C++标准库(五)之智能指针源码剖析
_Mutex_base
template<_Lock_policy _Lp>
class _Mutex_base
{
protected:
enum { _S_need_barriers = 0 };
};
template<>
class _Mutex_base<_S_mutex : public __gnu_cxx::__mutex
{
protected:
enum { _S_need_barriers = 1 };
};_Sp_counted_base
template<_Lock_policy _Lp = __default_lock_policy>
class _Sp_counted_base : public _Mutex_base<_Lp>
{
public:
_Sp_counted_base() : _M_use_count(1), _M_weak_count(1) { }
virtual ~_Sp_counted_base() { } //nothrow
virtual void _M_dispose() = 0; // nothrow
virtual void _M_destroy() { delete this; }
virtual void* _M_get_deleter(const std::type_info&) = 0;
void _M_add_ref_copy() { __gnu_cxx::__atomic_add_dispatch(&_M_use_count, 1); }
void _M_add_ref_lock();
void _M_release() // nothrow
{
_GLIBCXX_SYNCHRONIZATION_HAPPENS_BEFORE(&_M_use_count);
if (__gnu_cxx::__exchange_and_add_dispatch(&_M_use_count, -1) == 1)
{
_GLIBCXX_SYNCHRONIZATION_HAPPENS_AFTER(&_M_use_count);
_M_dispose();
if (_Mutex_base<_Lp>::_S_need_barriers)
__atomic_thread_fence (__ATOMIC_ACQ_REL);
_GLIBCXX_SYNCHRONIZATION_HAPPENS_BEFORE(&_M_weak_count);
if (__gnu_cxx::__exchange_and_add_dispatch(&_M_weak_count, -1) == 1)
{
_GLIBCXX_SYNCHRONIZATION_HAPPENS_AFTER(&_M_weak_count);
_M_destroy();
}
}
}
void _M_weak_add_ref() // nothrow
{ __gnu_cxx::__atomic_add_dispatch(&_M_weak_count, 1); }
void _M_weak_release() // nothrow
{
_GLIBCXX_SYNCHRONIZATION_HAPPENS_BEFORE(&_M_weak_count);
if (__gnu_cxx::__exchange_and_add_dispatch(&_M_weak_count, -1) == 1)
{
_GLIBCXX_SYNCHRONIZATION_HAPPENS_AFTER(&_M_weak_count);
if (_Mutex_base<_Lp>::_S_need_barriers)
__atomic_thread_fence (__ATOMIC_ACQ_REL);
_M_destroy();
}
}
long _M_get_use_count() const // nothrow
{ return const_cast<const volatile _Atomic_word&>(_M_use_count); }
private:
_Sp_counted_base(_Sp_counted_base const&);
_Sp_counted_base& operator=(_Sp_counted_base const&);
_Atomic_word _M_use_count; // #shared
_Atomic_word _M_weak_count; // #weak + (#shared != 0)
};
template<>
inline void _Sp_counted_base<_S_single>::_M_add_ref_lock()
{
if (__gnu_cxx::__exchange_and_add_dispatch(&_M_use_count, 1) == 0)
{
_M_use_count = 0;
__throw_bad_weak_ptr();
}
}
template<>
inline void _Sp_counted_base<_S_mutex>::_M_add_ref_lock()
{
__gnu_cxx::__scoped_lock sentry(*this);
if (__gnu_cxx::__exchange_and_add_dispatch(&_M_use_count, 1) == 0)
{
_M_use_count = 0;
__throw_bad_weak_ptr();
}
}
template<>
inline void _Sp_counted_base<_S_atomic>::_M_add_ref_lock()
{
_Atomic_word __count = _M_use_count;
do
{
if (__count == 0)
__throw_bad_weak_ptr();
}
while (!__atomic_compare_exchange_n(&_M_use_count, &__count, __count + 1,true, __ATOMIC_ACQ_REL, __ATOMIC_RELAXED));
}_Sp_counted_base_Impl
template<typename _Ptr, typename _Deleter, _Lock_policy _Lp>
class _Sp_counted_base_impl : public _Sp_counted_base<_Lp>
{
public:
_Sp_counted_base_impl(_Ptr __p, _Deleter __d) : _M_ptr(__p), _M_del(__d) { }
virtual void _M_dispose(){ _M_del(_M_ptr); }
virtual void* _M_get_deleter(const std::type_info& __ti){ return _M_del ; }
private:
_Sp_counted_base_impl(const _Sp_counted_base_impl&);
_Sp_counted_base_impl& operator=(const _Sp_counted_base_impl&);
_Ptr _M_ptr; // copy constructor must not throw
_Deleter _M_del; // copy constructor must not throw
};_Sp_deleter
template<typename _Tp>
struct _Sp_deleter
{
typedef void result_type;
typedef _Tp* argument_type;
void operator()(_Tp* __p) const { delete __p; }
};__shared_count
template<_Lock_policy _Lp = __default_lock_policy>
class __shared_count
{
public:
__shared_count() : _M_pi(0) { }
template<typename _Ptr>
__shared_count(_Ptr __p) : _M_pi(0)
{
__try
{
typedef typename std::tr1::remove_pointer<_Ptr>::type _Tp;
_M_pi = new _Sp_counted_base_impl<_Ptr, _Sp_deleter<_Tp>, _Lp>(
__p, _Sp_deleter<_Tp>());
}
__catch(...)
{
delete __p;
__throw_exception_again;
}
}
template<typename _Ptr, typename _Deleter>
__shared_count(_Ptr __p, _Deleter __d) : _M_pi(0)
{
__try
{
_M_pi = new _Sp_counted_base_impl<_Ptr, _Deleter, _Lp>(__p, __d);
