一、在eclipse下建立JMockit工程
1、下载最新版JMockit(jmockit-1.4.zip);
2、解压后的文件夹包含有:library jars, source files, samples, API javadocs, and additional documentation;
3、将jmockit.jar添加到项目classpath中;
特别的:
1)确保classpath中Jar包的顺序:jmockit的jar包必须在junit之前(通过Order and Export" 标签上下移动);
2)eclipse项目所用JRE来自于JDK,而不是“简洁”版的JRE,因为后者缺少本地类库“attach”。
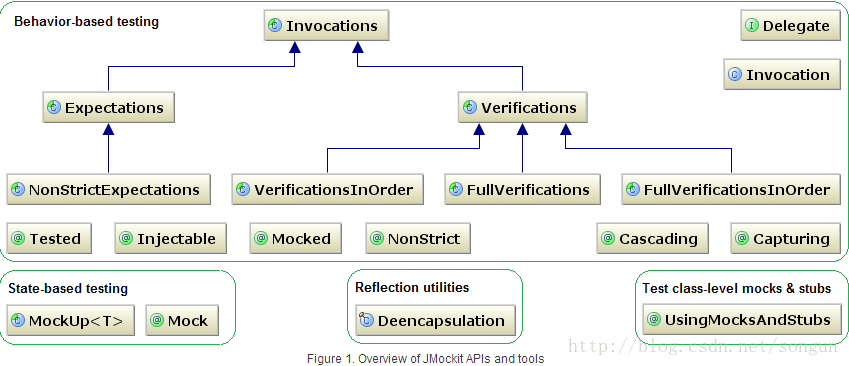
二、行为和状态的测试
基于行为(Behavior-based)的mock是站在目标测试代码外面的角度的,通常主要模拟行为,而基于状态
(State-based)的是站在目标测试代码内部的。我们可以对传入的参数进行检查、匹配,才返回某些结果。
Mockup用于State-based测试。
二、声明和使用mock类型
1、字段,期望块的字段与期望块内的局部属性字段使用@Mocked来声明Mock类型。
2、参数,方法的参数声明来引入一个Mock类型。
第一种情况,属性字段是属于测试类或者一个mockit.Expectations子类(一个expectation期望块的内部的局部
属性字段)。
第二种情况,参数必须是属于某个测试方法(@Test标签下的方法)。
在所有的情况,一个mock属性字段或者参数声明,都可以通过使用@Mocked声明。对于方法mock的参数或者
在expectations期望块中定义的mock属性字段来说,该注解是可选的,而对于定义在测试类(XXXTest类)中的
属性字段,@Mocked标签是必须,这是为了防止和该测试类的其它不需要mock的字段属性产生冲突。
package main; import static org.junit.Assert.*; import java.io.Serializable; import org.junit.Test; import mockit.Expectations; import mockit.Mocked; import mockit.NonStrictExpectations; import mockit.Verifications; /* * 一个用户接口(外部依赖) */ interface Dependency { String doSomething(boolean b); } // 声明变量类型MultiMock(它实现两个接口,作用域是整个测试类) public class MultiMocksTest<MultiMock extends Dependency & Runnable> { @Mocked MultiMock multiMock; @Test public void mockFieldWithTwoInterfaces() { new NonStrictExpectations() { { multiMock.doSomething(false); result = "test"; } }; multiMock.run(); assertEquals("test", multiMock.doSomething(false)); // 验证run()方法执行一次 new Verifications() { { multiMock.run(); } }; } @Test // 声明变量类型M,它实现两个接口,作用域为该测试方法 // final M mock 前的@Mocked注解是可选的 public <M extends Dependency & Serializable> void mockParameterWithTwoInterfaces( @Mocked final M mock) { new Expectations() { { mock.doSomething(true); result = ""; } }; assertEquals("", multiMock.doSomething(true)); } }
3、对于一个返回值不为void类型的方法,Expectations中如何模拟方法返回值:
1)其返回值可以通过Expectations的result属性域来记录
2)Expectations的returns(Object)方法来记录
例如,方法返回一个Throwable异常类,只需将一个类型实验赋给result(注意,异常类只能通过result方式
赋值)。
package main; import mockit.Expectations; import org.junit.Test; public class UnitUnderTest { // 1、构造方法 private OutWork work = new OutWork(); public void doSomthing() { // 2、intReturningMethod()方法 int n = work.intReturningMethod(); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { String s; try { // 3、stringReturningMethod()方法 s = work.stringReturningMethod(); } catch (Exception e) { // 处理异常 e.printStackTrace(); } } // 其它逻辑... } @Test public void test() { new Expectations() { OutWork work; { // 1、构造方法模拟 new OutWork(); // 2、intReturningMethod()方法模拟 work.intReturningMethod(); result = 3; // 3、stringReturningMethod()方法模拟 work.stringReturningMethod(); // 方法分别返回三个值,两个字符串,一个异常 returns("str1", "str2"); result = new Exception("testException"); } }; new UnitUnderTest().doSomthing(); } } class OutWork { public int intReturningMethod() { return 0; } public String stringReturningMethod() { return ""; } }
