一、简介
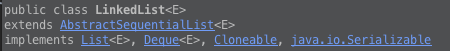
1、LinkedList继承关系
2、LinkedList底层实现
LinkedList使用双向链表存储数据,所以没有默认的容量,也不会有扩容一说。只有两个指针,永远指向链表的两端:first和last。定义了一个size属性,用于记录当前存储的元素个数。内部自定义了Node类,如下:

3、LinkedList中meta方法
所有对外暴露的方法其实都是对少数几个方法的包装,比如linkFirst(E e)、linkLast(E e)、node(int index)等,重点研究着几个方法即可快速了解LinkedList;
二、主要方法
1、void linkFirst(E e)
addFirst(E e)方法使用了改方法,将e元素作为第一个元素

2、linkLast(E e)
addLast(E e)、add(E e)、add(int index, E e)等方法有使用

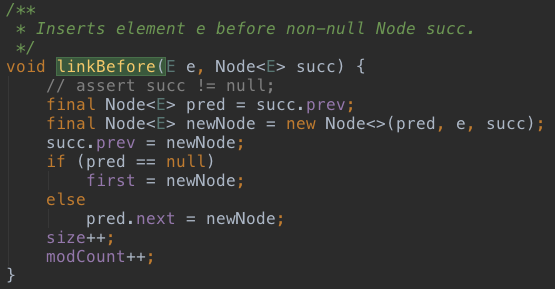
3、linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ)
add(int index, E e)方法有使用
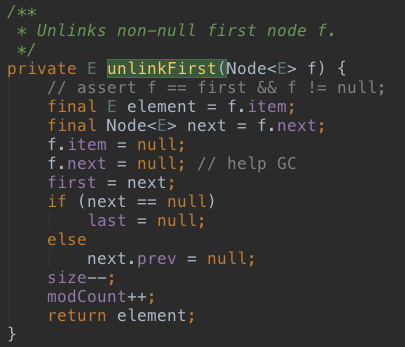
4、E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f)
removeFirst()、poll()、pollFirst()等方法有使用,作用就是移除元素f,一般这里传入的f都会是第一个元素,所以下面的代码中没有清理f的前一个元素。
5、E unlinkLast(Node<E> l)
removeLast()、pollLast()等方法有使用,和unlinkFirst()原理类似

6、E unlink(Node<E> x)
这个方法就是真正的移除元素x, 这里假设x前后都有元素的,稍微复杂些

7、Node<E> node(int index)
根据index,获取到index位置对应的Node<E>元素。这里采取了二分策略,判断index所在的区域,缩小范围,提高查找效率

有2个点值得注意:
1、遍历时,i要么大于index,要么小于index,都不等于index,这是因为x=x.next或者x=x.prev这句导致的;
2、倒序遍历时,从size位置往前遍历;
8、关于set(int index, E e)
LinkedList的set(int index, E e)方法实现比较特殊,首先根据index获取到listIterator,取到listIterator的当前位置的元素,然后替换掉其中E。有点想不明白为什么要采取这种方式,使用node(int index)方法取到元素,直接替换不是更好?
猜测的原因:
LinkedList并非直接继承自AbstractList,而是继承自AbstractSequentList,set(int index, E e)方法是在AbstractSequentList中实现的,这个方法中并没有之前提到的node(int index)方法,但是有listIterator()方法,所以要么不要在父类中实现set(),要么得使用父类中存在的方法来实现,尽管listIterator()方法是抽象的。
9、结尾
以上这些方法都是私有的,但是其他很多public的方法都是基于这几个方法实现的。另外LinkedList提供了类似队列/双头队列操作的几个方法,同时实现了ListItr,提供向前向后遍历,但是没有提供subList方法。
源码如下:

1 package java.util; 2 3 import java.util.function.Consumer; 4 5 /** 6 * Doubly-linked list implementation of the {@code List} and {@code Deque} 7 * interfaces. Implements all optional list operations, and permits all 8 * elements (including {@code null}). 9 * 10 * <p>All of the operations perform as could be expected for a doubly-linked 11 * list. Operations that index into the list will traverse the list from 12 * the beginning or the end, whichever is closer to the specified index. 13 * 14 * <p><strong>Note that this implementation is not synchronized.</strong> 15 * If multiple threads access a linked list concurrently, and at least 16 * one of the threads modifies the list structurally, it <i>must</i> be 17 * synchronized externally. (A structural modification is any operation 18 * that adds or deletes one or more elements; merely setting the value of 19 * an element is not a structural modification.) This is typically 20 * accomplished by synchronizing on some object that naturally 21 * encapsulates the list. 22 * 23 * If no such object exists, the list should be "wrapped" using the 24 * {@link Collections#synchronizedList Collections.synchronizedList} 25 * method. This is best done at creation time, to prevent accidental 26 * unsynchronized access to the list:<pre> 27 * List list = Collections.synchronizedList(new LinkedList(...));</pre> 28 * 29 * <p>The iterators returned by this class's {@code iterator} and 30 * {@code listIterator} methods are <i>fail-fast</i>: if the list is 31 * structurally modified at any time after the iterator is created, in 32 * any way except through the Iterator's own {@code remove} or 33 * {@code add} methods, the iterator will throw a {@link 34 * ConcurrentModificationException}. Thus, in the face of concurrent 35 * modification, the iterator fails quickly and cleanly, rather than 36 * risking arbitrary, non-deterministic behavior at an undetermined 37 * time in the future. 38 * 39 * <p>Note that the fail-fast behavior of an iterator cannot be guaranteed 40 * as it is, generally speaking, impossible to make any hard guarantees in the 41 * presence of unsynchronized concurrent modification. Fail-fast iterators 42 * throw {@code ConcurrentModificationException} on a best-effort basis. 43 * Therefore, it would be wrong to write a program that depended on this 44 * exception for its correctness: <i>the fail-fast behavior of iterators 45 * should be used only to detect bugs.</i> 46 * 47 * <p>This class is a member of the 48 * <a href="{@docRoot}/../technotes/guides/collections/index.html"> 49 * Java Collections Framework</a>. 50 * 51 * @author Josh Bloch 52 * @see List 53 * @see ArrayList 54 * @since 1.2 55 * @param <E> the type of elements held in this collection 56 */ 57 58 public class LinkedList<E> 59 extends AbstractSequentialList<E> 60 implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable 61 { 62 transient int size = 0; 63 64 /** 65 * Pointer to first node. 66 * Invariant: (first == null && last == null) || 67 * (first.prev == null && first.item != null) 68 */ 69 transient Node<E> first; 70 71 /** 72 * Pointer to last node. 73 * Invariant: (first == null && last == null) || 74 * (last.next == null && last.item != null) 75 */ 76 transient Node<E> last; 77 78 /** 79 * Constructs an empty list. 80 */ 81 public LinkedList() { 82 } 83 84 /** 85 * Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified 86 * collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's 87 * iterator. 88 * 89 * @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list 90 * @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null 91 */ 92 public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) { 93 this(); 94 addAll(c); 95 } 96 97 /** 98 * Links e as first element. 