}
__catch(...)
{
__d(__p); // Call _Deleter on __p.
__throw_exception_again;
}
}
template<typename _Tp>
explicit __shared_count(std::auto_ptr<_Tp>& __r) : _M_pi(new _Sp_counted_base_impl<_Tp*, _Sp_deleter<_Tp>, _Lp >(__r.get(), _Sp_deleter<_Tp>()))
{ __r.release(); }
explicit __shared_count(const __weak_count<_Lp>& __r);
~__shared_count() // nothrow
{
if (_M_pi != 0)
_M_pi->_M_release();
}
__shared_count(const __shared_count& __r) : _M_pi(__r._M_pi) // nothrow
{
if (_M_pi != 0)
_M_pi->_M_add_ref_copy();
}
__shared_count& operator=(const __shared_count& __r) // nothrow
{
_Sp_counted_base<_Lp>* __tmp = __r._M_pi;
if (__tmp != _M_pi)
{
if (__tmp != 0)
__tmp->_M_add_ref_copy();
if (_M_pi != 0)
_M_pi->_M_release();
_M_pi = __tmp;
}
return *this;
}
void _M_swap(__shared_count& __r) // nothrow
{
_Sp_counted_base<_Lp>* __tmp = __r._M_pi;
__r._M_pi = _M_pi;
_M_pi = __tmp;
}
long _M_get_use_count() const // nothrow
{ return _M_pi != 0 ? _M_pi->_M_get_use_count() : 0; }
bool _M_unique() const // nothrow
{ return this->_M_get_use_count() == 1; }
friend inline bool operator==(const __shared_count& __a, const __shared_count& __b)
{ return __a._M_pi == __b._M_pi; }
friend inline bool operator<(const __shared_count& __a, const __shared_count& __b)
{ return std::less<_Sp_counted_base<_Lp>*>()(__a._M_pi, __b._M_pi); }
void* _M_get_deleter(const std::type_info& __ti) const
{ return _M_pi ? _M_pi->_M_get_deleter(__ti) : 0; }
private:
friend class __weak_count<_Lp>;
_Sp_counted_base<_Lp>* _M_pi;
};
template<_Lock_policy _Lp>
inline __shared_count<_Lp>::__shared_count(const __weak_count<_Lp>& __r) : _M_pi(__r._M_pi)
{
if (_M_pi != 0)
_M_pi->_M_add_ref_lock();
else
__throw_bad_weak_ptr();
}
__weak_count
template<_Lock_policy _Lp = __default_lock_policy>
class __weak_count
{
public:
__weak_count() : _M_pi(0) {}
__weak_count(const __shared_count<_Lp>& __r) : _M_pi(__r._M_pi) // nothrow
{
if (_M_pi != 0)
_M_pi->_M_weak_add_ref();
}
__weak_count(const __weak_count<_Lp>& __r) : _M_pi(__r._M_pi) // nothrow
{
if (_M_pi != 0)
_M_pi->_M_weak_add_ref();
}
~__weak_count() // nothrow
{
if (_M_pi != 0)
_M_pi->_M_weak_release();
}
__weak_count<_Lp>& operator=(const __shared_count<_Lp>& __r) // nothrow
{
_Sp_counted_base<_Lp>* __tmp = __r._M_pi;
if (__tmp != 0)
__tmp->_M_weak_add_ref();
if (_M_pi != 0)
_M_pi->_M_weak_release();
_M_pi = __tmp;
return *this;
}
__weak_count<_Lp>& operator=(const __weak_count<_Lp>& __r) // nothrow
{
_Sp_counted_base<_Lp>* __tmp = __r._M_pi;
if (__tmp != 0)
__tmp->_M_weak_add_ref();
if (_M_pi != 0)
_M_pi->_M_weak_release();
_M_pi = __tmp;
return *this;
}
void _M_swap(__weak_count<_Lp>& __r) // nothrow
{
_Sp_counted_base<_Lp>* __tmp = __r._M_pi;
__r._M_pi = _M_pi;
_M_pi = __tmp;
}
long _M_get_use_count() const // nothrow
{ return _M_pi != 0 ? _M_pi->_M_get_use_count() : 0; }
friend inline bool operator==(const __weak_count<_Lp>& __a, const __weak_count<_Lp>& __b)
{ return __a._M_pi == __b._M_pi; }
friend inline bool operator<(const __weak_count<_Lp>& __a, const __weak_count<_Lp>& __b)
{ return std::less<_Sp_counted_base<_Lp>*>()(__a._M_pi, __b._M_pi); }
private:
friend class __shared_count<_Lp>;
_Sp_counted_base<_Lp>* _M_pi;
};__shared_ptr
template<typename _Tp, _Lock_policy _Lp>
class __shared_ptr
{
public:
typedef _Tp element_type;
__shared_ptr() : _M_ptr(0), _M_refcount() // never throws
{ }
template<typename _Tp1>
explicit __shared_ptr(_Tp1* __p) : _M_ptr(__p), _M_refcount(__p)
{
__glibcxx_function_requires(_ConvertibleConcept<_Tp1*, _Tp*>)
typedef int _IsComplete[sizeof(_Tp1)];
__enable_shared_from_this_helper(_M_refcount, __p, __p);
}
template<typename _Tp1, typename _Deleter>
__shared_ptr(_Tp1* __p, _Deleter __d) : _M_ptr(__p), _M_refcount(__p, __d)
{
__glibcxx_function_requires(_ConvertibleConcept<_Tp1*, _Tp*>)
__enable_shared_from_this_helper(_M_refcount, __p, __p);
}
template<typename _Tp1>
__shared_ptr(const __shared_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp>& __r) : _M_ptr(__r._M_ptr), _M_refcount(__r._M_refcount) // never throws
{ __glibcxx_function_requires(_ConvertibleConcept<_Tp1*, _Tp*>) }
template<typename _Tp1>
explicit __shared_ptr(const __weak_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp>& __r) : _M_refcount(__r._M_refcount) // may throw
{
__glibcxx_function_requires(_ConvertibleConcept<_Tp1*, _Tp*>)
_M_ptr = __r._M_ptr;
}
template<typename _Tp1>
__shared_ptr(const __shared_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp>& __r, __static_cast_tag) : _M_ptr(static_cast<element_type*>(__r._M_ptr)),_M_refcount(__r._M_refcount)
{ }
template<typename _Tp1>
__shared_ptr(const __shared_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp>& __r, __const_cast_tag) : _M_ptr(const_cast<element_type*>(__r._M_ptr)),_M_refcount(__r._M_refcount)
{ }
template<typename _Tp1>
__shared_ptr(const __shared_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp>& __r, __dynamic_cast_tag) : _M_ptr(dynamic_cast<element_type*>(__r._M_ptr)),_M_refcount(__r._M_refcount)
{
if (_M_ptr == 0) // need to allocate new counter -- the cast failed
_M_refcount = __shared_count<_Lp>();
}
template<typename _Tp1>
__shared_ptr& operator=(const __shared_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp>& __r) // never throws
{
_M_ptr = __r._M_ptr;
_M_refcount = __r._M_refcount; // __shared_count::op= doesn't throw
return *this;
}
void reset() // never throws
{ __shared_ptr().swap(*this); }
template<typename _Tp1>
void reset(_Tp1* __p) // _Tp1 must be complete.
