案例:
JDBCDemo2.jsp
package com.jdbc.com;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class JDBCDemo2 {
private static final String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jsp02";
private static final String user = "root";
private static final String password = "123456";
public static void query() {// 增删改
Connection connection = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
// a.导入驱动,加载具体的驱动类
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");// 加载具体的驱动类
// b.与数据库建立连接
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
// c.发送sql,执行(增删改、查)
stmt = connection.createStatement();
// 执行sql(增删改executeUpdate(),查询为executeQuery()
String sql = "select stuno,stuname from student";
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);// 返回值表示增删改了几条数据
// d.处理结果,增删改判断结果就行了
while(rs.next()) {
int sno = rs.getInt("stuno");
String sname = rs.getString("stuname");
System.out.println(sno+"----"+sname);
}
}catch(ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if(rs!=null)rs.close();
if(stmt!=null) stmt.close();
if(connection!=null) connection.close();
connection.close();
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//update();
query();
}
}
表中原有数据:
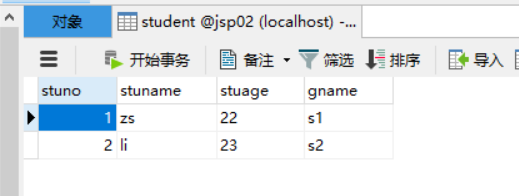
执行结果:

- 上面的获取字段也可以改为:
//也可以这样写,跟表中的字段一一对应,只适用于上面的字段查询,
如果查询的是 select * from student,就不适用了。下标从1开始
int sno = rs.getInt(1);
String sname = rs.getString(2);
System.out.println(sno+"----"+sname);
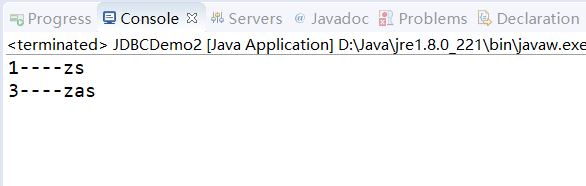
- 模糊查询:上面的sql语句改为如下
原表中的数据:

String sql = "select * from student where stuname like '%z%' ";
结果:
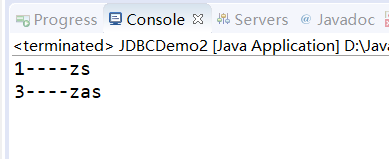
字符的拼接:
把上面模糊查询的语句改为如下:用变量的形式表示
String name = "z";
String sql = "select * from student where stuname like '%"+name+"%' ";
结果还是一样的:
-
JDBC:Java DataBase Connectivity 可以为多种关系型数据库DBMS 提供统一的访问方式,用Java来操作数据库
-
JDBC API 主要功能: 三件事,具体是通过以下类/接口实现: DriverManager : 管理jdbc驱动
Connection: 连接(通过DriverManager产生) -
Statement(PreparedStatement) :增删改查 (通过Connection产生 )
CallableStatement : 调用数据库中的 存储过程/存储函数 (通过Connection产生 ) -
Result :返回的结果集 (上面的Statement等产生 )
-
Connection产生操作数据库的对象:
-
Connection产生操作数据库的对象:
Connection产生Statement对象:createStatement()
Connection产生PreparedStatement对象:prepareStatement()
Connection产生CallableStatement对象:prepareCall();
-
Statement操作数据库:
增删改:executeUpdate()
查询:executeQuery();
ResultSet:保存结果集 select * from xxx
next():光标下移,判断是否有下一条数据;true/false
previous(): true/false
getXxx(字段名|位置):获取具体的字段值 -
PreparedStatement操作数据库:
public interface PreparedStatement extends Statement
因此
增删改:executeUpdate()
查询:executeQuery();
–此外
赋值操作 setXxx(); -
PreparedStatement与Statement在使用时的区别:
-
1.Statement:
sql
executeUpdate(sql) -
2.PreparedStatement:
sql(可能存在占位符?)
在创建PreparedStatement 对象时,将sql预编译 prepareStatement(sql)
executeUpdate()
setXxx()替换占位符? -
推荐使用PreparedStatement:原因如下:
-
1.编码更加简便(避免了字符串的拼接)
String name = “zs” ;
int age = 23 ; -
stmt:
String sql =" insert into student(stuno,stuname) values(’"+name+"’, “+age+” ) " ;
stmt.executeUpdate(sql); -
pstmt:
String sql =" insert into student(stuno,stuname) values(?,?) " ;
pstmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//预编译SQL
pstmt.setString(1,name);
pstmt.setInt(2,age);
-
-
-
2.提高性能(因为 有预编译操作,预编译只需要执行一次)
需要重复增加100条数
stmt:
String sql =" insert into student(stuno,stuname) values(’"+name+"’, “+age+” ) " ;
for(100)
stmt.executeUpdate(sql);- pstmt:
String sql =" insert into student(stuno,stuname) values(?,?) " ;
pstmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//预编译SQL
pstmt.setString(1,name);
pstmt.setInt(2,age);
for( 100){
pstmt.executeUpdate();
}
- pstmt:
-
3.安全(可以有效防止sql注入)
sql注入: 将客户输入的内容 和 开发人员的SQL语句 混为一体 -
stmt:存在被sql注入的风险
(例如输入 用户名:任意值 ’ or 1=1 –
密码:任意值)
分析:
select count() from login where uname=‘任意值 ’ or 1=1 --’ and upwd =‘任意值’ ;
select count() from login where uname='任意值 ’ or 1=1 ;
select count(*) from login ;
select count(*) from login where uname=’"+name+"’ and upwd =’"+pwd+"’
-
pstmt:有效防止sql注入
-
推荐使用pstmt
-
3.jdbc访问数据库的具体步骤:
a.导入驱动,加载具体的驱动类
b.与数据库建立连接
c.发送sql,执行
d.处理结果集 (查询)
案例1:使用preparedStatement 增删改 数据
JDBCPreparedStatementDemo.jsp
package com.jdbc.com;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
public class JDBCPreparedStatementDemo {
private static final String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jsp03";
private static final String user = "root";
private static final String password = "123456";
public static void update() {// 增删改
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
try {
// a.导入驱动,加载具体的驱动类
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");// 加载具体的驱动类
// b.与数据库建立连接
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
// c.发送sql,执行(增删改、查)
/*Statement
stmt = connection.createStatement();
// 执行sql
//String sql = "insert into student values(1,'zs',23,'s1')";
//String sql = "update student set stuname='ls' where stuno=1";
String sql = "delete from student where stuno=1";
int count = stmt.executeUpdate(sql);// 返回值表示增删改了几条数据
*/
//PreparedStatement
String sql = "insert into student values(4,'xi',30,'s4')";
pstmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//把sql提前处理
int count = pstmt.executeUpdate();
// d.处理结果,增删改判断结果就行了
if (count > 0) {
System.out.println("操作成功!");
}
}catch(ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if(pstmt!=null) pstmt.close();
if(connection!=null) connection.close();
connection.close();
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
update();
}
}
表中原数据:

