十六:自定义拦截器
参考文档
16.1 编写拦截器类
extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter 并重写WebMvcConfigurerAdapter,如下:

1 package com.wu.interceptor; 2 3 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; 4 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; 5 6 import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; 7 import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor; 8 import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView; 9 import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry; 10 import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurerAdapter; 11 12 @Configuration//声明这是一个配置 13 public class MyInterceptor extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter { 14 15 @Override 16 public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) { 17 //以内部类的创建拦截器 18 HandlerInterceptor interceptor=new HandlerInterceptor() { 19 20 @Override 21 public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest arg0, HttpServletResponse arg1, Object arg2) throws Exception { 22 System.out.println("自定义拦截器"); 23 //返回true时放行 24 return true; 25 } 26 27 @Override 28 public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest arg0, HttpServletResponse arg1, Object arg2, ModelAndView arg3) 29 throws Exception { 30 } 31 32 @Override 33 public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest arg0, HttpServletResponse arg1, Object arg2, Exception arg3) 34 throws Exception { 35 } 36 }; 37 //注册拦截器并设置拦截路径 38 registry.addInterceptor(interceptor).addPathPatterns("/**"); 39 } 40 41 }
注意:需要在拦截器类上添加 @Configuration,声明这是一个配置类,还需要在启动类中需要扫描到该类,如以下所示:

1 package com.wu.app; 2 3 import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; 4 import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; 5 6 //@EnableAutoConfiguration 7 //@ComponentScan("com.wu.controller")//默认扫描的是当前包和当前包的子包 8 @SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages={"com.wu.controller","com.wu.interceptor"}) 9 public class SpringApplications { 10 //程序启动入口 11 public static void main(String []args){ 12 SpringApplication.run(SpringApplications.class, args); 13 } 14 }
16.2 测试定义的拦截器是否生效
编写Controller类简单测试刚刚定义的拦截器是否有效,如下:

1 package com.wu.controller; 2 3 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; 4 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; 5 6 @RestController 7 public class TestController { 8 @RequestMapping("/test") 9 public String test(){ 10 System.out.println("这是一个测试"); 11 return "test"; 12 } 13 }
在控制台中可以看到输出顺序:

十七:全局异常处理器的简单实现
参考文档
17.1 编写异常处理器类

1 package com.wu.controller; 2 3 import java.util.HashMap; 4 import java.util.Map; 5 6 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler; 7 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestControllerAdvice; 8 9 @RestControllerAdvice 10 public class GlobalExceptionHandler { 11 @ExceptionHandler(Exception.class) 12 public Map<String,Object> handleException(Exception e){ 13 Map<String,Object> map=new HashMap<>(); 14 map.put("errorCode","500"); 15 map.put("Msg",e.toString()); 16 return map; 17 } 18 }
17.2 编写测试类

1 package com.wu.controller; 2 3 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; 4 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; 5 6 @RestController 7 public class TestController { 8 @RequestMapping("/test") 9 public String test(){ 10 int a=1/0; 11 return "test"; 12 } 13 }
测试结果:
![]()
十八:SpringBoot中的异步调用
18.1 相关知识
参考文档:Java中的Future, Future接口
Future接口的作用:
- 代表异步计算的执行结果;
- 用于可取消的task;(比使用interrupt实现取消要方便 )
18.2在Service层中编写异步测试类

1 package com.wu.service; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.Future; 4 5 public interface AsyncService { 6 Future<String> doTask1()throws Exception; 7 Future<String> doTask2()throws Exception; 8 Future<String> doTask3()throws Exception; 9 }