{
_GLIBCXX_DEBUG_ASSERT(__p == 0 || __p != _M_ptr);
__shared_ptr(__p).swap(*this);
}
template<typename _Tp1, typename _Deleter>
void reset(_Tp1* __p, _Deleter __d)
{ __shared_ptr(__p, __d).swap(*this); }
typename std::tr1::add_reference<_Tp>::type operator*() const // never throws
{
_GLIBCXX_DEBUG_ASSERT(_M_ptr != 0);
return *_M_ptr;
}
_Tp* operator->() const // never throws
{
_GLIBCXX_DEBUG_ASSERT(_M_ptr != 0);
return _M_ptr;
}
_Tp* get() const // never throws
{ return _M_ptr; }
private:
typedef _Tp* __shared_ptr::*__unspecified_bool_type;
public:
operator __unspecified_bool_type() const // never throws
{ return _M_ptr == 0 ? 0 : &__shared_ptr::_M_ptr; }
bool unique() const // never throws
{ return _M_refcount._M_unique(); }
long use_count() const // never throws
{ return _M_refcount._M_get_use_count(); }
void swap(__shared_ptr<_Tp, _Lp>& __other) // never throws
{
std::swap(_M_ptr, __other._M_ptr);
_M_refcount._M_swap(__other._M_refcount);
}
private:
void* _M_get_deleter(const std::type_info& __ti) const
{ return _M_refcount._M_get_deleter(__ti); }
template<typename _Tp1, _Lock_policy _Lp1>
bool _M_less(const __shared_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp1>& __rhs) const
{ return _M_refcount < __rhs._M_refcount; }
template<typename _Tp1, _Lock_policy _Lp1> friend class __shared_ptr;
template<typename _Tp1, _Lock_policy _Lp1> friend class __weak_ptr;
template<typename _Del, typename _Tp1, _Lock_policy _Lp1>
friend _Del* get_deleter(const __shared_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp1>&);
template<typename _Tp1>
friend inline bool operator==(const __shared_ptr& __a, const __shared_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp>& __b)
{ return __a.get() == __b.get(); }
template<typename _Tp1>
friend inline bool operator!=(const __shared_ptr& __a, const __shared_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp>& __b)
{ return __a.get() != __b.get(); }
template<typename _Tp1>
friend inline bool operator<(const __shared_ptr& __a, const __shared_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp>& __b)
{ return __a._M_less(__b); }
_Tp* _M_ptr; // Contained pointer.
__shared_count<_Lp> _M_refcount; // Reference counter.
};
template<typename _Tp, _Lock_policy _Lp>
inline void swap(__shared_ptr<_Tp, _Lp>& __a, __shared_ptr<_Tp, _Lp>& __b)
{ __a.swap(__b); }
template<typename _Tp, typename _Tp1, _Lock_policy _Lp>
inline __shared_ptr<_Tp, _Lp> static_pointer_cast(const __shared_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp>& __r)
{ return __shared_ptr<_Tp, _Lp>(__r, __static_cast_tag()); }
template<typename _Tp, typename _Tp1, _Lock_policy _Lp>
inline __shared_ptr<_Tp, _Lp> const_pointer_cast(const __shared_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp>& __r)
{ return __shared_ptr<_Tp, _Lp>(__r, __const_cast_tag()); }
template<typename _Tp, typename _Tp1, _Lock_policy _Lp>
inline __shared_ptr<_Tp, _Lp> dynamic_pointer_cast(const __shared_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp>& __r)
{ return __shared_ptr<_Tp, _Lp>(__r, __dynamic_cast_tag()); }
template<typename _Ch, typename _Tr, typename _Tp, _Lock_policy _Lp>
std::basic_ostream<_Ch, _Tr>& operator<<(std::basic_ostream<_Ch, _Tr>& __os, const __shared_ptr<_Tp, _Lp>& __p)
