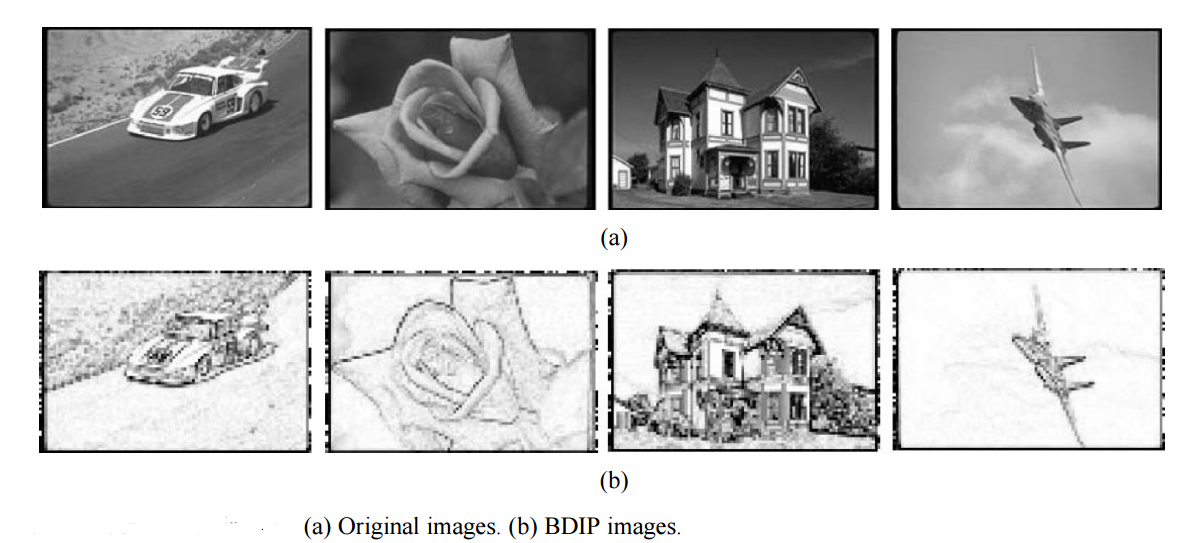
Young Deok Chun 等人提出了基于 BVLC 矩和 BDIP 矩的一种纹理分析方法。BVLC 能显示粗糙和光滑特性,BDIP 能够很好的提取波谷和边缘。它们直接在彩色空间上进行处理,能有效的结合颜色特征。
BDIP&BVLC
BDIP(block difference of inverse probabilities),基于块的逆转概率。描述了在一个M*M大小的块内,像素值变化的快慢,计算的BDIP值越大,原图像像素值变化越剧烈。
BVLC(block-based of variation of local correlation coefficients),基于块的局部相关系数。描述了一个像素点与周围四个方向(-90, 0, -45, 45)的相关度,计算的BVLC值越大,原图像越粗糙。
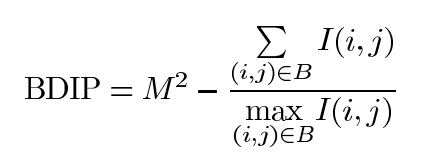
I(i, j)表示属于M*M块中某一个像素值 。

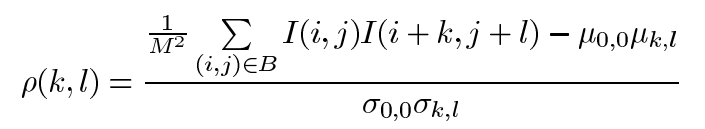
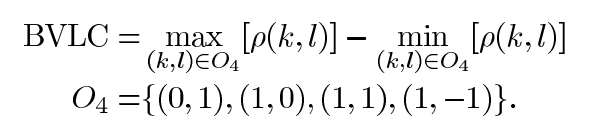
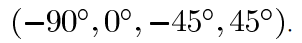 四个方向位移。
四个方向位移。
像素平移示意图:
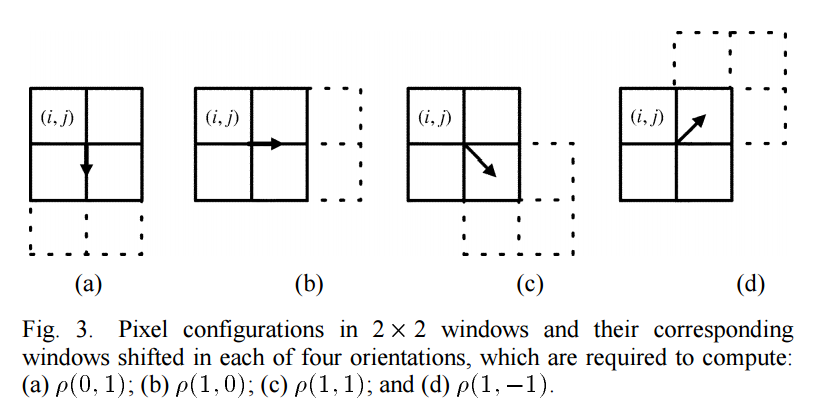
k,l分别表示水平和垂直移动 ,I(i, j)表示属于M*M块中某一个像素值,O(4)表示四个平移方向
σ(k,l)表示在平移后M*M像素块里的标准差 ,σ(0,0)表示当前M*M块的标准差
μ(k,l)表示在平移后M*M像素块里的均值 ,μ(0,0)表示当前M*M块的均值

