题目描述
Farmer John has been having trouble making his plants grow, and needs your help to water them properly. You are given the locations of N raindrops (1 <= N <= 100,000) in the 2D plane, where y represents vertical height of the drop, and x represents its location over a 1D number line:
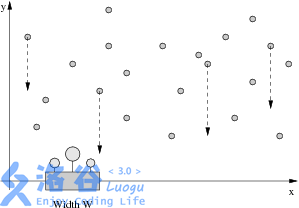
Each drop falls downward (towards the x axis) at a rate of 1 unit per second. You would like to place Farmer John's flowerpot of width W somewhere along the x axis so that the difference in time between the first raindrop to hit the flowerpot and the last raindrop to hit the flowerpot is at least some amount D (so that the flowers in the pot receive plenty of water). A drop of water that lands just on the edge of the flowerpot counts as hitting the flowerpot.
Given the value of D and the locations of the N raindrops, please compute the minimum possible value of W.
老板需要你帮忙浇花。给出N滴水的坐标,y表示水滴的高度,x表示它下落到x轴的位置。
每滴水以每秒1个单位长度的速度下落。你需要把花盆放在x轴上的某个位置,使得从被花盆接着的第1滴水开始,到被花盆接着的最后1滴水结束,之间的时间差至少为D。
我们认为,只要水滴落到x轴上,与花盆的边沿对齐,就认为被接住。给出N滴水的坐标和D的大小,请算出最小的花盆的宽度W。
输入输出格式
输入格式:
第一行2个整数 N 和 D。
第2.. N+1行每行2个整数,表示水滴的坐标(x,y)。
输出格式:
仅一行1个整数,表示最小的花盆的宽度。如果无法构造出足够宽的花盆,使得在D单位的时间接住满足要求的水滴,则输出-1。
输入输出样例
说明
【样例解释】
有4滴水, (6,3), (2,4), (4,10), (12,15).水滴必须用至少5秒时间落入花盆。花盆的宽度为2是必须且足够的。把花盆放在x=4..6的位置,它可以接到1和3水滴, 之间的时间差为10-3 = 7满足条件。
【数据范围】
40%的数据:1 ≤ N ≤ 1000,1 ≤ D ≤ 2000;
100%的数据:1 ≤ N ≤ 100000,1 ≤ D ≤ 1000000,0≤x,y≤10^6。
题意:
用一个宽度最小的花盆接雨滴,使得这个区间内的雨滴的纵坐标最大值和最小值之差大于等于d
思路:
一眼思路是用线段树维护区间最大值和最小值,二分答案。当然T了,而且WA,才拿了20分。好菜啊。
讲道理顶多会T,怎么会WA呢我好菜啊哭。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <set> 3 #include <cmath> 4 #include <stdio.h> 5 #include <cstring> 6 #include <algorithm> 7 #include <vector> 8 #include <queue> 9 #include <map> 10 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 11 using namespace std; 12 typedef long long LL; 13 #define inf 0x7f7f7f7f 14 15 const int maxn = 1e5 + 5; 16 const int maxd = 1e6 + 5; 17 int n, d, mmx, mmin; 18 int height[maxd]; 19 int tree_max[maxd << 2], tree_min[maxd << 2]; 20 21 void pushup(int rt) 22 { 23 tree_max[rt] = max(tree_max[rt << 1], tree_max[rt << 1 | 1]); 24 tree_min[rt] = min(tree_min[rt << 1], tree_min[rt << 1 | 1]); 25 } 26 27 void build(int rt, int l, int r) 28 { 29 if(l == r){ 30 if(height[l] == -1){ 31 tree_max[rt] = -inf; 32 tree_min[rt] = inf; 33 } 34 else{ 35 tree_max[rt] = tree_min[rt] = height[l]; 36 } 37 return; 38 } 39 int mid = (l + r) / 2; 40 build(rt << 1, l, mid); 41 build(rt << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r); 42 pushup(rt); 43 } 44 45 int query_max(int L, int R, int l, int r, int rt) 46 { 47 if(L <= l && R >= r){ 48 return tree_max[rt]; 49 } 50 int mid = (l + r) / 2; 51 int res = -inf; 52 if(L <= mid){ 53 res = max(res, query_max(L, R, l, mid, rt << 1)); 54 } 55 if(R > mid){ 56 res = max(res, query_max(L, R, mid + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1)); 57 } 58 return res; 59 } 60 61 int query_min(int L, int R, int l, int r, int rt) 62 { 63 if(L <= l && R >= r){ 64 return tree_min[rt]; 65 } 66 int mid = (l + r) / 2; 67 int res = inf; 68 if(L <= mid){ 69 res = min(res, query_min(L, R, l, mid, rt << 1)); 70 } 71 if(R > mid){ 72 res = min(res, query_min(L, R, mid + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1)); 73 } 74 return res; 75 } 76 77 bool check(int len) 78 { 79 for(int i = mmin; i <= mmx; i++){ 80 //cout<<query_max(i, i + len, 1, mmx, 1)<<endl; 81 //cout<<query_min(i, i + len, 1, mmx, 1)<<endl; 82 if(query_max(i, i + len, 1, mmx, 1) - query_min(i, i + len, 1, mmx, 1) >= d)return true; 83 } 84 return false; 85 } 86 87 int main() 88 { 89 scanf("%d%d", &n, &d); 90 mmx = -inf; 91 mmin = inf; 92 memset(tree_max, -inf, sizeof(tree_max)); 93 memset(tree_min, inf, sizeof(tree_min)); 94 memset(height, -1, sizeof(height)); 95 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){ 96 int x, y; 97 scanf("%d%d", &x, &y); 98 height[x] = y; 99 mmx = max(mmx, x); 100 mmin = min(mmin, x); 101 } 102 103 build(1, 1, mmx); 104 105 int ans = -1, st = mmin, ed = mmx; 106 while(st <= ed){ 107 int mid = (st + ed) / 2; 108 if(check(mid)){ 109 ed = mid - 1; 110 ans = mid; 111 } 112 else{ 113 st = mid + 1; 114 } 115 } 116 117 printf("%d ", ans); 118 return 0; 119 }
好吧既然是单调队列专题,就去学习一下单调队列吧。
其实刚开始想到了如果加入了一个雨滴之后,他和队头的高度差小于前面的,并且距离差也变大了的话,那这个雨滴肯定是没用的。之后就不会了。
应该要想到的是,当我们加入了一个雨滴之后,这一段的最大值只有可能增大或不变,最小值只有可能减小或者不变。他们都是单调的。
可以用一个单调队列来维护最大最小值,队头元素是最小值,队尾元素是最大值。
先按照横坐标对雨滴排个序,然后一个个加入,当队头和队尾纵坐标之差大于等于d的时候就把队头丢掉。因为之后加入队列的那个元素和队头虽然也会满足大于等于d但是宽度就不是最小的了。
但是这样只是找到了从左到右的一个单调序列,还应该再考虑一下从右到左。其实就相当于纪要考虑从左到右递增的,也要考虑从左到右递减的。
虽然这道题数据有问题,只考虑从左到右也能AC
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <set> 3 #include <cmath> 4 #include <stdio.h> 5 #include <cstring> 6 #include <algorithm> 7 #include <vector> 8 #include <queue> 9 #include <map> 10 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 11 using namespace std; 12 typedef long long LL; 13 #define inf 0x7f7f7f7f 14 15 const int maxn = 1e5 + 5; 16 const int maxd = 1e6 + 5; 17 int n, d, mmx, mmin; 18 int height[maxd]; 19 20 struct node{ 21 int x, y; 22 }drop[maxn], que1[maxn], que2[maxn]; 23 24 bool cmp(node a, node b) 25 { 26 return a.x < b.x; 27 } 28 29 int main() 30 { 31 scanf("%d%d", &n, &d); 32 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){ 33 scanf("%d%d", &drop[i].x, &drop[i].y); 34 } 35 sort(drop, drop + n, cmp); 36 37 int tail = 0, head = 1, ans = inf; 38 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){ 39 while(que1[tail].y >= drop[i].y && head <= tail)tail--; 40 que1[++tail] = drop[i]; 41 //cout<<"head"<<que[head].x<<" tail"<<que[tail].x<<endl; 42 while(que1[tail].y - que1[head].y >= d){ 43 ans = min(ans, que1[tail].x - que1[head].x); 44 head++; 45 } 46 } 47 //cout<<ans<<endl; 48 tail = 0; 49 head = 1; 50 for(int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--){ 51 while(que2[tail].y >= drop[i].y && head <= tail)tail--; 52 que2[++tail] = drop[i]; 53 while(que2[tail].y - que2[head].y >= d){ 54 ans = min(ans, que2[head].x - que2[tail].x); 55 head++; 56 } 57 } 58 59 if(ans == inf){ 60 printf("-1 "); 61 } 62 else{ 63 printf("%d ", ans); 64 } 65 return 0; 66 }