99 */ 100 private void linkFirst(E e) { 101 final Node<E> f = first; 102 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f); 103 first = newNode; 104 if (f == null) 105 last = newNode; 106 else 107 f.prev = newNode; 108 size++; 109 modCount++; 110 } 111 112 /** 113 * Links e as last element. 114 */ 115 void linkLast(E e) { 116 final Node<E> l = last; 117 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); 118 last = newNode; 119 if (l == null) 120 first = newNode; 121 else 122 l.next = newNode; 123 size++; 124 modCount++; 125 } 126 127 /** 128 * Inserts element e before non-null Node succ. 129 */ 130 void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) { 131 // assert succ != null; 132 final Node<E> pred = succ.prev; 133 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ); 134 succ.prev = newNode; 135 if (pred == null) 136 first = newNode; 137 else 138 pred.next = newNode; 139 size++; 140 modCount++; 141 } 142 143 /** 144 * Unlinks non-null first node f. 145 */ 146 private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) { 147 // assert f == first && f != null; 148 final E element = f.item; 149 final Node<E> next = f.next; 150 f.item = null; 151 f.next = null; // help GC 152 first = next; 153 if (next == null) 154 last = null; 155 else 156 next.prev = null; 157 size--; 158 modCount++; 159 return element; 160 } 161 162 /** 163 * Unlinks non-null last node l. 164 */ 165 private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l) { 166 // assert l == last && l != null; 167 final E element = l.item; 168 final Node<E> prev = l.prev; 169 l.item = null; 170 l.prev = null; // help GC 171 last = prev; 172 if (prev == null) 173 first = null; 174 else 175 prev.next = null; 176 size--; 177 modCount++; 178 return element; 179 } 180 181 /** 182 * Unlinks non-null node x. 183 */ 184 E unlink(Node<E> x) { 185 // assert x != null; 186 final E element = x.item; 187 final Node<E> next = x.next; 188 final Node<E> prev = x.prev; 189 190 if (prev == null) { 191 first = next; 192 } else { 193 prev.next = next; 194 x.prev = null; 195 } 196 197 if (next == null) { 198 last = prev; 199 } else { 200 next.prev = prev; 201 x.next = null; 202 } 203 204 x.item = null; 205 size--; 206 modCount++; 207 return element; 208 } 209 210 /** 211 * Returns the first element in this list. 212 * 213 * @return the first element in this list 214 * @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty 215 */ 216 public E getFirst() { 217 final Node<E> f = first; 218 if (f == null) 219 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 220 return f.item; 221 } 222 223 /** 224 * Returns the last element in this list. 225 * 226 * @return the last element in this list 227 * @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty 228 */ 229 public E getLast() { 230 final Node<E> l = last; 231 if (l == null) 232 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 233 return l.item; 234 } 235 236 /** 237 * Removes and returns the first element from this list. 238 * 239 * @return the first element from this list 240 * @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty 241 */ 242 public E removeFirst() { 243 final Node<E> f = first; 244 if (f == null) 245 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 246 return unlinkFirst(f); 247 } 248 249 /** 250 * Removes and returns the last element from this list. 251 * 252 * @return the last element from this list 253 * @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty 254 */ 255 public E removeLast() { 256 final Node<E> l = last; 257 if (l == null) 258 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 259 return unlinkLast(l); 260 } 261 262 /** 263 * Inserts the specified element at the beginning of this list. 264 * 265 * @param e the element to add 266 */ 267 public void addFirst(E e) { 268 linkFirst(e); 269 } 270 271 /** 272 * Appends the specified element to the end of this list. 273 * 274 * <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #add}. 275 * 276 * @param e the element to add 277 */ 278 public void addLast(E e) { 279 linkLast(e); 280 } 281 282 /** 283 * Returns {@code true} if this list contains the specified element. 284 * More formally, returns {@code true} if and only if this list contains 285 * at least one element {@code e} such that 286 * <tt>(o==null ? e==null : o.equals(e))</tt>. 287 * 288 * @param o element whose presence in this list is to be tested 289 * @return {@code true} if this list contains the specified element 290 */ 291 public boolean contains(Object o) { 292 return indexOf(o) != -1; 293 } 294 295 /** 296 * Returns the number of elements in this list. 297 * 298 * @return the number of elements in this list 299 */ 300 public int size() { 301 return size; 302 } 303 304 /** 305 * Appends the specified element to the end of this list. 306 * 307 * <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}. 