排序算法动态演示:http://www.atool.org/sort.php
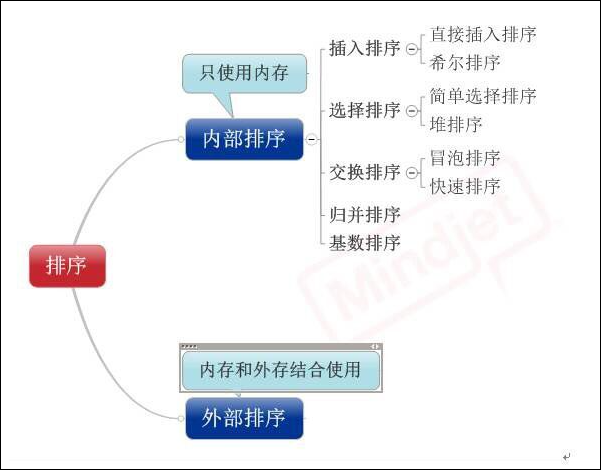
插冒快选n2,堆排归并nlog2n,基数排序d(n+r)
1.插入排序
■ 直接插入排序:
public class Insert { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] a = { 13, 22, 15, 7, 41, 24 }; insertSort(a); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); } private static void insertSort(int[] a) { for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) { int j = 0; int temp = a[i]; for (j = i - 1; j >= 0 && temp < a[j]; j--) { a[j + 1] = a[j]; } a[j + 1] = temp; } } }
■ 希尔排序:
public class Shell { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] a = { 2, 15, 6, 12, 32, 41 }; shellSort(a); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); } private static void shellSort(int[] a) { int temp; for (int i = a.length / 2; i > 0; i = i / 2) { for (int j = i; j < a.length; j++) { if (a[j - i] > a[j]) { temp = a[j - i]; a[j - i] = a[j]; a[j] = temp; } } } } }
2.选择排序
■ 简单选择排序:
public class SimpleSelect { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] a = {2, 15, 6, 12, 32, 41}; simpleSelectSort(a); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); } private static void simpleSelectSort(int[] arr){ int position=0;//剩余最小值所在的位置 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { position=i; int temp=arr[i]; for (int j=i+1; j < arr.length; j++) { if(arr[j]<temp){ temp=arr[j]; position=j; } } arr[position]=arr[i]; arr[i]=temp; } } }
■ 堆排序:
public class HeapSort { public static void main(String[] args) { int a[] = {49,36,65,79,13,27,78,34,12,64,5,4,62,99,98}; heapSort(a); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); } public static void heapSort(int[] a){ for (int i = 0; i < a.length-1; i++) { buildMaxHeap(a,a.length-1-i); swap(a,0,a.length-1-i); } } //两两交换位置 public static void swap(int[] a,int i,int j){ int temp = a[i]; a[i] = a[j]; a[j] = temp; } public static void buildMaxHeap(int[] a,int lastIndex){ for (int i = (lastIndex-1)/2; i >=0; i--) { int k=i; while(k*2+1<=lastIndex){ int biggerIndex=k*2+1; if(biggerIndex<lastIndex){ if(a[biggerIndex]<a[biggerIndex+1]) biggerIndex++; } if(a[k]<a[biggerIndex]){ swap(a,k,biggerIndex); k=biggerIndex; }else{ break; } } } } }
3.交换排序
■ 冒泡排序:
public class Bubble { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] a = { 62, 54, 68, 73, 99, 46, 83, 22, 70 }; bubbleSort(a); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); } private static void bubbleSort(int[] a) { int temp = 0; for (int i = 0; i < a.length - 1; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < a.length - i - 1; j++) { if (a[j] > a[j + 1]) { temp = a[j]; a[j] = a[j + 1]; a[j + 1] = temp; } } } } }
■ 快速排序:
public class QuickSort { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr ={2,1,3,4,7,9,8,6,5}; arr = quickSort(arr,0,arr.length-1); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); } public static void swap(int[] arr,int i,int j){ int temp; temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[j]; arr[j] = temp; } public static int[] quickSort(int[] arr,int low,int high){ if(low >= high) return arr; if(high-low == 1){ if(arr[0]>arr[1]) swap(arr,0,1); return arr; } int pivot = arr[low]; int left = low+1; int right = high; while(left<right){ while(left<right && left<=high){ if(arr[left]>pivot) break; left++; } while(left<=right && right>low){ if(arr[right]<=pivot) break; right--; } if(left<right) swap(arr,right,left); } swap(arr,low,right); quickSort(arr,low,right); quickSort(arr,right+1,high); return arr; } }