执行结果:
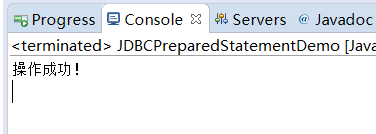

将上面的SQL语句改为:
增、删、改都是同样的格式
//先用“?”充当占位符,然后通过setXxx来设置值
String sql = "insert into student values(?,?,?,?)";
pstmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//把sql提前处理
pstmt.setInt(1, 05);//前面的参数表示和上面“?”对应的下标,第二个参数是对应的值。
pstmt.setString(2, "小明");
pstmt.setInt(3, 25);
pstmt.setString(4, "s5");
执行结果:
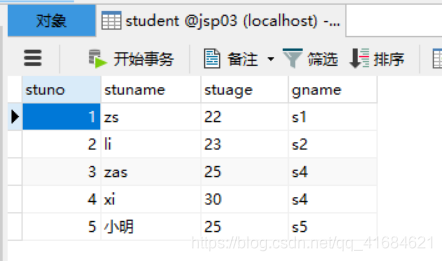
案例2:使用preparedStatement 查询数据
JDBCpreparedStatementDemo2.jsp
package com.jdbc.com;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
public class JDBCpreparedStatementDemo2 {
private static final String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jsp02";
private static final String user = "root";
private static final String password = "123456";
public static void query() {// 增删改
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
// a.导入驱动,加载具体的驱动类
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");// 加载具体的驱动类
// b.与数据库建立连接
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
// c.发送sql,执行(增删改、查)
String sql = "select * from student where stuname like ?";
pstmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1, "%z%");
// 执行sql(增删改executeUpdate(),查询为executeQuery()
//String sql = "select stuno,stuname from student";
//模糊查询(一)
//String sql = "select * from student where stuname like '%z%' ";
//模糊查询(二)
//String name = "z";
//String sql = "select * from student where stuname like '%"+name+"%' ";
rs = pstmt.executeQuery();// 返回值表示增删改了几条数据
// d.处理结果,增删改判断结果就行了
while(rs.next()) {
//也可以这样写,跟表中的字段一一对应,只适用于上面的字段查询,如果查询的是 select * from student,就不适用了,下标从1开始
//int sno = rs.getInt(1);
//String sname = rs.getString(2);
int sno = rs.getInt("stuno");
String sname = rs.getString("stuname");
System.out.println(sno+"----"+sname);
}
}catch(ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if(rs!=null)rs.close();
if(pstmt!=null) pstmt.close();
if(connection!=null) connection.close();
connection.close();
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//update();
query();
}
}
原表数据:
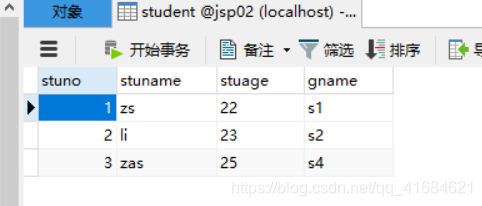
结果:
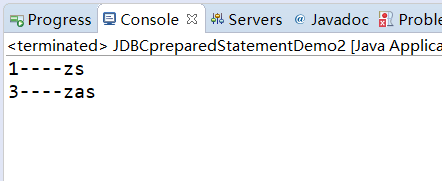
一般建议使用PreparedStatement来增删改查数据