{
__os << __p.get();
return __os;
}
template<typename _Del, typename _Tp, _Lock_policy _Lp>
inline _Del* get_deleter(const __shared_ptr<_Tp, _Lp>& __p)
{return static_cast<_Del*>(__p._M_get_deleter(typeid(_Del)));}shared_ptr
template<typename _Tp>
class shared_ptr : public __shared_ptr<_Tp>
{
public:
shared_ptr() : __shared_ptr<_Tp>() { }
template<typename _Tp1>
explicit shared_ptr(_Tp1* __p) : __shared_ptr<_Tp>(__p) { }
template<typename _Tp1, typename _Deleter>
shared_ptr(_Tp1* __p, _Deleter __d) : __shared_ptr<_Tp>(__p, __d) { }
template<typename _Tp1>
shared_ptr(const shared_ptr<_Tp1>& __r) : __shared_ptr<_Tp>(__r) { }
template<typename _Tp1>
explicit shared_ptr(const weak_ptr<_Tp1>& __r) : __shared_ptr<_Tp>(__r) { }
template<typename _Tp1>
shared_ptr(const shared_ptr<_Tp1>& __r, __static_cast_tag) : __shared_ptr<_Tp>(__r, __static_cast_tag()) { }
template<typename _Tp1>
shared_ptr(const shared_ptr<_Tp1>& __r, __const_cast_tag) : __shared_ptr<_Tp>(__r, __const_cast_tag()) { }
template<typename _Tp1>
shared_ptr(const shared_ptr<_Tp1>& __r, __dynamic_cast_tag) : __shared_ptr<_Tp>(__r, __dynamic_cast_tag()) { }
template<typename _Tp1>
shared_ptr& operator=(const shared_ptr<_Tp1>& __r) // never throws
{
this->__shared_ptr<_Tp>::operator=(__r);
return *this;
}
};
template<typename _Tp>
inline void swap(__shared_ptr<_Tp>& __a, __shared_ptr<_Tp>& __b)
{ __a.swap(__b); }
template<typename _Tp, typename _Tp1>
inline shared_ptr<_Tp> static_pointer_cast(const shared_ptr<_Tp1>& __r)
{ return shared_ptr<_Tp>(__r, __static_cast_tag()); }
template<typename _Tp, typename _Tp1>
inline shared_ptr<_Tp> const_pointer_cast(const shared_ptr<_Tp1>& __r)
{ return shared_ptr<_Tp>(__r, __const_cast_tag()); }
template<typename _Tp, typename _Tp1>
inline shared_ptr<_Tp> dynamic_pointer_cast(const shared_ptr<_Tp1>& __r)
{ return shared_ptr<_Tp>(__r, __dynamic_cast_tag()); }
__weak_ptr
template<typename _Tp, _Lock_policy _Lp>
class __weak_ptr
{
public:
typedef _Tp element_type;
__weak_ptr() : _M_ptr(0), _M_refcount() // never throws
{ }
template<typename _Tp1>
__weak_ptr(const __weak_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp>& __r) : _M_refcount(__r._M_refcount) // never throws
{
__glibcxx_function_requires(_ConvertibleConcept<_Tp1*, _Tp*>)
_M_ptr = __r.lock().get();
}
template<typename _Tp1>
__weak_ptr(const __shared_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp>& __r) : _M_ptr(__r._M_ptr), _M_refcount(__r._M_refcount) // never throws
{ __glibcxx_function_requires(_ConvertibleConcept<_Tp1*, _Tp*>) }
template<typename _Tp1>
__weak_ptr& operator=(const __weak_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp>& __r) // never throws
{
_M_ptr = __r.lock().get();
_M_refcount = __r._M_refcount;
return *this;
}
template<typename _Tp1>
__weak_ptr& operator=(const __shared_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp>& __r) // never throws
{
_M_ptr = __r._M_ptr;
_M_refcount = __r._M_refcount;
return *this;
}
__shared_ptr<_Tp, _Lp>lock() const // never throws
{
return expired() ? __shared_ptr<element_type, _Lp>()
: __shared_ptr<element_type, _Lp>(*this);
} // XXX MT
long use_count() const // never throws
{ return _M_refcount._M_get_use_count(); }