308 * 309 * @param e element to be appended to this list 310 * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add}) 311 */ 312 public boolean add(E e) { 313 linkLast(e); 314 return true; 315 } 316 317 /** 318 * Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list, 319 * if it is present. If this list does not contain the element, it is 320 * unchanged. More formally, removes the element with the lowest index 321 * {@code i} such that 322 * <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt> 323 * (if such an element exists). Returns {@code true} if this list 324 * contained the specified element (or equivalently, if this list 325 * changed as a result of the call). 326 * 327 * @param o element to be removed from this list, if present 328 * @return {@code true} if this list contained the specified element 329 */ 330 public boolean remove(Object o) { 331 if (o == null) { 332 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { 333 if (x.item == null) { 334 unlink(x); 335 return true; 336 } 337 } 338 } else { 339 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { 340 if (o.equals(x.item)) { 341 unlink(x); 342 return true; 343 } 344 } 345 } 346 return false; 347 } 348 349 /** 350 * Appends all of the elements in the specified collection to the end of 351 * this list, in the order that they are returned by the specified 352 * collection's iterator. The behavior of this operation is undefined if 353 * the specified collection is modified while the operation is in 354 * progress. (Note that this will occur if the specified collection is 355 * this list, and it's nonempty.) 356 * 357 * @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list 358 * @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call 359 * @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null 360 */ 361 public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { 362 return addAll(size, c); 363 } 364 365 /** 366 * Inserts all of the elements in the specified collection into this 367 * list, starting at the specified position. Shifts the element 368 * currently at that position (if any) and any subsequent elements to 369 * the right (increases their indices). The new elements will appear 370 * in the list in the order that they are returned by the 371 * specified collection's iterator. 372 * 373 * @param index index at which to insert the first element 374 * from the specified collection 375 * @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list 376 * @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call 377 * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} 378 * @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null 379 */ 380 public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { 381 checkPositionIndex(index); 382 383 Object[] a = c.toArray(); 384 int numNew = a.length; 385 if (numNew == 0) 386 return false; 387 388 Node<E> pred, succ; 389 if (index == size) { 390 succ = null; 391 pred = last; 392 } else { 393 succ = node(index); 394 pred = succ.prev; 395 } 396 397 for (Object o : a) { 398 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o; 399 Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null); 400 if (pred == null) 401 first = newNode; 402 else 403 pred.next = newNode; 404 pred = newNode; 405 } 406 407 if (succ == null) { 408 last = pred; 409 } else { 410 pred.next = succ; 411 succ.prev = pred; 412 } 413 414 size += numNew; 415 modCount++; 416 return true; 417 } 418 419 /** 420 * Removes all of the elements from this list. 421 * The list will be empty after this call returns. 422 */ 423 public void clear() { 424 // Clearing all of the links between nodes is "unnecessary", but: 425 // - helps a generational GC if the discarded nodes inhabit 426 // more than one generation 427 // - is sure to free memory even if there is a reachable Iterator 428 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; ) { 429 Node<E> next = x.next; 430 x.item = null; 431 x.next = null; 432 x.prev = null; 433 x = next; 434 } 435 first = last = null; 436 size = 0; 437 modCount++; 438 } 439 440 441 // Positional Access Operations 442 443 /** 444 * Returns the element at the specified position in this list. 445 * 446 * @param index index of the element to return 447 * @return the element at the specified position in this list 448 * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} 449 */ 450 public E get(int index) { 451 checkElementIndex(index); 452 return node(index).item; 453 } 454 455 /** 456 * Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with the 457 * specified element. 458 * 459 * @param index index of the element to replace 460 * @param element element to be stored at the specified position 461 * @return the element previously at the specified position 462 * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} 463 */ 464 public E set(int index, E element) { 465 checkElementIndex(index); 466 Node<E> x = node(index); 467 E oldVal = x.item; 468 x.item = element; 469 return oldVal; 470 } 471 472 /** 473 * Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list. 474 * Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and any 475 * subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices). 476 * 477 * @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted 478 * @param element element to be inserted 479 * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} 480 */ 481 public void add(int index, E element) { 482 checkPositionIndex(index); 483 484 if (index == size) 485 linkLast(element); 486 else 487 linkBefore(element, node(index)); 488 } 489 490 /** 491 * Removes the element at the specified position in this list. Shifts any 492 * subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their indices). 