1 package com.wu.service; 2 3 import java.util.Random; 4 import java.util.concurrent.Future; 5 6 import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async; 7 import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncResult; 8 import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; 9 @Service 10 public class AsyncServiceImp implements AsyncService { 11 @Async 12 @Override 13 public Future<String> doTask1() throws Exception { 14 System.out.println("任务一开始"); 15 long start=System.currentTimeMillis(); 16 Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(10000)); 17 long end =System.currentTimeMillis(); 18 System.out.println("任务一结束时间:"+(end-start)+"ms"); 19 return new AsyncResult<String>("任务一结束"); 20 } 21 @Async 22 @Override 23 public Future<String> doTask2() throws Exception { 24 System.out.println("任务二开始"); 25 long start=System.currentTimeMillis(); 26 Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(10000)); 27 long end =System.currentTimeMillis(); 28 System.out.println("任务二结束时间:"+(end-start)+"ms"); 29 return new AsyncResult<String>("任务二结束"); 30 } 31 @Async 32 @Override 33 public Future<String> doTask3() throws Exception { 34 System.out.println("任务三开始"); 35 long start=System.currentTimeMillis(); 36 Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(10000)); 37 long end =System.currentTimeMillis(); 38 System.out.println("任务三结束时间:"+(end-start)+"ms"); 39 return new AsyncResult<String>("任务三结束"); 40 } 41 42 }

1 package com.wu.controller; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.Future; 4 5 import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; 6 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; 7 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; 8 9 import com.wu.service.AsyncService; 10 import com.wu.service.AsyncServiceImp; 11 12 @RestController 13 public class TestController { 14 @Autowired 15 private AsyncService asyncService =new AsyncServiceImp(); 16 17 @RequestMapping("/async") 18 public String testAsync() throws Exception{ 19 long start=System.currentTimeMillis(); 20 Future<String> task1 = asyncService.doTask1(); 21 Future<String> task2 = asyncService.doTask2(); 22 Future<String> task3 = asyncService.doTask3(); 23 //判断三个任务是否结束 24 while(true){ 25 if(task1.isDone()&&task2.isDone()&&task3.isDone()){ 26 break; 27 } 28 //当前线程停一会再判断 29 Thread.sleep(1000); 30 } 31 long end =System.currentTimeMillis(); 32 return "总耗时:"+(end-start)+"ms"; 33 } 34 }

1 package com.wu.app; 2 3 import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; 4 import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; 5 import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync; 6 7 8 @SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages={"com.wu.controller","com.wu.service"}) 9 @EnableAsync//启用异步调用 10 public class SpringApplications { 11 //程序启动入口 12 public static void main(String []args){ 13 SpringApplication.run(SpringApplications.class, args); 14 } 15 }
18.3 显示结果
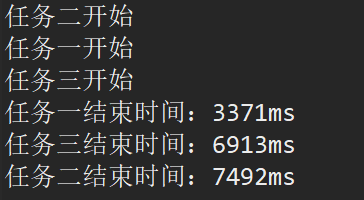
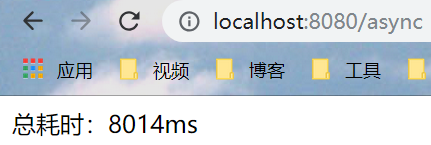
18.4 总结
在需要异步加载的方法上加上注解 @Async
在启动类中需要扫描相应的包,和启动异步调用 @EnableAsync
十九:SpringBoot整合Jsp
19.1 前言
SpringBoot官方不推荐使用Jsp,因为Jsp相对于一些模板引擎,性能较低,官方推荐使用Thymeleaf
19.2 创建war工程,并添加相应依赖
注意:SpringBoot整合Jsp需要创建的是war工程

1 <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> 2 <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> 3 <parent> 4 <groupId>com.wu</groupId> 5 <artifactId>SpringBoot_Parent</artifactId> 6 <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> 7 </parent> 8 <artifactId>SpringBoot_Child4</artifactId> 9 <packaging>war</packaging> 10 11 <dependencies> 12 <dependency> 13 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 14 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> 15 </dependency> 16 17 <!-- 添加servlet依赖模块 --> 18 <dependency> 19 <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> 20 <artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId> 21 <scope>provided</scope> 22 </dependency> 23 <!-- 添加jstl标签库依赖模块 --> 24 <dependency> 25 <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> 26 <artifactId>jstl</artifactId> 27 </dependency> 28 <!--添加tomcat依赖模块.--> 29 <dependency> 30 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 31 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId> 32 <scope>provided</scope> 33 </dependency> 34 <!-- 使用jsp引擎,springboot内置tomcat没有此依赖 --> 35 <dependency> 36 <groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId> 37 <artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasper</artifactId> 38 <scope>provided</scope> 39 </dependency> 40 41 </dependencies> 42 </project>