bool expired() const // never throws
{ return _M_refcount._M_get_use_count() == 0; }
void reset() // never throws
{ __weak_ptr().swap(*this); }
void swap(__weak_ptr& __s) // never throws
{
std::swap(_M_ptr, __s._M_ptr);
_M_refcount._M_swap(__s._M_refcount);
}
private:
void _M_assign(_Tp* __ptr, const __shared_count<_Lp>& __refcount)
{
_M_ptr = __ptr;
_M_refcount = __refcount;
}
template<typename _Tp1>
bool _M_less(const __weak_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp>& __rhs) const
{ return _M_refcount < __rhs._M_refcount; }
template<typename _Tp1, _Lock_policy _Lp1> friend class __shared_ptr;
template<typename _Tp1, _Lock_policy _Lp1> friend class __weak_ptr;
friend class __enable_shared_from_this<_Tp, _Lp>;
friend class enable_shared_from_this<_Tp>;
template<typename _Tp1>
friend inline bool operator<(const __weak_ptr& __lhs, const __weak_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp>& __rhs)
{ return __lhs._M_less(__rhs); }
_Tp* _M_ptr; // Contained pointer.
__weak_count<_Lp> _M_refcount; // Reference counter.
};
template<typename _Tp, _Lock_policy _Lp>
inline void swap(__weak_ptr<_Tp, _Lp>& __a, __weak_ptr<_Tp, _Lp>& __b)
{ __a.swap(__b); }
weak_ptr
template<typename _Tp>
class weak_ptr : public __weak_ptr<_Tp>
{
public:
weak_ptr() : __weak_ptr<_Tp>() { }
template<typename _Tp1>
weak_ptr(const weak_ptr<_Tp1>& __r) : __weak_ptr<_Tp>(__r) { }
template<typename _Tp1>
weak_ptr(const shared_ptr<_Tp1>& __r) : __weak_ptr<_Tp>(__r) { }
template<typename _Tp1>
weak_ptr& operator=(const weak_ptr<_Tp1>& __r) // never throws
{
this->__weak_ptr<_Tp>::operator=(__r);
return *this;
}
template<typename _Tp1>
weak_ptr& operator=(const shared_ptr<_Tp1>& __r) // never throws
{
this->__weak_ptr<_Tp>::operator=(__r);
return *this;
}
shared_ptr<_Tp> lock() const // never throws
{
return this->expired() ? shared_ptr<_Tp>() : shared_ptr<_Tp>(*this);
}
};类型声明
struct __static_cast_tag { };
struct __const_cast_tag { };
struct __dynamic_cast_tag { };
template<typename _Tp, _Lock_policy _Lp = __default_lock_policy>
class __shared_ptr;
template<typename _Tp, _Lock_policy _Lp = __default_lock_policy>
class __weak_ptr;
template<typename _Tp, _Lock_policy _Lp = __default_lock_policy>
class __enable_shared_from_this;
template<typename _Tp>
class shared_ptr;
template<typename _Tp>
class weak_ptr;
template<typename _Tp>
class enable_shared_from_this;继承关系
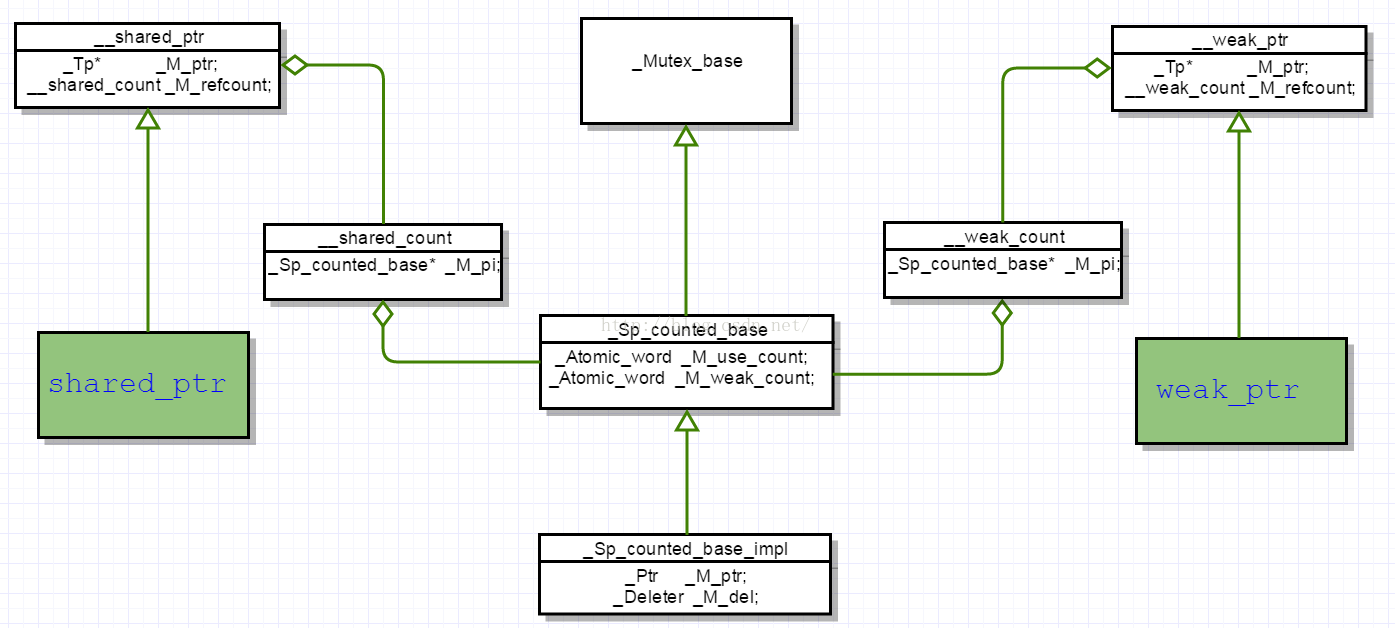
其中,很明显的可以看出,shared_ptr指向内部含有两个指针:指向被管理对象的指针,一个指向管理对象基类的指针。其中,管理对象由具有原子属性的use_count和weak_count组成,指向被管理对象的T的指针以及用来销毁被管理对象的deleter指针。
被new创建的后托管给shared_ptr的指针称为被管理对象;智能指针内部创建的用来维护被管理对象生命周期的实例称作管理对象。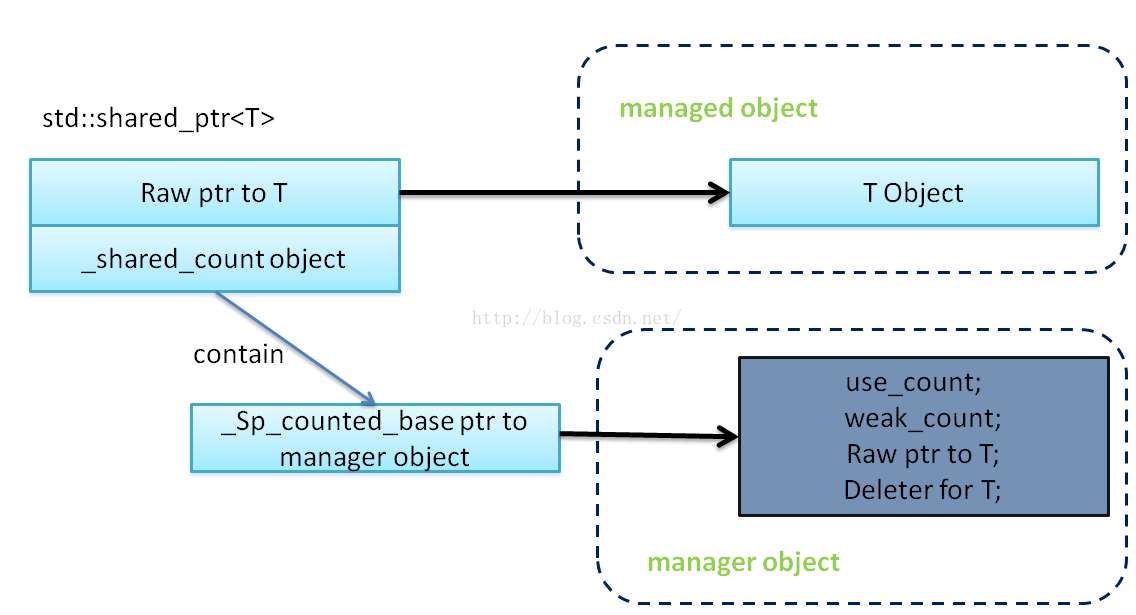
shared_ptr
创建shared_ptr的时候不但需要动态的在堆上创建一个被管理对象(_M_ptr),同样需要在堆上创建一个管理对象(_M_refcount):
template<typename _Tp1> explicit __shared_ptr(_Tp1* __p)
: _M_ptr(__p), _M_refcount(__p) {
__glibcxx_function_requires(_ConvertibleConcept<_Tp1*, _Tp*>)
typedef int _IsComplete[sizeof(_Tp1)];
__enable_shared_from_this_helper(_M_refcount, __p, __p);
}
template<typename _Ptr>
__shared_count(_Ptr __p) : _M_pi(0)
{
__try
{
typedef typename std::tr1::remove_pointer<_Ptr>::type _Tp;
_M_pi = new _Sp_counted_base_impl<_Ptr, _Sp_deleter<_Tp>, _Lp>(__p, _Sp_deleter<_Tp>());