493 * Returns the element that was removed from the list. 494 * 495 * @param index the index of the element to be removed 496 * @return the element previously at the specified position 497 * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} 498 */ 499 public E remove(int index) { 500 checkElementIndex(index); 501 return unlink(node(index)); 502 } 503 504 /** 505 * Tells if the argument is the index of an existing element. 506 */ 507 private boolean isElementIndex(int index) { 508 return index >= 0 && index < size; 509 } 510 511 /** 512 * Tells if the argument is the index of a valid position for an 513 * iterator or an add operation. 514 */ 515 private boolean isPositionIndex(int index) { 516 return index >= 0 && index <= size; 517 } 518 519 /** 520 * Constructs an IndexOutOfBoundsException detail message. 521 * Of the many possible refactorings of the error handling code, 522 * this "outlining" performs best with both server and client VMs. 523 */ 524 private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) { 525 return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size; 526 } 527 528 private void checkElementIndex(int index) { 529 if (!isElementIndex(index)) 530 throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); 531 } 532 533 private void checkPositionIndex(int index) { 534 if (!isPositionIndex(index)) 535 throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); 536 } 537 538 /** 539 * Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index. 540 */ 541 Node<E> node(int index) { 542 // assert isElementIndex(index); 543 544 if (index < (size >> 1)) { 545 Node<E> x = first; 546 for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) 547 x = x.next; 548 return x; 549 } else { 550 Node<E> x = last; 551 for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) 552 x = x.prev; 553 return x; 554 } 555 } 556 557 // Search Operations 558 559 /** 560 * Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element 561 * in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element. 562 * More formally, returns the lowest index {@code i} such that 563 * <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>, 564 * or -1 if there is no such index. 565 * 566 * @param o element to search for 567 * @return the index of the first occurrence of the specified element in 568 * this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element 569 */ 570 public int indexOf(Object o) { 571 int index = 0; 572 if (o == null) { 573 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { 574 if (x.item == null) 575 return index; 576 index++; 577 } 578 } else { 579 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { 580 if (o.equals(x.item)) 581 return index; 582 index++; 583 } 584 } 585 return -1; 586 } 587 588 /** 589 * Returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified element 590 * in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element. 591 * More formally, returns the highest index {@code i} such that 592 * <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>, 593 * or -1 if there is no such index. 594 * 595 * @param o element to search for 596 * @return the index of the last occurrence of the specified element in 597 * this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element 598 */ 599 public int lastIndexOf(Object o) { 600 int index = size; 601 if (o == null) { 602 for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { 603 index--; 604 if (x.item == null) 605 return index; 606 } 607 } else { 608 for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { 609 index--; 610 if (o.equals(x.item)) 611 return index; 612 } 613 } 614 return -1; 615 } 616 617 // Queue operations. 618 619 /** 620 * Retrieves, but does not remove, the head (first element) of this list. 621 * 622 * @return the head of this list, or {@code null} if this list is empty 623 * @since 1.5 624 */ 625 public E peek() { 626 final Node<E> f = first; 627 return (f == null) ? null : f.item; 628 } 629 630 /** 631 * Retrieves, but does not remove, the head (first element) of this list. 632 * 633 * @return the head of this list 634 * @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty 635 * @since 1.5 636 */ 637 public E element() { 638 return getFirst(); 639 } 640 641 /** 642 * Retrieves and removes the head (first element) of this list. 643 * 644 * @return the head of this list, or {@code null} if this list is empty 645 * @since 1.5 646 */ 647 public E poll() { 648 final Node<E> f = first; 649 return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f); 650 } 651 652 /** 653 * Retrieves and removes the head (first element) of this list. 654 * 655 * @return the head of this list 656 * @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty 657 * @since 1.5 658 */ 659 public E remove() { 660 return removeFirst(); 661 } 662 663 /** 664 * Adds the specified element as the tail (last element) of this list. 665 * 666 * @param e the element to add 667 * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Queue#offer}) 