Given a linked list and a value x, partition it such that all nodes less than x come before nodes greater than or equal to x.
You should preserve the original relative order of the nodes in each of the two partitions.
For example,
Given 1->4->3->2->5->2 and x = 3,
return 1->2->2->4->3->5.
C++实现代码:
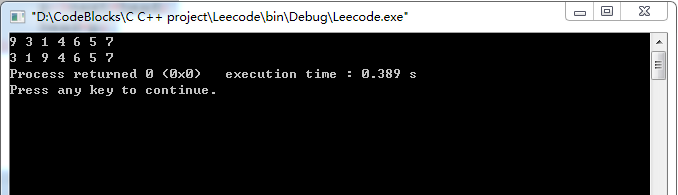
#include<iostream> #include<new> using namespace std; //Definition for singly-linked list. struct ListNode { int val; ListNode *next; ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} }; class Solution { public: ListNode *partition(ListNode *head, int x) { if(head==NULL||head->next==NULL) return head; ListNode *pre=head; ListNode *p=head; ListNode *l1=NULL; ListNode *q=NULL; ListNode *k=NULL; while(p) { if(p->val<x) { pre=p; p=p->next; } else { q=p; if(p==head) { pre=p->next; head=p->next; } p=p->next; if(pre!=p) pre->next=p; q->next=NULL; if(l1==NULL) { l1=q; k=q; } else { k->next=q; k=q; } } } //判断head以防要返回的链表为空 if(head) pre->next=l1; else head=l1; return head; } void createList(ListNode *&head) { ListNode *p=NULL; int i=0; int arr[10]= {7,5,6,4,1,3,9,8,2,10}; for(i=0; i<7; i++) { if(head==NULL) { head=new ListNode(arr[i]); if(head==NULL) return; } else { p=new ListNode(arr[i]); p->next=head; head=p; } } } }; int main() { Solution s; ListNode *L=NULL; s.createList(L); ListNode *head=L; while(head) { cout<<head->val<<" "; head=head->next; } cout<<endl; L=s.partition(L,4); while(L) { cout<<L->val<<" "; L=L->next; } }
运行结果: