1. 导入相关的依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<groupId>cn.jxy</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>springDataRedisDemo</artifactId>
<name>springDataRedisDemo</name>
<!-- FIXME change it to the project's website -->
<url>http://www.example.com</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.7</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.7</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.11</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>4.2.4.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId>
<version>4.2.4.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context-support</artifactId>
<version>4.2.4.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>4.2.4.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
<version>2.8.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-data-redis</artifactId>
<version>1.7.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<pluginManagement><!-- lock down plugins versions to avoid using Maven defaults (may be moved to parent pom) -->
<plugins>
<!-- clean lifecycle, see https://maven.apache.org/ref/current/maven-core/lifecycles.html#clean_Lifecycle -->
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-clean-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
</plugin>
<!-- default lifecycle, jar packaging: see https://maven.apache.org/ref/current/maven-core/default-bindings.html#Plugin_bindings_for_jar_packaging -->
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-resources-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.0.2</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.0</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.22.1</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-jar-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.0.2</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-install-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.5.2</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-deploy-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.8.2</version>
</plugin>
<!-- site lifecycle, see https://maven.apache.org/ref/current/maven-core/lifecycles.html#site_Lifecycle -->
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-site-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.7.1</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-project-info-reports-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0</version>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</pluginManagement>
</build>
</project>
2. 配置相关的文件
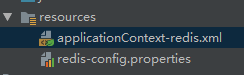
applicationCaontext-redis.xml文件的内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xsd:schema xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:tool="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tool"
targetNamespace="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
elementFormDefault="qualified"
attributeFormDefault="unqualified">
<xsd:import namespace="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd"/>
<xsd:import namespace="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tool" schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tool/spring-tool-4.2.xsd"/>
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
Defines the configuration elements for the Spring Framework's application
context support. Effects the activation of various configuration styles
for the containing Spring ApplicationContext.
]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
<xsd:complexType name="propertyLoading">
<xsd:attribute name="location" type="xsd:string">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
The location of the properties file to resolve placeholders against, as a Spring
resource location: a URL, a "classpath:" pseudo URL, or a relative file path.
Multiple locations may be specified, separated by commas. If neither location nor
properties-ref is specified, placeholders will be resolved against system properties.
]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:attribute>
<xsd:attribute name="properties-ref" type="xsd:string">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation source="java:java.util.Properties"><![CDATA[
The bean name of a Properties object that will be used for property substitution.
If neither location nor properties-ref is specified, placeholders will be resolved
against system properties.
]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:attribute>
<xsd:attribute name="file-encoding" type="xsd:string">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
Specifies the encoding to use for parsing properties files. Default is none,
using the java.util.Properties default encoding. Only applies to classic
properties files, not to XML files.
]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:attribute>
<xsd:attribute name="order" type="xsd:token">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
Specifies the order for this placeholder configurer. If more than one is present
in a context, the order can be important since the first one to be match a
placeholder will win.
]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:attribute>
<xsd:attribute name="ignore-resource-not-found" type="xsd:boolean" default="false">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
Specifies if failure to find the property resource location should be ignored.
Default is "false", meaning that if there is no file in the location specified
an exception will be raised at runtime.
]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:attribute>
<xsd:attribute name="ignore-unresolvable" type="xsd:boolean" default="false">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
Specifies if failure to find the property value to replace a key should be ignored.
Default is "false", meaning that this placeholder configurer will raise an exception
if it cannot resolve a key. Set to "true" to allow the configurer to pass on the key
to any others in the context that have not yet visited the key in question.
]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:attribute>
<xsd:attribute name="local-override" type="xsd:boolean" default="false">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
Specifies whether local properties override properties from files.
Default is "false": Properties from files override local defaults.
]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:attribute>
</xsd:complexType>
<xsd:element name="property-placeholder">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
Activates replacement of ${...} placeholders by registering a
PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer within the application context. Properties will
be resolved against the specified properties file or Properties object -- so called
"local properties", if any, and against the Spring Environment's current set of
PropertySources.