668 * @since 1.5 669 */ 670 public boolean offer(E e) { 671 return add(e); 672 } 673 674 // Deque operations 675 /** 676 * Inserts the specified element at the front of this list. 677 * 678 * @param e the element to insert 679 * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Deque#offerFirst}) 680 * @since 1.6 681 */ 682 public boolean offerFirst(E e) { 683 addFirst(e); 684 return true; 685 } 686 687 /** 688 * Inserts the specified element at the end of this list. 689 * 690 * @param e the element to insert 691 * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Deque#offerLast}) 692 * @since 1.6 693 */ 694 public boolean offerLast(E e) { 695 addLast(e); 696 return true; 697 } 698 699 /** 700 * Retrieves, but does not remove, the first element of this list, 701 * or returns {@code null} if this list is empty. 702 * 703 * @return the first element of this list, or {@code null} 704 * if this list is empty 705 * @since 1.6 706 */ 707 public E peekFirst() { 708 final Node<E> f = first; 709 return (f == null) ? null : f.item; 710 } 711 712 /** 713 * Retrieves, but does not remove, the last element of this list, 714 * or returns {@code null} if this list is empty. 715 * 716 * @return the last element of this list, or {@code null} 717 * if this list is empty 718 * @since 1.6 719 */ 720 public E peekLast() { 721 final Node<E> l = last; 722 return (l == null) ? null : l.item; 723 } 724 725 /** 726 * Retrieves and removes the first element of this list, 727 * or returns {@code null} if this list is empty. 728 * 729 * @return the first element of this list, or {@code null} if 730 * this list is empty 731 * @since 1.6 732 */ 733 public E pollFirst() { 734 final Node<E> f = first; 735 return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f); 736 } 737 738 /** 739 * Retrieves and removes the last element of this list, 740 * or returns {@code null} if this list is empty. 741 * 742 * @return the last element of this list, or {@code null} if 743 * this list is empty 744 * @since 1.6 745 */ 746 public E pollLast() { 747 final Node<E> l = last; 748 return (l == null) ? null : unlinkLast(l); 749 } 750 751 /** 752 * Pushes an element onto the stack represented by this list. In other 753 * words, inserts the element at the front of this list. 754 * 755 * <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addFirst}. 756 * 757 * @param e the element to push 758 * @since 1.6 759 */ 760 public void push(E e) { 761 addFirst(e); 762 } 763 764 /** 765 * Pops an element from the stack represented by this list. In other 766 * words, removes and returns the first element of this list. 767 * 768 * <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #removeFirst()}. 769 * 770 * @return the element at the front of this list (which is the top 771 * of the stack represented by this list) 772 * @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty 773 * @since 1.6 774 */ 775 public E pop() { 776 return removeFirst(); 777 } 778 779 /** 780 * Removes the first occurrence of the specified element in this 781 * list (when traversing the list from head to tail). If the list 782 * does not contain the element, it is unchanged. 783 * 784 * @param o element to be removed from this list, if present 785 * @return {@code true} if the list contained the specified element 786 * @since 1.6 787 */ 788 public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) { 789 return remove(o); 790 } 791 792 /** 793 * Removes the last occurrence of the specified element in this 794 * list (when traversing the list from head to tail). If the list 795 * does not contain the element, it is unchanged. 796 * 797 * @param o element to be removed from this list, if present 798 * @return {@code true} if the list contained the specified element 799 * @since 1.6 800 */ 801 public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) { 802 if (o == null) { 803 for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { 804 if (x.item == null) { 805 unlink(x); 806 return true; 807 } 808 } 809 } else { 810 for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { 811 if (o.equals(x.item)) { 812 unlink(x); 813 return true; 814 } 815 } 816 } 817 return false; 818 } 819 820 /** 821 * Returns a list-iterator of the elements in this list (in proper 822 * sequence), starting at the specified position in the list. 823 * Obeys the general contract of {@code List.listIterator(int)}.<p> 824 * 825 * The list-iterator is <i>fail-fast</i>: if the list is structurally 826 * modified at any time after the Iterator is created, in any way except 827 * through the list-iterator's own {@code remove} or {@code add} 828 * methods, the list-iterator will throw a 829 * {@code ConcurrentModificationException}. Thus, in the face of 830 * concurrent modification, the iterator fails quickly and cleanly, rather 831 * than risking arbitrary, non-deterministic behavior at an undetermined 832 * time in the future. 