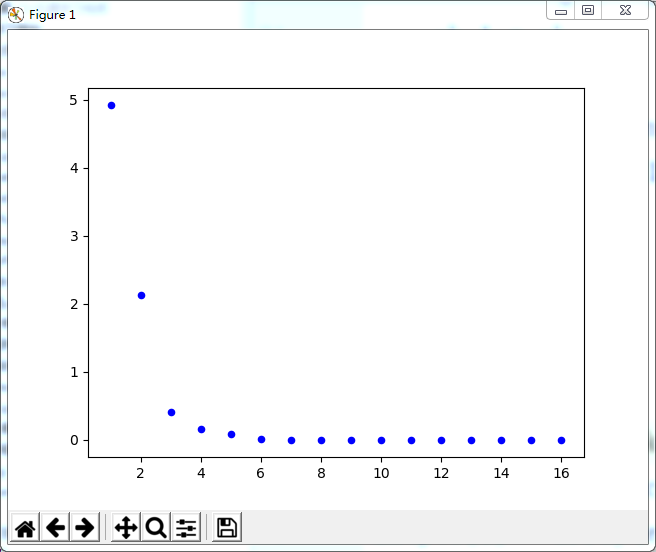
迭代法求方程组的解:
import numpy as np from numpy import * from common_libs import * import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #消元法求原方程组的解 A = mat([[8,-3,2],[4,11,-1],[6,3,12]]) b = mat([20,33,36]) result = linalg.solve(A,b.T) print(result) #迭代法求方程组的解 error = 1.0e-6 steps = 100 n=3 xk = zeros((n,1)) errorlist=[] B0 = mat([[0,3/8,-1/4],[-4/11,0,1/11],[-1/2,-1/4,0]]) f = mat([5/2,3,3]).T for k in range(steps): xk_1 = xk xk = B0*xk + f errorlist.append(linalg.norm(xk - xk_1)) if errorlist[-1] < error: print(k+1) break print(xk) matpts = zeros((2,k+1)) matpts[0] = linspace(1,k+1,k+1) matpts[1] = array(errorlist) drawScatter(plt,matpts) plt.show()
logistic_test
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Filename : Recommand_lib.py from numpy import * import numpy as np import operator import scipy.spatial.distance as dist import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def savefile(savepath, content): fp = open(savepath, "wb") fp.write(content) fp.close() # 数据文件转矩阵 # path: 数据文件路径 # delimiter: 文件分隔符 def file2matrix(path, delimiter): fp = open(path, "rb") # 读取文件内容 content = fp.read().decode() fp.close() rowlist = content.splitlines() # 按行转换为一维表 # 逐行遍历,结果按分隔符分割为行向量 testlist = [row.split(delimiter) for row in rowlist if row.strip()] # 返回转换后的矩阵形式 return mat(testlist) # 欧氏距离 eps = 1.0e-6 def distEclud(vecA, vecB): return linalg.norm(vecA - vecB) + eps # 相关系数 def distCorrcoef(vecA, vecB): return corrcoef(vecA, vecB, rowvar=0)[0][1] # Jaccard距离 def distJaccard(vecA, vecB): temp = mat([array(vecA.tolist()[0]), array(vecB.tolist()[0])]) return dist.pdist(temp, 'jaccard') # 余弦相似度 def cosSim(vecA, vecB): return (dot(vecA, vecB.T) / ((linalg.norm(vecA) * linalg.norm(vecB)) + eps))[0, 0] # 绘制散点图 def drawScatter(plt, mydata, size=20, color='blue', mrkr='o'): m, n = shape(mydata) if m > n and m > 2: plt.scatter(mydata.T[0], mydata.T[1], s=size, c=color, marker=mrkr) else: plt.scatter(mydata[0], mydata[1], s=size, c=color, marker=mrkr) # 绘制分类点 def drawScatterbyLabel(plt, Input): m, n = shape(Input) target = Input[:, -1] for i in range(m): if float(target[i,0]) == 1.0: # print("a:",Input[i, 0], Input[i, 1]) plt.scatter(float(Input[i, 0]), float(Input[i, 1]), c='blue', marker='o') else: # print("b:",Input[i, 0], Input[i, 1]) plt.scatter(float(Input[i, 0]), float(Input[i, 1]), c='red', marker='s') # 硬限幅函数 def hardlim(dataSet): dataSet[nonzero(dataSet.A > 0)[0]] = 1 dataSet[nonzero(dataSet.A <= 0)[0]] = 0 return dataSet # Logistic函数 def logistic(wTx): return 1.0 / (1.0 + exp(-wTx)) def buildMat(dataSet): m, n = shape(dataSet) dataMat = zeros((m, n)) dataMat[:, 0] = 1 #矩阵的第一列全为1 dataMat[:, 1:] = dataSet[:, :-1] #第二列到倒数第二列保持原数据,最后一列被删除 return dataMat # 分类函数 def classifier(testData, weights): prob = logistic(sum(testData * weights)) # 求取概率--判别算法 if prob > 0.5: return 1.0 # prob>0.5 返回为1 else: return 0.0 # prob<=0.5 返回为0 # 最小二乘回归,用于测试 def standRegres(xArr, yArr): xMat = mat(ones((len(xArr), 2))) yMat = mat(ones((len(yArr), 1))) xMat[:, 1:] = (mat(xArr).T)[:, 0:] yMat[:, 0:] = (mat(yArr).T)[:, 0:] xTx = xMat.T * xMat if linalg.det(xTx) == 0.0: print("This matrix is singular, cannot do inverse") return ws = xTx.I * (xMat.T * yMat) return ws
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import os import sys import numpy as np import operator from numpy import * from common_libs import * import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 1.导入数据 Input = file2matrix(r"D:cgwcode estSet.txt"," ") # print(Input) target1 = Input[:,-1] #获取分类标签列表 target = target1.astype(np.float32) [m,n] = shape(Input) # # 2.按分类绘制散点图 drawScatterbyLabel(plt,Input) # 3.构建b+x 系数矩阵:b这里默认为1 dataMat = buildMat(Input) # print(dataMat[:10,:]) # 4. 定义步长和迭代次数 alpha = 0.001 # 步长 steps = 500 # 迭代次数 weights = ones((n,1))# 初始化权重向量 # 5. 主程序 for k in range(steps): gradient = dataMat*mat(weights) # 梯度 output = logistic(gradient) errors = target - output # 计算误差 weights = weights + alpha*dataMat.T*errors print(weights) # 输出训练后的权重 # 6. 绘制训练后超平面 X = np.linspace(-7,7,100) #y= -b-w*x # b:weights[0]/weights[2] # w:weights[1]/weights[2] Y = -(double(weights[0])+X*(double(weights[1])))/double(weights[2]) plt.plot(X,Y) plt.show()
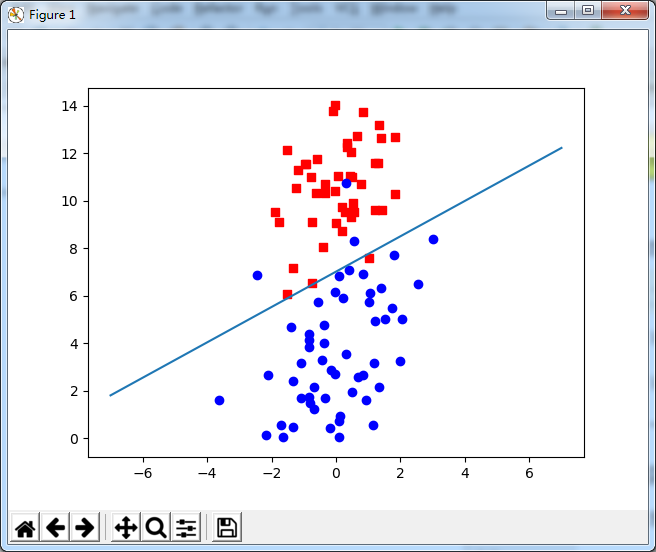
随机梯度下降算法
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import os import sys import numpy as np import operator from numpy import * from common_libs import * import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # # 1.导入数据 # Input = file2matrix(r"D:cgwcode estSet.txt"," ") # # print(Input) # target1 = Input[:,-1] #获取分类标签列表 # target = target1.astype(np.float32) # [m,n] = shape(Input) # # # 2.按分类绘制散点图 # drawScatterbyLabel(plt,Input) # # # 3.构建b+x 系数矩阵:b这里默认为1 # dataMat = buildMat(Input) # # print(dataMat[:10,:]) # # 4. 定义步长和迭代次数 # alpha = 0.001 # 步长 # steps = 500 # 迭代次数 # weights = ones((n,1))# 初始化权重向量 # weightlist = [] # # 5. 