BDIP code:

void bdip(const Mat& src) { Mat bdip; bdip = src.clone(); int nRows; int nCols; nRows = src.rows; nCols = src.cols; //计算bdip特征图 for(int r = 0; r < nRows; ++r) { for(int c = 0; c < nCols; ++c) { float blockValue = 0.0; int blockSum = 0; int blockMax = 0; //边缘不做考虑 if(0 == r || nRows - 1 == r || 0 == c || nCols - 1 == c) { blockValue = 0; } else { uchar v1, v2, v3, v4; v1 = src.ptr<uchar>(r)[c]; v2 = src.ptr<uchar>(r)[c + 1]; v3 = src.ptr<uchar>(r + 1)[c]; v4 = src.ptr<uchar>(r + 1)[c + 1]; blockSum = v1 + v2 + v3 + v4; blockMax = MAX(MAX(v1, v2), MAX(v3, v4)); blockValue = 4 - blockSum*1.0/blockMax; } bdip.ptr<uchar>(r)[c] = 64*blockValue; } } #if 1 imshow("bdip", bdip); cvWaitKey(0); #endif return; }
BVLC code:

struct SHIFTDIRECTION { int x; int y; }; const SHIFTDIRECTION shift[5] = {0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1}; void bvlc(const Mat& src) { int nRows; int nCols; nRows = src.rows; nCols = src.cols; //填充边界 Mat tmp; copyMakeBorder(src, tmp, 2, 2, 2, 2,BORDER_REFLECT); tmp.convertTo(tmp, CV_32FC1, 1.0, 0); Mat bvlc; bvlc = src.clone(); //计算blvc特征图 for(int r = 2; r < nRows + 2; ++r) { for(int c = 2; c < nCols + 2; ++c) { float variance[5] = {0.0}; float mean[5] = {0.0}; float value[4] = {0,0}; for(int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) { int curR = r + shift[i].x; int curC = c + shift[i].y; //计算平移后四个像素均值、方差 if(i < 4) { mean[i] = tmp.ptr<float>(curR)[curC] + tmp.ptr<float>(curR + 1)[curC] + tmp.ptr<float>(curR)[curC + 1] + tmp.ptr<float>(curR + 1)[curC + 1]; mean[i] /= 4; variance[i] = pow((tmp.ptr<float>(curR)[curC] - mean[i]), 2) + pow((tmp.ptr<float>(curR + 1)[curC] - mean[i]), 2) + pow((tmp.ptr<float>(curR)[curC + 1] - mean[i]), 2) + pow((tmp.ptr<float>(curR + 1)[curC + 1] - mean[i]), 2); } //最后一个块的位置方向与前三块有区别 else { mean[i] = tmp.ptr<float>(curR)[curC] + tmp.ptr<float>(curR - 1)[curC] + tmp.ptr<float>(curR)[curC + 1] + tmp.ptr<float>(curR - 1)[curC + 1]; mean[i] /= 4; variance[i] = pow((tmp.ptr<float>(curR)[curC] - mean[i]), 2) + pow((tmp.ptr<float>(curR - 1)[curC] - mean[i]), 2) + pow((tmp.ptr<float>(curR)[curC + 1] - mean[i]), 2) + pow((tmp.ptr<float>(curR - 1)[curC + 1] - mean[i]), 2); } variance[i] /= 4; variance[i] = sqrt(variance[i]); } //计算四个方向块与原块的相关系数value[i] for(int i = 1; i < 5; ++i) { value[i - 1] = tmp.ptr<float>(r)[c]*tmp.ptr<float>(r + shift[i].x)[c +shift[i].y] - mean[0]*mean[i] + tmp.ptr<float>(r + 1)[c]*tmp.ptr<float>(r + shift[i].x)[c +shift[i].y] - mean[0]*mean[i] + tmp.ptr<float>(r)[c + 1]*tmp.ptr<float>(r + shift[i].x)[c +shift[i].y] - mean[0]*mean[i] + tmp.ptr<float>(r + 1)[c + 1]*tmp.ptr<float>(r + shift[i].x)[c +shift[i].y] - mean[0]*mean[i]; value[i - 1] /= 4; value[i - 1] /= (variance[0]*variance[i]); } //获取最大和最小相关系数 float max = value[0]; float min = value[0]; for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) { if(value[i] > max) { max = value[i]; } if(value[i] < min) { min = value[i]; } } //计算BLVC数值 bvlc.ptr<uchar>(r - 2)[c - 2] = max - min; } } #if 1 imshow("bvlc", bvlc); waitKey(0); #endif return; }
【转载自】
BDIP-BVLC纹理 - xxxxyxxxx的博客 - CSDN博客 https://blog.csdn.net/xxxxyxxxx/article/details/76358491
Image retrieval using bdip and bvlc moments_百度学术 http://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=6fe4e1826e57f7007558cb9414214fd3&site=xueshu_se