833 * 834 * @param index index of the first element to be returned from the 835 * list-iterator (by a call to {@code next}) 836 * @return a ListIterator of the elements in this list (in proper 837 * sequence), starting at the specified position in the list 838 * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} 839 * @see List#listIterator(int) 840 */ 841 public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) { 842 checkPositionIndex(index); 843 return new ListItr(index); 844 } 845 846 private class ListItr implements ListIterator<E> { 847 private Node<E> lastReturned; 848 private Node<E> next; 849 private int nextIndex; 850 private int expectedModCount = modCount; 851 852 ListItr(int index) { 853 // assert isPositionIndex(index); 854 next = (index == size) ? null : node(index); 855 nextIndex = index; 856 } 857 858 public boolean hasNext() { 859 return nextIndex < size; 860 } 861 862 public E next() { 863 checkForComodification(); 864 if (!hasNext()) 865 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 866 867 lastReturned = next; 868 next = next.next; 869 nextIndex++; 870 return lastReturned.item; 871 } 872 873 public boolean hasPrevious() { 874 return nextIndex > 0; 875 } 876 877 public E previous() { 878 checkForComodification(); 879 if (!hasPrevious()) 880 throw new NoSuchElementException(); 881 882 lastReturned = next = (next == null) ? last : next.prev; 883 nextIndex--; 884 return lastReturned.item; 885 } 886 887 public int nextIndex() { 888 return nextIndex; 889 } 890 891 public int previousIndex() { 892 return nextIndex - 1; 893 } 894 895 public void remove() { 896 checkForComodification(); 897 if (lastReturned == null) 898 throw new IllegalStateException(); 899 900 Node<E> lastNext = lastReturned.next; 901 unlink(lastReturned); 902 if (next == lastReturned) 903 next = lastNext; 904 else 905 nextIndex--; 906 lastReturned = null; 907 expectedModCount++; 908 } 909 910 public void set(E e) { 911 if (lastReturned == null) 912 throw new IllegalStateException(); 913 checkForComodification(); 914 lastReturned.item = e; 915 } 916 917 public void add(E e) { 918 checkForComodification(); 919 lastReturned = null; 920 if (next == null) 921 linkLast(e); 922 else 923 linkBefore(e, next); 924 nextIndex++; 925 expectedModCount++; 926 } 927 928 public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) { 929 Objects.requireNonNull(action); 930 while (modCount == expectedModCount && nextIndex < size) { 931 action.accept(next.item); 932 lastReturned = next; 933 next = next.next; 934 nextIndex++; 935 } 936 checkForComodification(); 937 } 938 939 final void checkForComodification() { 940 if (modCount != expectedModCount) 941 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 942 } 943 } 944 945 private static class Node<E> { 946 E item; 947 Node<E> next; 948 Node<E> prev; 949 950 Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) { 951 this.item = element; 952 this.next = next; 953 this.prev = prev; 954 } 955 } 956 957 /** 958 * @since 1.6 959 */ 960 public Iterator<E> descendingIterator() { 961 return new DescendingIterator(); 962 } 963 964 /** 965 * Adapter to provide descending iterators via ListItr.previous 966 */ 967 private class DescendingIterator implements Iterator<E> { 968 private final ListItr itr = new ListItr(size()); 969 public boolean hasNext() { 970 return itr.hasPrevious(); 971 } 972 public E next() { 973 return itr.previous(); 974 } 975 public void remove() { 976 itr.remove(); 977 } 978 } 979 980 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 981 private LinkedList<E> superClone() { 982 try { 983 return (LinkedList<E>) super.clone(); 984 } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { 985 throw new InternalError(e); 986 } 987 } 988 989 /** 990 * Returns a shallow copy of this {@code LinkedList}. (The elements 991 * themselves are not cloned.) 992 * 993 * @return a shallow copy of this {@code LinkedList} instance 994 */ 995 public Object clone() { 996 LinkedList<E> clone = superClone(); 997 998 // Put clone into "virgin" state 999 clone.first = clone.last = null; 1000 clone.size = 0; 1001 clone.modCount = 0; 1002 1003 // Initialize clone with our elements 1004 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) 1005 clone.add(x.item); 1006 1007 return clone; 1008 } 1009 1010 /** 1011 * Returns an array containing all of the elements in this list 1012 * in proper sequence (from first to last element). 1013 * 1014 * <p>The returned array will be "safe" in that no references to it are 1015 * maintained by this list. (In other words, this method must allocate 1016 * a new array). The caller is thus free to modify the returned array. 1017 * 1018 * <p>This method acts as bridge between array-based and collection-based 1019 * APIs. 1020 * 1021 * @return an array containing all of the elements in this list 1022 * in proper sequence 1023 */ 1024 public Object[] toArray() { 1025 Object[] result = new Object[size]; 1026 int i = 0; 1027 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) 1028 result[i++] = x.item; 1029 return result; 1030 } 1031 1032 /** 1033 * Returns an array containing all of the elements in this list in 1034 * proper sequence (from first to last element); the runtime type of 1035 * the returned array is that of the specified array. If the list fits 1036 * in the specified array, it is returned therein. Otherwise, a new 1037 * array is allocated with the runtime type of the specified array and 1038 * the size of this list. 1039 * 1040 * <p>If the list fits in the specified array with room to spare (i.e., 1041 * the array has more elements than the list), the element in the array 1042 * immediately following the end of the list is set to {@code null}. 