}
__catch(...)
{
delete __p;
__throw_exception_again;
}
}shared_ptr的内部包含一个指向被管理对象的指针(_M_ptr),_Sp_counted_base_impl中也存在一个指向被管理对象的指针(_M_ptr),为什么呢?让我们从shared_ptr的复制说起:
template<typename _Tp1>
__shared_ptr(const __shared_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp>& __r)
: _M_ptr(__r._M_ptr), _M_refcount(__r._M_refcount) // never throws
{__glibcxx_function_requires(_ConvertibleConcept<_Tp1*, _Tp*>)}
template<typename _Tp1>
__shared_ptr& operator=(const __shared_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp>& __r) // never throws
{
_M_ptr = __r._M_ptr;
_M_refcount = __r._M_refcount; // __shared_count::op= doesn't throw
return *this;
}
__shared_count&
operator=(const __shared_count& __r) // nothrow
{
_Sp_counted_base<_Lp>* __tmp = __r._M_pi; //指向sp2的管理计数对象
if (__tmp != _M_pi)
{
if (__tmp != 0)
__tmp->_M_add_ref_copy(); //增加sp2的引用计数
if (_M_pi != 0)
_M_pi->_M_release(); //减少sp1的引用计数
_M_pi = __tmp; //令sp1的count指向sp2?有点多余啊
}
return *this;
}根据上面描述的代码,考虑这种情形:sp1指向a1,sp2指向a2(a1 != a2)。当把sp1赋给sp2时,就会出现__tmp!= _M_pi的情况。假设,初始时有且仅有一个sp1指向a1,有且仅有一个sp2指向a2。指向代码:sp1 = sp2,当赋值结束时,sp1和sp2都指向a2,没有指针指向a1,sp1指向的a1及其对应的管理对象均应该被析构。在上面代码的描述中:首先获取sp2的_Sp_counted_base*指针,紧接着判断sp2的_Sp_counted_base与sp1的_Sp_counted_base是否相等,因为已经调整了sp2的指向,肯定是不相等的,于是,进入sp1的析构阶段。此时,__tmp描述的是sp2的指针,_M_pi描述的是sp1的指针。因为此时,sp1和sp2都指向同一个管理对象,增加sp2的管理计数,然后减少sp1的管理计数。最后,将sp1的管理对象指针指向sp2?有点多余啊。
//************_Sp_counted_base*****************//
void
_M_add_ref_copy()
{ __gnu_cxx::__atomic_add_dispatch(&_M_use_count, 1); }
//************_Sp_counted_base*****************//
void
_M_release() // nothrow
{
// Be race-detector-friendly. For more info see bits/c++config.
_GLIBCXX_SYNCHRONIZATION_HAPPENS_BEFORE(&_M_use_count);
if (__gnu_cxx::__exchange_and_add_dispatch(&_M_use_count, -1) == 1)
{
_GLIBCXX_SYNCHRONIZATION_HAPPENS_AFTER(&_M_use_count);
_M_dispose();
if (_Mutex_base<_Lp>::_S_need_barriers)
{
__atomic_thread_fence (__ATOMIC_ACQ_REL);
}
// Be race-detector-friendly. For more info see bits/c++config.
_GLIBCXX_SYNCHRONIZATION_HAPPENS_BEFORE(&_M_weak_count);
if (__gnu_cxx::__exchange_and_add_dispatch(&_M_weak_count, -1) == 1)
{
_GLIBCXX_SYNCHRONIZATION_HAPPENS_AFTER(&_M_weak_count);
_M_destroy();
}
}
}
//************_Sp_counted_base*****************//
// Called when _M_use_count drops to zero, to release the resources
// managed by *this.
virtual void
_M_dispose() = 0; // nothrow
// Called when _M_weak_count drops to zero.
virtual void
_M_destroy() // nothrow
{ delete this; }
//************_Sp_counted_base_impl*************//
virtual void
_M_dispose() // nothrow
{ _M_del(_M_ptr); }_M_release()函数首先对a1的use_count减去1,并对比减之前的值,如果减之前是1,说明减后是0,a1没有任何shared_ptr指针指向了,就应该将a1销毁了,于是调用_M_dispose()函数销毁a1;同时,应该对a1的weak_count减去1,并对比减之前的值,如果减之前是1,说明减之后是0,此时已经没有任何weak_ptr指针指向它了,应该将管理对象销毁,于是调用_M_destory()销毁管理对象。这就解释了为什么shared_ptr对象内部包含两指向被管理对象的指针了:**__shared_ptr直接包含的裸指针是为了实现向*,->之类的操作,通过__shared_count间接包含的指针是为了管理对象的生命周期,回收相关资源。
同时,__shared_count内部的use_count主要用来标记被管理对象的生命周期,weak_count主要用来标记管理对象的生命周期**
当一个shared_ptr超出作用域被销毁时,它会调用__shared_count的_M_release()对use_count和weak_count进行自减并判断是否需要释放管理对象和被管理对象:
~__shared_count() // nothrow
{
if (_M_pi != 0)
_M_pi->_M_release();
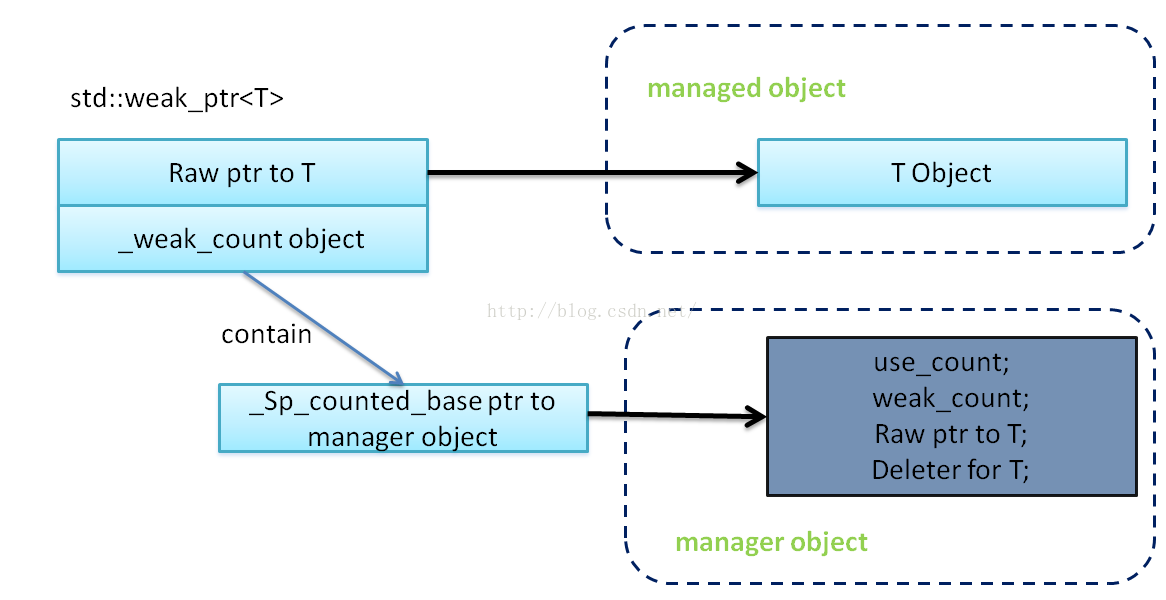
}weak_ptr
对于weak_ptr,我们从其对应的__weak_count说起:
//************_Sp_counted_base*****************//
void
_M_weak_add_ref() // nothrow
{ __gnu_cxx::__atomic_add_dispatch(&_M_weak_count, 1); }
//************_Sp_counted_base*****************//
void
_M_weak_release() // nothrow
{
// Be race-detector-friendly. For more info see bits/c++config.