Note that as of Spring 3.1 the system-properties-mode attribute has been removed in
favor of the more flexible PropertySources mechanism. However, applications may
continue to use the 3.0 (and older) versions of the spring-context schema in order
to preserve system-properties-mode behavior. In this case, the traditional
PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer component will be registered instead of the newer
PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer.
See ConfigurableEnvironment javadoc for more information on usage.
]]></xsd:documentation>
<xsd:appinfo>
<tool:annotation>
<tool:exports type="org.springframework.context.support.PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer"/>
</tool:annotation>
</xsd:appinfo>
</xsd:annotation>
<xsd:complexType>
<xsd:complexContent>
<xsd:extension base="propertyLoading">
<xsd:attribute name="system-properties-mode" default="ENVIRONMENT">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
Controls how to resolve placeholders against system properties. As of Spring 3.1, this
attribute value defaults to "ENVIRONMENT", indicating that resolution of placeholders
against system properties is handled via PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer and its
delegation to the current Spring Environment object.
For maximum backward compatibility, this attribute is preserved going forward with the
3.1 version of the context schema, and any values other than the default "ENVIRONMENT"
will cause a traditional PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer to be registered instead of the
newer PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer variant. In this case, the Spring Environment
and its property sources are not interrogated when resolving placeholders. Users are
encouraged to consider this attribute deprecated, and to take advantage of the
Environment and PropertySource mechanisms. See ConfigurableEnvironment javadoc for examples.
"ENVIRONMENT" indicates placeholders should be resolved against the current Environment and against any local properties;
"NEVER" indicates placeholders should be resolved only against local properties and never against system properties;
"FALLBACK" indicates placeholders should be resolved against any local properties and then against system properties;
"OVERRIDE" indicates placeholders should be resolved first against system properties and then against any local properties;
]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
<xsd:simpleType>
<xsd:restriction base="xsd:string">
<xsd:enumeration value="ENVIRONMENT"/>
<xsd:enumeration value="NEVER"/>
<xsd:enumeration value="FALLBACK"/>
<xsd:enumeration value="OVERRIDE"/>
</xsd:restriction>
</xsd:simpleType>
</xsd:attribute>
<xsd:attribute name="value-separator" default=":">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
The separating character between the placeholder variable and the associated
default value: by default, a ':' symbol.
]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:attribute>
<xsd:attribute name="null-value">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
A value that should be treated as 'null' when resolved as a placeholder value:
e.g. "" (empty String) or "null". By default, no such null value is defined.
]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:attribute>
</xsd:extension>
</xsd:complexContent>
</xsd:complexType>
</xsd:element>
<xsd:element name="property-override">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
Activates pushing of override values into bean properties, based on configuration
lines of the following format: beanName.property=value
]]></xsd:documentation>
<xsd:appinfo>
<tool:annotation>
<tool:exports type="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyOverrideConfigurer"/>
</tool:annotation>
</xsd:appinfo>
</xsd:annotation>
<xsd:complexType>
<xsd:complexContent>
<xsd:extension base="propertyLoading"/>
</xsd:complexContent>
</xsd:complexType>
</xsd:element>
<xsd:element name="annotation-config">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
Activates various annotations to be detected in bean classes: Spring's @Required and
@Autowired, as well as JSR 250's @PostConstruct, @PreDestroy and @Resource (if available),
JAX-WS's @WebServiceRef (if available), EJB 3's @EJB (if available), and JPA's
@PersistenceContext and @PersistenceUnit (if available). Alternatively, you may
choose to activate the individual BeanPostProcessors for those annotations.
Note: This tag does not activate processing of Spring's @Transactional or EJB 3's
@TransactionAttribute annotation. Consider the use of the <tx:annotation-driven>
tag for that purpose.
See javadoc for org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
for information on code-based alternatives to bootstrapping annotation-driven support.
]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:element>
<xsd:element name="component-scan">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
Scans the classpath for annotated components that will be auto-registered as
Spring beans. By default, the Spring-provided @Component, @Repository, @Service,
@Controller, @RestController, @ControllerAdvice, and @Configuration stereotypes
will be detected.
Note: This tag implies the effects of the 'annotation-config' tag, activating @Required,
@Autowired, @PostConstruct, @PreDestroy, @Resource, @PersistenceContext and @PersistenceUnit
annotations in the component classes, which is usually desired for autodetected components
(without external configuration). Turn off the 'annotation-config' attribute to deactivate
this default behavior, for example in order to use custom BeanPostProcessor definitions
for handling those annotations.
Note: You may use placeholders in package paths, but only resolved against system
properties (analogous to resource paths). A component scan results in new bean definitions
being registered; Spring's PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer will apply to those bean
definitions just like to regular bean definitions, but it won't apply to the component
scan settings themselves.
See javadoc for org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan for information
on code-based alternatives to bootstrapping component-scanning.
]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
<xsd:complexType>
<xsd:sequence>
<xsd:element name="include-filter" type="filterType"
minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
Controls which eligible types to include for component scanning.
]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:element>
<xsd:element name="exclude-filter" type="filterType"
minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
Controls which eligible types to exclude for component scanning.
]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:element>
</xsd:sequence>
<xsd:attribute name="base-package" type="xsd:string"
use="required">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
The comma/semicolon/space/tab/linefeed-separated list of packages to scan for annotated components.
]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:attribute>
<xsd:attribute name="resource-pattern" type="xsd:string">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
Controls the class files eligible for component detection. Defaults to "**/*.class", the recommended value.
Consider use of the include-filter and exclude-filter elements for a more fine-grained approach.
]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:attribute>
<xsd:attribute name="use-default-filters" type="xsd:boolean"
default="true">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
Indicates whether automatic detection of classes annotated with @Component, @Repository, @Service,
or @Controller should be enabled. Default is "true".
]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:attribute>
<xsd:attribute name="annotation-config" type="xsd:boolean"
default="true">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
Indicates whether the implicit annotation post-processors should be enabled. Default is "true".
]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:attribute>
<xsd:attribute name="name-generator" type="xsd:string">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
The fully-qualified class name of the BeanNameGenerator to be used for naming detected components.
]]></xsd:documentation>
<xsd:appinfo>
<tool:annotation>
<tool:expected-type type="java.lang.Class"/>
<tool:assignable-to type="org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanNameGenerator"/>
</tool:annotation>
</xsd:appinfo>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:attribute>
<xsd:attribute name="scope-resolver" type="xsd:string">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
The fully-qualified class name of the ScopeMetadataResolver to be used for resolving the scope of
detected components.
]]></xsd:documentation>
<xsd:appinfo>
<tool:annotation>
<tool:expected-type type="java.lang.Class"/>
<tool:assignable-to type="org.springframework.context.annotation.ScopeMetadataResolver"/>
</tool:annotation>
</xsd:appinfo>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:attribute>
<xsd:attribute name="scoped-proxy">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
Indicates whether proxies should be generated for detected components, which may be necessary
when using scopes in a proxy-style fashion. Default is to generate no such proxies.
]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
<xsd:simpleType>
<xsd:restriction base="xsd:string">
<xsd:enumeration value="no"/>
<xsd:enumeration value="interfaces"/>
<xsd:enumeration value="targetClass"/>
</xsd:restriction>
</xsd:simpleType>
</xsd:attribute>
</xsd:complexType>
</xsd:element>
<xsd:element name="load-time-weaver">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
Activates a Spring LoadTimeWeaver for this application context, available as
a bean with the name "loadTimeWeaver". Any bean that implements the
LoadTimeWeaverAware interface will then receive the LoadTimeWeaver reference
automatically; for example, Spring's JPA bootstrap support.
The default weaver is determined automatically: see DefaultContextLoadTimeWeaver's
javadoc for details.
The activation of AspectJ load-time weaving is specified via a simple flag
(the 'aspectj-weaving' attribute), with the AspectJ class transformer
registered through Spring's LoadTimeWeaver. AspectJ weaving will be activated
by default if a "META-INF/aop.xml" resource is present in the classpath.
This also activates the current application context for applying dependency
injection to non-managed classes that are instantiated outside of the Spring
bean factory (typically classes annotated with the @Configurable annotation).
This will only happen if the AnnotationBeanConfigurerAspect is on the classpath
(i.e. spring-aspects.jar), effectively activating "spring-configured" by default.