1043 * (This is useful in determining the length of the list <i>only</i> if 1044 * the caller knows that the list does not contain any null elements.) 1045 * 1046 * <p>Like the {@link #toArray()} method, this method acts as bridge between 1047 * array-based and collection-based APIs. Further, this method allows 1048 * precise control over the runtime type of the output array, and may, 1049 * under certain circumstances, be used to save allocation costs. 1050 * 1051 * <p>Suppose {@code x} is a list known to contain only strings. 1052 * The following code can be used to dump the list into a newly 1053 * allocated array of {@code String}: 1054 * 1055 * <pre> 1056 * String[] y = x.toArray(new String[0]);</pre> 1057 * 1058 * Note that {@code toArray(new Object[0])} is identical in function to 1059 * {@code toArray()}. 1060 * 1061 * @param a the array into which the elements of the list are to 1062 * be stored, if it is big enough; otherwise, a new array of the 1063 * same runtime type is allocated for this purpose. 1064 * @return an array containing the elements of the list 1065 * @throws ArrayStoreException if the runtime type of the specified array 1066 * is not a supertype of the runtime type of every element in 1067 * this list 1068 * @throws NullPointerException if the specified array is null 1069 */ 1070 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 1071 public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) { 1072 if (a.length < size) 1073 a = (T[])java.lang.reflect.Array.newInstance( 1074 a.getClass().getComponentType(), size); 1075 int i = 0; 1076 Object[] result = a; 1077 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) 1078 result[i++] = x.item; 1079 1080 if (a.length > size) 1081 a[size] = null; 1082 1083 return a; 1084 } 1085 1086 private static final long serialVersionUID = 876323262645176354L; 1087 1088 /** 1089 * Saves the state of this {@code LinkedList} instance to a stream 1090 * (that is, serializes it). 1091 * 1092 * @serialData The size of the list (the number of elements it 1093 * contains) is emitted (int), followed by all of its 1094 * elements (each an Object) in the proper order. 1095 */ 1096 private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s) 1097 throws java.io.IOException { 1098 // Write out any hidden serialization magic 1099 s.defaultWriteObject(); 1100 1101 // Write out size 1102 s.writeInt(size); 1103 1104 // Write out all elements in the proper order. 1105 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) 1106 s.writeObject(x.item); 1107 } 1108 1109 /** 1110 * Reconstitutes this {@code LinkedList} instance from a stream 1111 * (that is, deserializes it). 1112 */ 1113 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 1114 private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s) 1115 throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException { 1116 // Read in any hidden serialization magic 1117 s.defaultReadObject(); 1118 1119 // Read in size 1120 int size = s.readInt(); 1121 1122 // Read in all elements in the proper order. 1123 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) 1124 linkLast((E)s.readObject()); 1125 } 1126 1127 /** 1128 * Creates a <em><a href="Spliterator.html#binding">late-binding</a></em> 1129 * and <em>fail-fast</em> {@link Spliterator} over the elements in this 1130 * list. 1131 * 1132 * <p>The {@code Spliterator} reports {@link Spliterator#SIZED} and 1133 * {@link Spliterator#ORDERED}. Overriding implementations should document 1134 * the reporting of additional characteristic values. 1135 * 1136 * @implNote 1137 * The {@code Spliterator} additionally reports {@link Spliterator#SUBSIZED} 1138 * and implements {@code trySplit} to permit limited parallelism.. 1139 * 1140 * @return a {@code Spliterator} over the elements in this list 1141 * @since 1.8 1142 */ 1143 @Override 1144 public Spliterator<E> spliterator() { 1145 return new LLSpliterator<E>(this, -1, 0); 1146 } 1147 1148 /** A customized variant of Spliterators.IteratorSpliterator */ 1149 static final class LLSpliterator<E> implements Spliterator<E> { 1150 static final int BATCH_UNIT = 1 << 10; // batch array size increment 1151 static final int MAX_BATCH = 1 << 25; // max batch array size; 1152 final LinkedList<E> list; // null OK unless traversed 1153 Node<E> current; // current node; null until initialized 1154 int est; // size estimate; -1 until first needed 1155 int expectedModCount; // initialized when est set 1156 int batch; // batch size for splits 1157 1158 LLSpliterator(LinkedList<E> list, int est, int expectedModCount) { 1159 this.list = list; 1160 this.est = est; 1161 this.expectedModCount = expectedModCount; 1162 } 1163 1164 final int getEst() { 1165 int s; // force initialization 1166 final LinkedList<E> lst; 1167 if ((s = est) < 0) { 1168 if ((lst = list) == null) 1169 s = est = 0; 1170 else { 1171 expectedModCount = lst.modCount; 1172 current = lst.first; 1173 s = est = lst.size; 1174 } 1175 } 1176 return s; 1177 } 1178 1179 public long estimateSize() { return (long) getEst(); } 1180 1181 