_GLIBCXX_SYNCHRONIZATION_HAPPENS_BEFORE(&_M_weak_count);
if (__gnu_cxx::__exchange_and_add_dispatch(&_M_weak_count, -1) == 1)
{
_GLIBCXX_SYNCHRONIZATION_HAPPENS_AFTER(&_M_weak_count);
if (_Mutex_base<_Lp>::_S_need_barriers)
{
// See _M_release(),
// destroy() must observe results of dispose()
__atomic_thread_fence (__ATOMIC_ACQ_REL);
}
_M_destroy();
}
}
__weak_count<_Lp>& operator=(const __shared_count<_Lp>& __r) // nothrow
{
_Sp_counted_base<_Lp>* __tmp = __r._M_pi;
if (__tmp != 0)
__tmp->_M_weak_add_ref();
if (_M_pi != 0)
_M_pi->_M_weak_release();
_M_pi = __tmp;
return *this;
}
__weak_count<_Lp>& operator=(const __weak_count<_Lp>& __r) // nothrow
{
_Sp_counted_base<_Lp>* __tmp = __r._M_pi;
if (__tmp != 0)
__tmp->_M_weak_add_ref();
if (_M_pi != 0)
_M_pi->_M_weak_release();
_M_pi = __tmp;
return *this;
}
__weak_count<_Lp>& operator=(const __shared_count<_Lp>& __r) // nothrow
{
_Sp_counted_base<_Lp>* __tmp = __r._M_pi;
if (__tmp != 0)
__tmp->_M_weak_add_ref();
if (_M_pi != 0)
_M_pi->_M_weak_release();
_M_pi = __tmp;
return *this;
}
~__weak_count() // nothrow
{
if (_M_pi != 0)
_M_pi->_M_weak_release();
}从上面可以看出:
- __weak_count相关的复制拷贝以及析构函数只会影响到weak_count的值,对use_count没有影响;当weak_count为0时,释放管理对象。也就是说,**__weak_ptr不影响被管理对象的生命周期。同时,由于__weak_ptr没有像shared_ptr那样实现->,*之类的指针操作,__weak_ptr不能直接操作被管理的对象**。
- __weak_count自身间的赋值以及__shared_count对__weak_count的赋值时,他们都具有相同的指向管理对象的指针;也就是说:**当多个__weak_ptr和__shared_ptr指向同一个管理对象时,他们共享同一个管理对象**,这就保证了可以通过__weak_ptr可以判断__shared_ptr指向的被管理对象是否存在以及获取到被管理对象的指针。
__shared_ptr和__weak_ptr在管理同一对象时,他们之间的关系如下: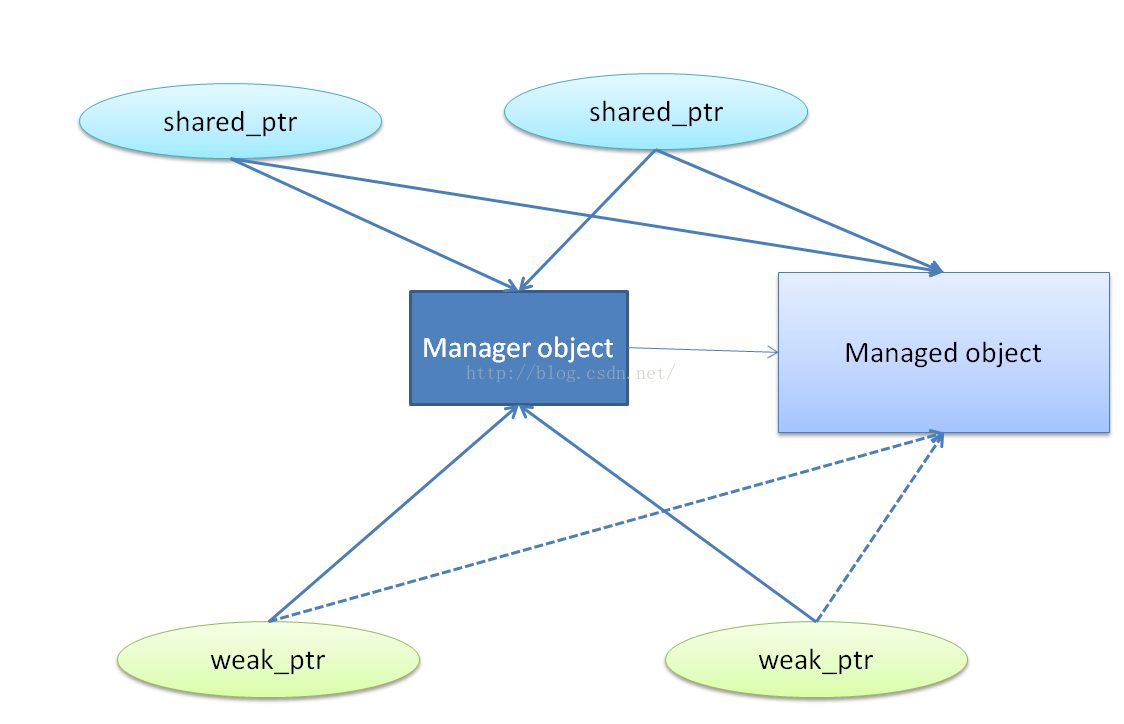
由于weak_ptr不能直接操作被管理对象的但仍然持有指向被管理对象的指针(用来初始化内部的__weak_count对象),weak_ptr与被管理对象用虚线连接。
同时,weak_ptr有几个重要的成员函数: expired():判断该对象是否已经被释放use_count():返回目前有多少个shared_ptr指向被管理的对象lock():返回一个指向被管理对象的shared_ptr
/*************_weak_ptr*************************/
long
use_count() const // never throws
{ return _M_refcount._M_get_use_count(); }
bool
expired() const // never throws
{ return _M_refcount._M_get_use_count() == 0; }
long
_M_get_use_count() const // nothrow
{ return const_cast<const volatile _Atomic_word&>(_M_use_count); }
__shared_ptr<_Tp, _Lp>
lock() const // never throws
{
#ifdef __GTHREADS
// Optimization: avoid throw overhead.