1 spring.mvc.view.prefix=/ 2 spring.mvc.view.suffix=.jsp

1 package com.wu.controller; 2 3 import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; 4 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; 5 6 @Controller 7 public class TestJspController { 8 @RequestMapping("/test") 9 public String test(){ 10 return "test"; 11 } 12 }

1 package com.wu.app; 2 3 import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; 4 import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; 5 import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync; 6 7 8 @SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages={"com.wu.controller"}) 9 public class SpringApplications { 10 //程序启动入口 11 public static void main(String []args){ 12 SpringApplication.run(SpringApplications.class, args); 13 } 14 }
test.jsp文件所在位置:
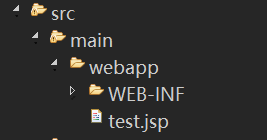
19.3 简单测试结果
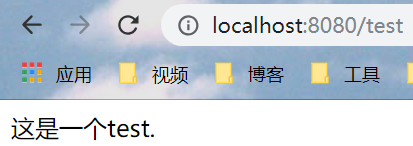
二十:SpringBoot整合Freemarker
20.0 参考文档1 Freemarker基本语法入门
20.1 在pom.xml中加入相关依赖

1 <!-- Freemarker --> 2 <dependency> 3 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 4 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-freemarker</artifactId> 5 </dependency>
20.2 简单应用
SpringBoot默认读取的是src/main/resources/templates
如:
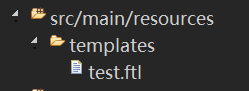

1 <html> 2 <head> 3 <title>Welcome!</title> 4 </head> 5 <body> 6 ${name} 7 </body> 8 </html>

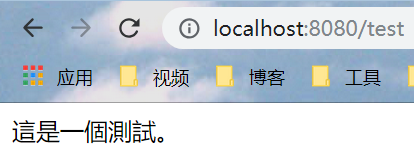
1 package com.wu.controller; 2 3 import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; 4 import org.springframework.ui.Model; 5 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; 6 7 @Controller 8 public class TestFreemarkerController { 9 @RequestMapping("/test") 10 public String test(Model model){ 11 model.addAttribute("name","這是一個測試。"); 12 return "test"; 13 } 14 }
记得在启动类中扫描相应的包,之后启动,结果如下:
20.3 SpringBoot与Freemarker相关的配置可以在application.properties配置

1 # 是否允许HttpServletRequest属性覆盖(隐藏)控制器生成的同名模型属性。 2 spring.freemarker.allow-request-override=false 3 # 是否允许HttpSession属性覆盖(隐藏)控制器生成的同名模型属性。 4 spring.freemarker.allow-session-override=false 5 # 是否启用模板缓存。 6 spring.freemarker.cache=false 7 # 模板编码。 8 spring.freemarker.charset=UTF-8 9 # 是否检查模板位置是否存在。 10 spring.freemarker.check-template-location=true 11 # Content-Type value. 12 spring.freemarker.content-type=text/html 13 # 是否启用freemarker 14 spring.freemarker.enabled=true 15 # 设定所有request的属性在merge到模板的时候,是否要都添加到model中. 16 spring.freemarker.expose-request-attributes=false 17 # 是否在merge模板的时候,将HttpSession属性都添加到model中 18 spring.freemarker.expose-session-attributes=false 19 # 设定是否以springMacroRequestContext的形式暴露RequestContext给Spring’s macro library使用 20 spring.freemarker.expose-spring-macro-helpers=true 21 # 是否优先从文件系统加载template,以支持热加载,默认为true 22 spring.freemarker.prefer-file-system-access=true 23 # 设定模板的后缀. 24 spring.freemarker.suffix=.ftl 25 # 设定模板的加载路径,多个以逗号分隔,默认: 26 spring.freemarker.template-loader-path=classpath:/templates/ 27 # 设定FreeMarker keys. 28 spring.freemarker.settings.template_update_delay=0 29 spring.freemarker.settings.default_encoding=UTF-8 30 spring.freemarker.settings.classic_compatible=true 31 32 SpringBoot整合Freemarker的相关属性配置
二十一:SpringBoot整合Thymeleaf
21.0 Thymeleaf的常用语法解析 参考文档2
21.1 在pom.xml中加入相关依赖

