使用POSIX编写多线程C++程序
创建线程
#include <pthread.h>
pthread_create(thread,attr,start_routine,arg)
pthread_create创建一个新的线程。下面是各参数的说明:
| 参数 | 描述 |
| thread | 指向线程标识符指针。 |
| attr | 一个不透明的属性对象,可以被用来设置线程属性。您可以指定线程属性对象,也可以使用默认值 NULL。 |
| start_routine | 线程运行函数起始地址,一旦线程被创建就会执行。 |
| arg | 运行函数的参数。它必须通过把引用作为指针强制转换为 void 类型进行传递。如果没有传递参数,则使用 NULL。 |
终止线程
#include <pthread.h>
pthread_exit(status)
pthread_exit 用于显式地退出一个线程。
在主线程中调用pthread_exit, 则仅仅是主线程结束,进程不会结束,进程内的其他线程也不会结束,直到所有线程结束,进程才会终止。
下面通过实例来感受一下改函数的作用。
#include <iostream> #include <pthread.h> #include <unistd.h> using namespace std; #define NUM_THREADS 5 void* say_hello(void* args) { sleep(2); /*------------------ 关键点 ------------------*/ cout << "Hello Runoob!" << endl; return 0; } int main() { //定义线程的id变量 ,多个变量使用数组 pthread_t tids[NUM_THREADS]; for(int i=0;i<NUM_THREADS;i++) { int ret = pthread_create(&tids[i],NULL,say_hello,NULL); if(ret!=0) { cout << "pthread_create error:error_code=" << ret << endl; } } //等各个线程退出后,进程才结束,否则进程强制结束了,线程还没反应过来 pthread_exit(NULL); return 0; }
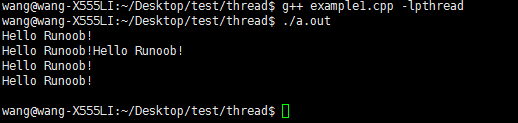
如果把 pthread_exit() 函数注释掉 ,编译运行如下:

没有输出线程函数中的输出,这就是主函数中的return导致进程强制结束了,线程还没反应过来。
连接和分离线程
pthread_join (threadid, status)
pthread_detach (threadid)
在很多情况下,主线程生成并起动了子线程,如果子线程里要进行大量的耗时的运算,主线程往往将于子线程之前结束,但是如果主线程处理完其他的事务后,需要用到子线程的处理结果,也就是主线程需要等待子线程执行完成之后再结束,
这个时候就要用到pthread_join()方法了。即pthread_join()的作用可以这样理解:主线程等待子线程的终止。
#include "stdafx.h" #include <pthread.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <Windows.h> #pragma comment(lib, "pthreadVC2.lib") static int count = 0; void* thread_run(void* parm) { for (int i=0;i<5;i++) { count++; printf("The thread_run method count is = %d ",count); Sleep(1000); } return NULL; } int main() { pthread_t tid; pthread_create(&tid, NULL, thread_run,NULL); // 加入pthread_join后,主线程"main"会一直等待直到tid这个线程执行完毕自己才结束 // 一般项目中需要子线程计算后的值就需要加join方法 pthread_join(tid,NULL); // 如果没有join方法可以看看打印的顺序 printf("The count is = %d ",count); getchar(); return 0; }
pthread_detach(threadid)函数的功能是使线程ID为threadid的线程处于分离状态,一旦线程处于分离状态,该线程终止时底 层资源立即被回收;否则终止子线程的状态会一直保存(占用系统资源)直到主线程调用pthread_join(threadid,NULL)获取线程的退 出状态。通常是主线程使用pthread_create()创建子线程以后,一般可以调用pthread_detach(threadid)分离刚刚创建的子线程,这里的threadid是指子线程的threadid;
#include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <stdio.h> void print_message_function( void *ptr ); main ( ) { pthread_t thread1; pthread_create(&thread1,NULL,(void *)&print_message_function,(void *)0); int i; for(i=0;i<5;i++) { printf("%d ",thread1); } exit (0) ; } void print_message_function( void *ptr ) {
pthread_detach(pthread_self()); static int g; printf("%d ", g++); pthread_exit(0) ; }
C++11 之后有了标准的线程库
#include <iostream> #include <thread> std::thread::id main_thread_id = std::this_thread::get_id(); void hello() { std::cout << "Hello Concurrent World "; if(main_thread_id == std::this_thread::get_id()) std::cout << "This is the main thread. "; else std::cout << "This is not the main thread. "; } void pause_thread(int n) { std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(n)); std::cout << "pause of" << n << "seconds ended"; } int main() { std::thread t(hello); std::cout << t.hardware_concurrency() << std::endl; //可以并发执行多少个(不准确) std::cout << "native_handle " << t.native_handle() << std::endl; //可以并发执行多少个(不准确) t.join(); std::thread a(hello); a.detach(); std::thread threads[5]; std::cout << "Spawning 5 threads... "; for(int i = 0;i < 5;++i) threads[i] = std::thread(pause_thread,i+1); std::cout << "Donw spawning threads.Now waiting for them to join: "; for(auto &thread : threads) thread.join(); std::cout << "All threads joined! "; }
之前一些编译器使用 C++11 的编译参数是 -std=c++11