主程序 # for k in range(steps): # gradient = dataMat*mat(weights) # 梯度 # output = logistic(gradient) # errors = target - output # 计算误差 # weights = weights + alpha*dataMat.T*errors # weightlist.append(weights) # # X = np.linspace(-5,5,100) # Ylist = [] # lenw = len(weightlist) # for indx in range(lenw): # if indx % 20 == 0: # weight = weightlist[indx] # Y=-(double(weight[0]) + X*(double(weight[1])))/double(weight[2]) # plt.plot(X,Y) # plt.annotate("hplane:"+str(indx),xy = (X[99],Y[99]))#分类超平面注释 # # plt.show() # # # # # # #分类器函数 # # def classifier(testData,weights): # # prob = logistic(sum(testData*weights)) # # if prob > 0.5: # # return 1.0 # # else: # # return 0.0 # # # # # # weights = mat([[4.12414349],[0.48007329],[-0.6168482]]) # # testdata = mat([-0.147324,2.874846]) # # m,n = shape(testdata) # # print(m,n) # # testmat = zeros((m,n+1)) # # print(testmat) # # testmat[:,0] = 1 # # print(testmat) # # testmat[:,1:] = testdata # # print(testmat) # # print(classifier(testmat,weights)) #随机梯度下降 # 1.导入数据 Input = file2matrix(r"D:cgwcode estSet.txt"," ") # print(Input) target1 = Input[:,-1] #获取分类标签列表 target = target1.astype(np.float32) [m,n] = shape(Input) #2.按分类绘制散点图 drawScatterbyLabel(plt,Input) #3.构建b+x系数矩阵,b默认为1 dataMat = buildMat(Input) # print(dataMat) weightlist = [] #4. 定义迭代次数 steps = 500 weights = ones(n) #初始化权重向量 #算法主程序 #1.对数据集的每个行向量进行m次随机抽取,保证每个向量都能抽取到,且不重复 #2.对抽取之后的行向量计算动态步长 #3.进行梯度计算 #4.求得行向量的权值,合并为矩阵的权值 for j in range(steps): dataIndex = list(range(m)) #以导入数据的行数m为个数产生索引向量:0-99 for i in range(m): alpha = 2/(1.0+j+i) + 0.0001 #动态修改alpha步长 randIndex = int(random.uniform(0,len(dataIndex)))#生成0-m之间的随机索引 #计算dataMat随机索引与权重的点积和 vectSum = sum(dataMat[randIndex] * weights.T) grad = logistic(vectSum) #计算点积和的梯度 errors = target[randIndex] - grad #计算误差 weights = weights + alpha*errors *dataMat[randIndex]#计算行向量权重 del(dataIndex[randIndex]) weightlist.append(weights) lenwl = len(weightlist) weightmat = zeros((lenwl,n)) i = 0 for weight in weightlist: weightmat[i,:] = weight i += 1 print(weights) weights = weights.tolist()[0] #6.绘制训练后的超平面 X = np.linspace(-5,5,100) Y = -(double(weights[0]) + X * (double(weights[1])))/double(weights[2]) plt.plot(X,Y) fig = plt.figure() axes1 = plt.subplot(211) axes2 = plt.subplot(212) X1 = np.linspace(0,lenwl,lenwl) axes1.plot(X1,-weightmat[:,0]/weightmat[:,2])#绘制斜距 axes2.plot(X1,-weightmat[:,1]/weightmat[:,2])#绘制斜率 #生成斜距回归线 ws = standRegres(X1,-weightmat[:,0]/weightmat[:,2]) Y1 = ws[0,0] + X1*ws[1,0] axes1.plot(X1,Y1,color='red',linewidth=2,linestyle="-") plt.show()