if (expired())
return __shared_ptr<element_type, _Lp>();
__try
{
return __shared_ptr<element_type, _Lp>(*this);
}
__catch(const bad_weak_ptr&)
{
// Q: How can we get here?
// A: Another thread may have invalidated r after the
// use_count test above.
return __shared_ptr<element_type, _Lp>();
}
#else
// Optimization: avoid try/catch overhead when single threaded.
return expired() ? __shared_ptr<element_type, _Lp>()
: __shared_ptr<element_type, _Lp>(*this);
#endif
} // XXX MT当然了,shared_ptr也会给在某些地方挖坑。在正常情况下,多个shared_ptr只用同一个管理对象管理同一个被管理对象。但是,在某些情况下,会出现多个管理对象管理同一个被管理对象的情况,这种情况下会出现double free的错误。在下面这种描述中,两个sp拥有不同的管理对象,但是指向了同一块堆内存,这就导致了sp1和sp2析构时会将被管理对象析构两次。
class Thing {
public:
void foo();
void defrangulate();
};
void transmogrify(shared_ptr<Thing>);
int main()
{
shared_ptr<Thing> t1(new Thing); // create manager object A for the Thing
t1->foo();
}
void Thing::foo()
{
shared_ptr<Thing> sp_for_this(this);
transmogrify(sp_for_this);
}
void transmogrify(shared_ptr<Thing> ptr)
{
ptr->defrangulate();
}怎么解决上述的问题:当一个对象M创建之后,如果一个函数foo的形参为M类型的智能指针,如何在对象M内部将对象M的指针作为实参传递给该函数foo呢?C++引入了enable_shared_from_this用weak_ptr的特性解决了这一问题。其基本思想是通过让M继承enable_shared_from_this,这样对象M的内部将会有一个__weak_shared指针_M__weak_this,在第一次创建指向M的shared_ptr sp的时候,通过模板特例化,将会初始化_M_weak_this;这样,M内部也会产生一个指向自身的weak_ptr,并且该weak_ptr内部的管理对象与sp的管理对象是相同的(这可以从weak_ptr年内不得_M_assign函数看出)。
// Friend of enable_shared_from_this.
template<typename _Tp1, typename _Tp2>
void __enable_shared_from_this_helper(const __shared_count<>&, const enable_shared_from_this<_Tp1>*, const _Tp2*);
template<typename _Tp1>
explicit __shared_ptr(_Tp1* __p)
: _M_ptr(__p), _M_refcount(__p)
{
__glibcxx_function_requires(_ConvertibleConcept<_Tp1*, _Tp*>) typedef int _IsComplete[sizeof(_Tp1)];
__enable_shared_from_this_helper(_M_refcount, __p, __p);
}
template<typename _Tp>
class enable_shared_from_this
{
protected:
enable_shared_from_this() { }
enable_shared_from_this(const enable_shared_from_this&) { }
enable_shared_from_this&
operator=(const enable_shared_from_this&)
{ return *this; }
~enable_shared_from_this() { }
public:
shared_ptr<_Tp>
shared_from_this()
{ return shared_ptr<_Tp>(this->_M_weak_this); }
shared_ptr<const _Tp>
shared_from_this() const
{ return shared_ptr<const _Tp>(this->_M_weak_this); }
private:
template<typename _Tp1>
void
_M_weak_assign(_Tp1* __p, const __shared_count<>& __n) const
{ _M_weak_this._M_assign(__p, __n); }
template<typename _Tp1>
friend void
__enable_shared_from_this_helper(const __shared_count<>& __pn, const enable_shared_from_this* __pe, const _Tp1* __px)
{
if (__pe != 0)
__pe->_M_weak_assign(const_cast<_Tp1*>(__px), __pn);
}
mutable weak_ptr<_Tp> _M_weak_this;
};
_M_assign(_Tp* __ptr, const __shared_count<_Lp>& __refcount)
{
_M_ptr = __ptr;
_M_refcount = __refcount;
}最后,在效率上需要注意一点:在采用shared_ptr<T> sp(new T)形式来创建sp管理对象时,将会出现两次堆内存分配:一是为被管理对象分配内存;二是为管理对象分配内存。怎么办呢?
可以采用shared_ptr<T> sp(make_shared<T>)的方式,采用这种方式将会一次分配一大块内存用于存放管理对象与被管理对象,这就避免了上面所说的二次内存分配的问题。
使用shared_ptr与weak_ptr时还需要注意一点:即使shared_ptr的use_count已经为0,被管理对象已经被析构,但是如果weak_ptr对象依旧存在,weak_count不为0,管理对象就不会被释放。
结论:
shared_ptr的引用计数是安全且无锁的,但对象的读写不是,因为shared_ptr有两个数据成员,读写操作不能原子化。即:
- 一个shared_ptr对象实体可以被多个线程同时读取
- 两个shared_ptr对象实体可以被两个线程同时写入,“析构算写操作”
- 如果多个线程同时读取一个shared_ptr对象,需要加锁。
参考:
1.https://blog.csdn.net/ithiker/article/details/51532484
2.https://blog.csdn.net/Solstice/article/details/8547547