See javadoc for org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableLoadTimeWeaving
for information on code-based alternatives to bootstrapping load-time weaving support.
]]></xsd:documentation>
<xsd:appinfo>
<tool:annotation>
<tool:exports type="org.springframework.instrument.classloading.LoadTimeWeaver"/>
</tool:annotation>
</xsd:appinfo>
</xsd:annotation>
<xsd:complexType>
<xsd:attribute name="weaver-class" type="xsd:string">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
The fully-qualified classname of the LoadTimeWeaver that is to be activated.
]]></xsd:documentation>
<xsd:appinfo>
<tool:annotation>
<tool:expected-type type="java.lang.Class"/>
<tool:assignable-to type="org.springframework.instrument.classloading.LoadTimeWeaver"/>
</tool:annotation>
</xsd:appinfo>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:attribute>
<xsd:attribute name="aspectj-weaving" default="autodetect">
<xsd:simpleType>
<xsd:restriction base="xsd:string">
<xsd:enumeration value="on">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
Switches Spring-based AspectJ load-time weaving on.
]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:enumeration>
<xsd:enumeration value="off">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
Switches Spring-based AspectJ load-time weaving off.
]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:enumeration>
<xsd:enumeration value="autodetect">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
Switches AspectJ load-time weaving on if a "META-INF/aop.xml" resource
is present in the classpath. If there is no such resource, then AspectJ
load-time weaving will be switched off.
]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:enumeration>
</xsd:restriction>
</xsd:simpleType>
</xsd:attribute>
</xsd:complexType>
</xsd:element>
<xsd:element name="spring-configured">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation source="java:org.springframework.beans.factory.aspectj.AnnotationBeanConfigurerAspect"><![CDATA[
Signals the current application context to apply dependency injection
to non-managed classes that are instantiated outside of the Spring bean
factory (typically classes annotated with the @Configurable annotation).
]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
<xsd:simpleType>
<xsd:restriction base="xsd:string"/>
</xsd:simpleType>
</xsd:element>
<xsd:element name="mbean-export">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation source="java:org.springframework.jmx.export.annotation.AnnotationMBeanExporter"><![CDATA[
Activates default exporting of MBeans by detecting standard MBeans in the Spring
context as well as @ManagedResource annotations on Spring-defined beans.
The resulting MBeanExporter bean is defined under the name "mbeanExporter".
Alternatively, consider defining a custom AnnotationMBeanExporter bean explicitly.
]]></xsd:documentation>
<xsd:appinfo>
<tool:annotation>
<tool:exports type="org.springframework.jmx.export.annotation.AnnotationMBeanExporter"/>
</tool:annotation>
</xsd:appinfo>
</xsd:annotation>
<xsd:complexType>
<xsd:attribute name="default-domain" type="xsd:string">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
The default domain to use when generating JMX ObjectNames.
]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:attribute>
<xsd:attribute name="server" type="xsd:string">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
The bean name of the MBeanServer to which MBeans should be exported.
Default is to use the platform's default MBeanServer (autodetecting
WebLogic, WebSphere and the JVM's platform MBeanServer).
]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:attribute>
<xsd:attribute name="registration">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
The registration behavior, indicating how to deal with existing MBeans
of the same name: fail with an exception, ignore and keep the existing
MBean, or replace the existing one with the new MBean.
Default is to fail with an exception.
]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
<xsd:simpleType>
<xsd:restriction base="xsd:NMTOKEN">
<xsd:enumeration value="failOnExisting"/>
<xsd:enumeration value="ignoreExisting"/>
<xsd:enumeration value="replaceExisting"/>
</xsd:restriction>
</xsd:simpleType>
</xsd:attribute>
</xsd:complexType>
</xsd:element>
<xsd:element name="mbean-server">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation source="java:org.springframework.jmx.support.MBeanServerFactoryBean"><![CDATA[
Exposes a default MBeanServer for the current platform.
Autodetects WebLogic, WebSphere and the JVM's platform MBeanServer.
The default bean name for the exposed MBeanServer is "mbeanServer".
This may be customized through specifying the "id" attribute.