三、从严格到非严格
1、@Mocked+Expections块:会进行隐式校验(执行顺序和次数)
2、@Mocked+NonStrictExpections块:NonStrictExpections块中的Incovation可以非严格执行(不执行或者
执行N次,除非显示地指定执行次数)。
package main; /* * 用于Mock的接口 */ public interface WinportUrlService { public boolean hasWinport(String id); public String getMsg(); public Throwable getWinportUrlThrowException(String id); } package main; import static org.junit.Assert.*; import mockit.Expectations; import mockit.Mocked; import mockit.NonStrictExpectations; import org.junit.Test; public class IntroductionTest { // @Mocked注解+Expectations/NonStrictExpectations块 @Mocked private WinportUrlService winportUrlService = null; @Test public void testNoExceptions() { final String memberId = "test"; // 未指定期望块,方法返回默认值 assertEquals(false, winportUrlService.hasWinport(memberId)); assertEquals(null, winportUrlService.getMsg()); assertEquals(null, winportUrlService.getWinportUrlThrowException(memberId)); } @Test public void testWithExpectations() { final String memerId = "test"; // 步骤一:record // 严格期望块 new Expectations() { { // 下面的Invocation必须严格执行 winportUrlService.hasWinport(memerId); result = false;// 也可以是returns(false) // 未指定执行次数 } }; // 非严格期望块 new NonStrictExpectations() { { // 下面的Invocation非严格执行 winportUrlService.getMsg(); result = "test";// 也可以是returns("test") // 未指定执行次数 } }; // 步骤二:replay阶段 // hasWinport必须严格执行一次 assertEquals(false, winportUrlService.hasWinport(memerId)); // getMsg可以不执行或执行多次 assertEquals("test", winportUrlService.getMsg()); assertEquals("test", winportUrlService.getMsg()); // 下面的Invocation失败 // winportUrlService.getWinportUrlThrowException(memerId); } }
3、@NonStrict:可以在replay中调用或不调用。@NonStrict可以避免需要记录调用构造函数,或任何不感兴
趣的方法。
注意:@NonStrict它是针对类的属性非严格,类的属性适用于类中的所有测试方法。这个非严格的范围比
NonStrictExpections块的作用范围大很多,一旦使用了@NonStrict,Expections中的Incovation就变成了非严
格的invocation,因此其它测试方法还想在该属性的基础上使用Expections块是不可能的了。如果是这种情况
就需要这样使用(@Mocked+NonStrictExpectations块)。
package main; import static org.junit.Assert.*; import mockit.Expectations; import mockit.NonStrict; import org.junit.Test; public class IntroductionTest2 { // @NonStrict注解 @NonStrict private WinportUrlService winportUrlService = null; @Test public void testWithExpectations() { final String memberId = "test"; // 步骤一:record // 用了@NonStrict,Expectation中的invocation就变成了非严格的invocation new Expectations() { { // 下面的Invocation非严格执行 winportUrlService.hasWinport(memberId); result = false;// 也可以是returns(false) // 未指定执行次数 } }; // 步骤二:replay阶段 // hasWinport可以不执行或执行多次 assertEquals(false, winportUrlService.hasWinport(memberId)); assertEquals(false, winportUrlService.hasWinport(memberId)); // 下面的Invocation成功 winportUrlService.getWinportUrlThrowException(memberId); } }
4、此外,若不指定执行次数,Expections块默认必须执行一次,NonStrictExpections块中的Invocation可执行
N次或不执行;若显式地指定执行次数(N次),二者的Invocation都必须执行N次