1 <!-- Thymeleaf --> 2 <dependency> 3 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 4 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId> 5 </dependency>
21.2 简单应用
默认读取的是src/main/resources/templates/
如:
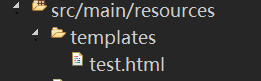

1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>Thymeleaf_Test</title> 6 </head> 7 <body> 8 <span th:text="${name}"></span> 9 </body> 10 </html>

1 package com.wu.controller; 2 3 import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; 4 import org.springframework.ui.Model; 5 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; 6 7 @Controller 8 public class TestThymeleafController { 9 @RequestMapping("/test") 10 public String test(Model model){ 11 model.addAttribute("name","这也是一个测试!"); 12 return "test"; 13 } 14 }

1 #关闭thymeleaf缓存,开发时使用,否者不能实时显示 2 spring.thymeleaf.cache=false 3 #检查模板是否纯在,然后再呈现 4 spring.thymeleaf.check-template-location=true 5 #content-type的值 6 spring.thymeleaf.content-type=text/html 7 #启用MVC Thymeleaf视图分辨率 8 spring.thymeleaf.enabled=true 9 #编码格式 10 spring.thymeleaf.encoding=UTF-8 11 #前缀,此为默认 12 spring.thymeleaf.prefix=classpath:/templates/ 13 #后缀,常用.html 14 spring.thymeleaf.suffix=.html 15 #模板编码,thymeleaf对html的标签约束非常严格,所有的标签必须有开有闭,比如<br></br>或者<br/>是可以的,但是<br>会报错,配置spring.thymeleaf.mode=LEGACYHTML5 目的就是为了解决这个问题,可以使页面松校验。 16 spring.thymeleaf.mode=LEGACYHTML5
在启动类中启动,查看

报错,原因:在全局配置中配置了spring.thymeleaf.mode=LEGACYHTML5,是非严格检查,需要加入nekohtml的依赖,如:

1 <!-- nekohtml --> 2 <dependency> 3 <groupId>net.sourceforge.nekohtml</groupId> 4 <artifactId>nekohtml</artifactId> 5 <version>1.9.15</version> 6 </dependency>
之后重新启动,查看结果如下:

二十二:SpringBoot实现定时任务调用
22.1 spring-boot-quartz 推荐参考
22.2 spring-boot-scheduler
编写任务类:

1 package com.wu.job; 2 3 import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled; 4 import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; 5 6 @Component 7 public class MyJob { 8 @Scheduled(fixedRate=2000)//每两秒执行一次 9 public void run(){ 10 System.out.println("执行作业"); 11 } 12 }
在启动类中开启任务调度

1 package com.wu.app; 2 3 import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; 4 import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; 5 import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync; 6 import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableScheduling; 7 8 9 @SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages={"com.wu.job"}) 10 @EnableScheduling//开启任务调度 11 public class SpringApplications { 12 //程序启动入口 13 public static void main(String []args){ 14 SpringApplication.run(SpringApplications.class, args); 15 } 16 }
结果:每隔2秒打印一次(v_v)

注意:在需要定时任务调度的方法上添加@Scheduled 注解;在启动类上加上 @EnableScheduling 并扫描方法所在类的包
