1.字节流
1.1字节流顾名思义就是操作字节的流。字节流是可以操作任意数据的,比如说媒体数据,音乐,电影,图片等,当然它也是可以操作字符的。字符流就是基于字节流来实现的,我们知道一个字节是8个二进制位,在UTF-8中一个字节对应一个英文字符,人们发现用单个字节操作文本比较麻烦,所以就对字节流进行封装,当对文本进行操作的时候就不直接对字节流进行操作,而直接对封装后的字节流也就是字符流进行操作,这样就比较方便。
1.2通过上述概述我们可以知道,使用字节流操作字符是完全行得通的。那么字符流是专门针对字符进行操作的,但是字符流能不能对除了字符以外的数据进行操作呢?
1.3如果你对除字符外的数据,比如说多媒体数据(音乐,电影,图片)进行操作,比如说复制一个音乐文件,程序编译时不会报错的,但是操作过程中可能会出现数据丢失的情况,当你复制结束打开该文件的时候,可能会因为数据的丢失而无法打开。所以强烈建议对字符文本的操作使用字符流,对字符以外的数据,使用字节流。
1.4字节流的基类:InputStream和OutputStream
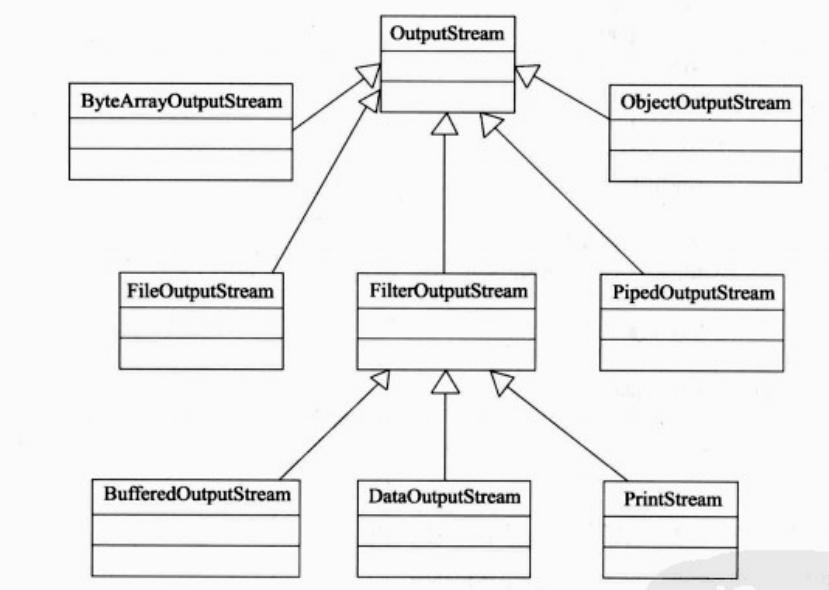
2.字节流类图
2.1 InputStream类实现结构

2.2 OutputStream 结构图
3.常用类的具体使用
3.1字节数组作为输入输出源(ByteArrayInputStream和ByteArrayOutputStream)
package se.io; import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream; import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class ByteArrayStream { public static void main(String[] args) { try { byte[] data = new byte[3]; data[0] = 100; data[1] = 101; data[2] = 102; ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(data); byte[] buf = new byte[3]; byteArrayInputStream.read(buf); System.out.println(new String(buf)); ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); byteArrayOutputStream.write(buf); System.out.println(byteArrayOutputStream.toString()); byteArrayOutputStream.close(); byteArrayInputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
3.2文件作为输入输出源(FileInputStream 和FileOutputStream )
package se.io; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class FileStream { public static void main(String[] args) { try { FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("E:\test\file.txt"); byte[] buf = new byte[3]; fileInputStream.read(buf); FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("E:\test\file3.txt"); fileOutputStream.write(buf); fileOutputStream.close(); fileInputStream.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
3.3 对象作为输入输出源(ObjectInputStream 和ObjectOutputStream )
package se.io; import java.io.*; import java.util.Date; public class ObjectStream { public static void main(String[] args) { try { FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("E:\test\file.tmp"); ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOutputStream); objectOutputStream.writeInt(100); objectOutputStream.writeObject("hello,world"); objectOutputStream.writeObject(new Date()); FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("E:\test\file.tmp"); ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(fileInputStream); System.out.println(objectInputStream.readInt()); System.out.println((String)objectInputStream.readObject()); System.out.println((Date)objectInputStream.readObject()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
3.4管道作为输入输出源(PipedInputStream和PipedOutputStream)
package se.io; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PipedInputStream; import java.io.PipedOutputStream; public class PipedStream { public static void main(String[] args) { Sender sender = new Sender(); PipedOutputStream pipedOutputStream = sender.getPipedOutputStream(); Reciever reciever = new Reciever(); PipedInputStream pipedInputStream = reciever.getPipedInputStream(); try { pipedOutputStream.connect(pipedInputStream); new Thread(sender).start(); new Thread(reciever).start(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } //创建发送者类 class Sender extends Thread{ private PipedOutputStream pipedOutputStream = new PipedOutputStream(); public PipedOutputStream getPipedOutputStream(){ return pipedOutputStream; } public void run(){ try { String s = new String("hello,receive you "); pipedOutputStream.write(s.getBytes()); pipedOutputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } //创建接受者类 class Reciever extends Thread{ private PipedInputStream pipedInputStream = new PipedInputStream(); byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; public PipedInputStream getPipedInputStream() { return pipedInputStream; } public void run(){ String s = null; byte[] rec = new byte[1024]; try { int len = pipedInputStream.read(rec); s = new String(rec,0,len); System.out.println(s); pipedInputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
3.5 缓存输入流输出流(BufferedInputStream 和BufferedOutputStream )
package se.io; import java.io.*; public class BufferStream { public static void main(String[] args) { FileInputStream fileInputStream = null; try { fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("E:\test\file.txt"); BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(fileInputStream); byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; int i = bufferedInputStream.read(bytes); FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("E:\test\buffer.txt"); BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(fileOutputStream); bufferedOutputStream.write(bytes,0,i); bufferedOutputStream.close(); bufferedInputStream.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
3.6 数据输入输出流(DataOutputStream 和DataInputStream )
package se.io; import java.io.*; public class DataStream { public static void main(String[] args) { try { FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("E:\test\data.txt"); DataOutputStream dataOutputStream = new DataOutputStream(fileOutputStream); dataOutputStream.writeInt(123); dataOutputStream.writeBoolean(true); dataOutputStream.writeDouble(12.555); FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("E:\test\data.txt"); DataInputStream dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(fileInputStream); int i = dataInputStream.readInt(); boolean f = dataInputStream.readBoolean(); double d = dataInputStream.readDouble(); System.out.println(i); System.out.println(f); System.out.println(d); dataInputStream.close(); fileInputStream.close(); dataOutputStream.close(); fileOutputStream.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }