构造方法
ThreadPoolExecutor共4个构造方法:

直接看参数最多的7个参数分别代表:
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, ThreadFactory threadFactory, RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
- corePoolSize: 线程池核心线程数
- maximumPoolSize:线程池最大数
- keepAliveTime: 空闲线程存活时间
- unit: 时间单位
- workQueue: 线程池所使用的缓冲队列
- threadFactory:线程池创建线程使用的工厂
- handler: 线程池对拒绝任务的处理策略 RejectedExecutionHandler来处理;ThreadPoolExecutor内部有实现4个拒绝策略,默认为AbortPolicy策略:
- CallerRunsPolicy:由调用execute方法提交任务的线程来执行这个任务
- AbortPolicy:抛出异常RejectedExecutionException拒绝提交任务
- DiscardPolicy:直接抛弃任务,不做任何处理
- DiscardOldestPolicy:去除任务队列中的第一个任务,重新提交
1.当池中正在运行的线程数(包括空闲线程数)小于corePoolSize时,新建线程执行任务
public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 3, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(1)); // 任务1 pool.execute(() -> { try { Thread.sleep(3 * 1000); System.out.println("--helloWorld_001--" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); //任务2 pool.execute(() -> System.out.println("--helloWorld_002--" + Thread.currentThread().getName())); }
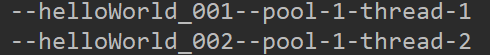
结论:线程1 结束后 没有继续线程1 而是启动线程2
2.当池中正在运行的线程数(包括空闲线程数)大于等于corePoolSize时,新插入的任务进入workQueue排队(如果workQueue长度允许),等待空闲线程来执行。
public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 3, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(1)); // 任务1 pool.execute(() -> { try { Thread.sleep(3 * 1000); System.out.println("--helloWorld_001--" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); // 任务2 pool.execute(() -> { try { Thread.sleep(5 * 1000); System.out.println("--helloWorld_002--" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); // 任务3 pool.execute(() -> System.out.println("--helloWorld_003--" + Thread.currentThread().getName())); }
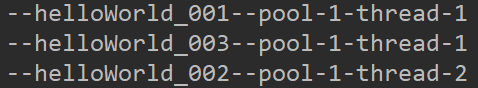
结论:任务2在运行过程中,任务3启动不会新建线程,因为有一个队列是空的,maximumPoolSize=3这个参数不起作用。
3.当队列里的任务达到上限,并且池中正在进行的线程小于maxinumPoolSize,对于新加入的任务,新建线程。
public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 3, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(1)); // 任务1 pool.execute(() -> { try { Thread.sleep(3 * 1000); System.out.println("--helloWorld_001--" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); // 任务2 pool.execute(() -> { try { Thread.sleep(5 * 1000); System.out.println("--helloWorld_002--" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); // 任务3 pool.execute(() -> System.out.println("--helloWorld_003--" + Thread.currentThread().getName())); // 任务4 pool.execute(() -> System.out.println("--helloWorld_004--" + Thread.currentThread().getName())); }
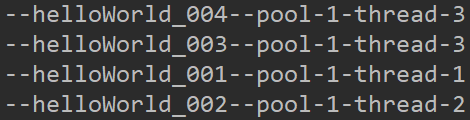
结果:任务1,2启动后 任务3在队列 ,队列就满了,由于正在进行的线程数是2<maximumPoolSize,只能新建一个线程了 然后任务4就进了新线程-3,任务4结束,队列里的任务3在线程3 进行。
4.队列里的任务达到上限,并且池中正在运行的线程等于maximumPoolSize,对于新加入的任务,执行拒绝策略(线程池默认的策略是抛异常)。
public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 3, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(1)); // 任务1 pool.execute(() -> { try { Thread.sleep(3 * 1000); System.out.println("--helloWorld_001--" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); // 任务2 pool.execute(() -> { try { Thread.sleep(5 * 1000); System.out.println("--helloWorld_002--" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); // 任务3 pool.execute(() -> System.out.println("--helloWorld_003--" + Thread.currentThread().getName())); // 任务4 pool.execute(() -> { try { Thread.sleep(2 * 1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("--helloWorld_004--" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); }); // 任务5 pool.execute(() -> System.out.println("--helloWorld_005--" + Thread.currentThread().getName())); }
运行结果: Exception in thread "main" java.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionException: Task ExecutorDemo$$Lambda$5/999966131@7699a589 rejected from java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor@58372a00[Running, pool size = 3, active threads = 3, queued tasks = 1, completed tasks = 0] at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$AbortPolicy.rejectedExecution(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:2063) at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.reject(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:830) at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.execute(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1379) at ExecutorDemo.main(ExecutorDemo.java:40) --helloWorld_004----pool-1-thread-3 --helloWorld_003--pool-1-thread-3 --helloWorld_001--pool-1-thread-1 --helloWorld_002--pool-1-thread-2
结论:队列达到上限,线程池达到最大值,故抛出异常。
关闭线程
分为两种方式:
pool.shutdown();//平缓关闭,不允许新的线程加入,正在运行的都跑完即可关闭。
pool.shutdownNow();//暴力关闭。不允许新的线程加入,且直接停到正在进行的线程。