 的客户
1 @Test
2 public void testSpec() {
实现Specification接口( 提供泛型 :查询的对象属性)
3 Specification<Customer> spec = new Specification<Customer>() {
实现toPredicate方法(构造查询条件)
4 public Predicate toPredicate(Root<Customer> root, CriteriaQuery<?> query, CriteriaBuilder cb) {
5 //1.获取比较的属性
6 Path<Object> custname = root.get("custname");
7 //2.构造查询条件
8 Predicate predicate = cb.equal(custname, "传智"); //进行精准的匹配(custname:比较的属性 , “传智”:比较的属性取值)
9 return predicate;
10 }};
11 Customer customer = customerDao.findOne(spec);
12 System.out.println(customer);
13 }
查询客户名为 “黑马2” 并且行业为 "it教育" 的的客户
1 @Test 2 public void testSpec1() { 3 Specification<Customer> spec = new Specification<Customer>() { 4 public Predicate toPredicate(Root<Customer> root, CriteriaQuery<?> query, CriteriaBuilder cb) { 5 //1.获取比较的属性 6 Path<Object> custname = root.get("custname"); 7 Path<Object> custindustry = root.get("custindustry"); 8 //2.构造查询条件 9 Predicate p1 = cb.equal(custname, "黑马2"); 10 Predicate p2 = cb.equal(custindustry, "it教育");
and(与关系):满足条件1并且满足条件2 or(或关系):满足条件1或满足条件2 11 Predicate and = cb.and(p1, p2); 12 return and; 13 } 14 }; 15 Customer customer = customerDao.findOne(spec); 16 System.out.println(customer); 17 }
案例:完成根据客户名称的模糊匹配,返回客户列表 >>客户名称以 “传智播客” 开头
默认: equal:直接得到 path对象(属性),然后进行比较即可
gt(大于),lt(小于),ge(大于等于),le(小于等于),like:得到path对象,根据path指定比较的参数类型,再去进行比较
指定参数类型:path.as(类型的字节码对象)
1 @Test 2 public void testSpec2() { 3 Specification<Customer> spec = new Specification<Customer>() { 4 public Predicate toPredicate(Root<Customer> root, CriteriaQuery<?> query, CriteriaBuilder cb) { 5 Path<Object> custname = root.get("custname"); //查询属性:客户名 6 Predicate predicate = cb.like(custname.as(String.class), "传智播客%"); //查询方式:模糊匹配 7 return predicate; 8 } 9 }; 10 List<Customer> list = customerDao.findAll(spec); 11 for (Customer customer : list) { 12 System.out.println(customer); 13 } }
添加排序 >>创建排序对象,需要调用构造方法实例化sort对象
第一个参数:排序的顺序(倒序,正序)
- Sort.Direction.DESC:倒序
- Sort.Direction.ASC:升序
第二个参数:排序的属性名称
1 Sort sort = new Sort(Sort.Direction.DESC, "custid");
2 List<Customer> list = customerDao.findAll(spec, sort);
分页查询
- 不带参数的分页查询
创建PageRequest的过程中,需要调用他的构造方法传入两个参数
第一个参数:当前查询的页数(从e开始)
第二个参数:每页查询的数量
1 @Test
2 public void testSpec3() {
3 Specification spec = null; //不带参数
4 Pageable pageable = new PageRequest(0, 2);
5 //分页查询
6 Page<Customer> page = customerDao.findAll(null, pageable);
7 System.out.println(page.getContent());//得到数据集合列表
8 System.out.println(page.getTotalElements());//得到总条数
9 System.out.println(page.getTotalPages());//得到总页数
10 }
- 带参数分页查询
1 @Test 2 public void testSpec4() { 3 Specification spec = new Specification() { 4 public Predicate toPredicate(Root root, CriteriaQuery criteriaQuery, CriteriaBuilder criteriaBuilder) { 5 Path custname = root.get("custname"); 6 Predicate predicate = criteriaBuilder.equal(custname, "传智播客"); 7 return predicate; 8 }}; 9 Pageable pageable = new PageRequest(0, 2); 10 //分页查询 11 Page<Customer> page = customerDao.findAll(spec, pageable); 12 System.out.println(page.getContent());//得到数据集合列表 13 System.out.println(page.getTotalElements());//得到总条数 14 System.out.println(page.getTotalPages());//得到总页数 15 }