]]></xsd:documentation>
<xsd:appinfo>
<tool:annotation>
<tool:exports type="javax.management.MBeanServer"/>
</tool:annotation>
</xsd:appinfo>
</xsd:annotation>
<xsd:complexType>
<xsd:complexContent>
<xsd:extension base="beans:identifiedType">
<xsd:attribute name="agent-id" type="xsd:string">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
The agent id of the target MBeanServer, if any.
]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:attribute>
</xsd:extension>
</xsd:complexContent>
</xsd:complexType>
</xsd:element>
<xsd:complexType name="filterType">
<xsd:attribute name="type" use="required">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
Controls the type of filtering to apply to the expression.
"annotation" indicates an annotation to be present at the type level in target components;
"assignable" indicates a class (or interface) that the target components are assignable to (extend/implement);
"aspectj" indicates an AspectJ type pattern expression to be matched by the target components;
"regex" indicates a regex pattern to be matched by the target components' class names;
"custom" indicates a custom implementation of the org.springframework.core.type.TypeFilter interface.
Note: This attribute will not be inherited by child bean definitions.
Hence, it needs to be specified per concrete bean definition.
]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
<xsd:simpleType>
<xsd:restriction base="xsd:string">
<xsd:enumeration value="annotation"/>
<xsd:enumeration value="assignable"/>
<xsd:enumeration value="aspectj"/>
<xsd:enumeration value="regex"/>
<xsd:enumeration value="custom"/>
</xsd:restriction>
</xsd:simpleType>
</xsd:attribute>
<xsd:attribute name="expression" type="xsd:string" use="required">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[
Indicates the filter expression, the type of which is indicated by "type".
]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:attribute>
</xsd:complexType>
</xsd:schema>
redis-config.properties文件的内容如下:
redis.host=192.168.200.128 redis.port=6379 redis.pass= redis.database=0 redis.maxIdle=300 redis.maxWait=3000 redis.testOnBorrow=true
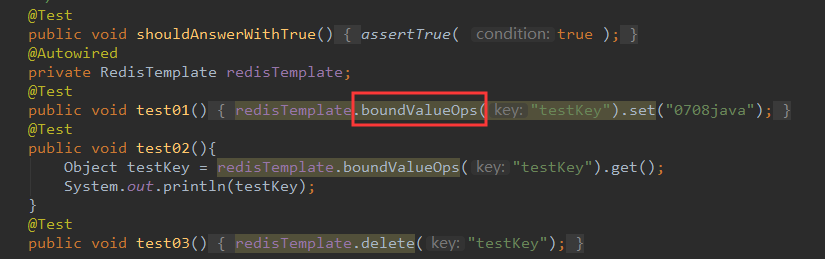
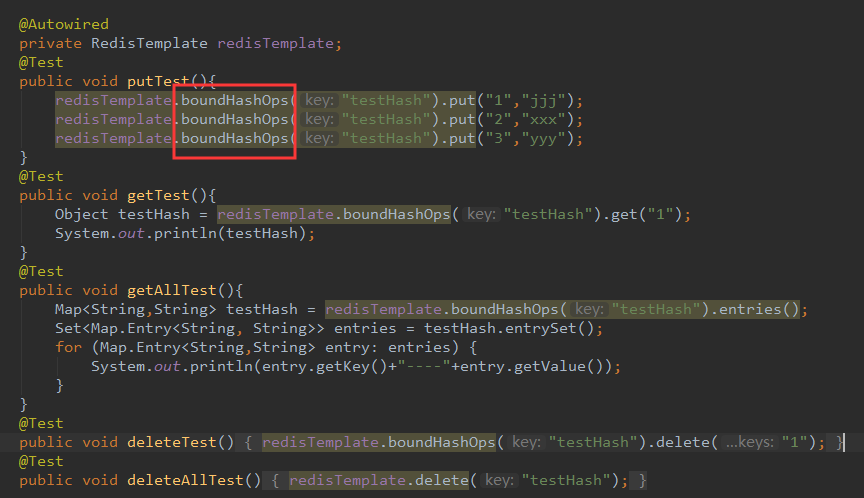
3.测试代码如下