public Spliterator<E> trySplit() { 1182 Node<E> p; 1183 int s = getEst(); 1184 if (s > 1 && (p = current) != null) { 1185 int n = batch + BATCH_UNIT; 1186 if (n > s) 1187 n = s; 1188 if (n > MAX_BATCH) 1189 n = MAX_BATCH; 1190 Object[] a = new Object[n]; 1191 int j = 0; 1192 do { a[j++] = p.item; } while ((p = p.next) != null && j < n); 1193 current = p; 1194 batch = j; 1195 est = s - j; 1196 return Spliterators.spliterator(a, 0, j, Spliterator.ORDERED); 1197 } 1198 return null; 1199 } 1200 1201 public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) { 1202 Node<E> p; int n; 1203 if (action == null) throw new NullPointerException(); 1204 if ((n = getEst()) > 0 && (p = current) != null) { 1205 current = null; 1206 est = 0; 1207 do { 1208 E e = p.item; 1209 p = p.next; 1210 action.accept(e); 1211 } while (p != null && --n > 0); 1212 } 1213 if (list.modCount != expectedModCount) 1214 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 1215 } 1216 1217 public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super E> action) { 1218 Node<E> p; 1219 if (action == null) throw new NullPointerException(); 1220 if (getEst() > 0 && (p = current) != null) { 1221 --est; 1222 E e = p.item; 1223 current = p.next; 1224 action.accept(e); 1225 if (list.modCount != expectedModCount) 1226 throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); 1227 return true; 1228 } 1229 return false; 1230 } 1231 1232 public int characteristics() { 1233 return Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.SUBSIZED; 1234 } 1235 } 1236 1237 }
AbstractSequentialList.java

1 package java.util; 2 3 /** 4 * This class provides a skeletal implementation of the <tt>List</tt> 5 * interface to minimize the effort required to implement this interface 6 * backed by a "sequential access" data store (such as a linked list). For 7 * random access data (such as an array), <tt>AbstractList</tt> should be used 8 * in preference to this class.<p> 9 * 10 * This class is the opposite of the <tt>AbstractList</tt> class in the sense 11 * that it implements the "random access" methods (<tt>get(int index)</tt>, 12 * <tt>set(int index, E element)</tt>, <tt>add(int index, E element)</tt> and 13 * <tt>remove(int index)</tt>) on top of the list's list iterator, instead of 14 * the other way around.<p> 15 * 16 * To implement a list the programmer needs only to extend this class and 17 * provide implementations for the <tt>listIterator</tt> and <tt>size</tt> 18 * methods. For an unmodifiable list, the programmer need only implement the 19 * list iterator's <tt>hasNext</tt>, <tt>next</tt>, <tt>hasPrevious</tt>, 20 * <tt>previous</tt> and <tt>index</tt> methods.<p> 21 * 22 * For a modifiable list the programmer should additionally implement the list 23 * iterator's <tt>set</tt> method. For a variable-size list the programmer 24 * should additionally implement the list iterator's <tt>remove</tt> and 25 * <tt>add</tt> methods.<p> 26 * 27 * The programmer should generally provide a void (no argument) and collection 28 * constructor, as per the recommendation in the <tt>Collection</tt> interface 29 * specification.<p> 30 * 31 * This class is a member of the 32 * <a href="{@docRoot}/../technotes/guides/collections/index.html"> 33 * Java Collections Framework</a>. 34 * 35 * @author Josh Bloch 36 * @author Neal Gafter 37 * @see Collection 38 * @see List 39 * @see AbstractList 40 * @see AbstractCollection 41 * @since 1.2 42 */ 43 44 public abstract class AbstractSequentialList<E> extends AbstractList<E> { 45 /** 46 * Sole constructor. (For invocation by subclass constructors, typically 47 * implicit.) 48 */ 49 protected AbstractSequentialList() { 50 } 51 52 /** 53 * Returns the element at the specified position in this list. 54 * 55 * <p>This implementation first gets a list iterator pointing to the 56 * indexed element (with <tt>listIterator(index)</tt>). Then, it gets 57 * the element using <tt>ListIterator.next</tt> and returns it. 58 * 59 * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} 60 */ 61 public E get(int index) { 62 try { 63 return listIterator(index).next(); 64 } catch (NoSuchElementException exc) { 65 throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index); 66 } 67 } 68 69 /** 70 * Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with the 71 * specified element (optional operation). 72 * 73 * <p>This implementation first gets a list iterator pointing to the 74 * indexed element (with <tt>listIterator(index)</tt>). Then, it gets 75 * the current element using <tt>ListIterator.next</tt> and replaces it 76 * with <tt>ListIterator.set</tt>. 77 * 78 * <p>Note that this implementation will throw an 79 * <tt>UnsupportedOperationException</tt> if the list iterator does not 80 * implement the <tt>set</tt> operation. 81 * 82 * @throws UnsupportedOperationException {@inheritDoc} 83 * @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc} 84 * @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc} 85 * @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc} 86 * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} 87 */ 88 public E set(int index, E element) { 89 try { 90 ListIterator<E> e = listIterator(index); 91 E oldVal = e.next(); 92 e.set(element); 93 return oldVal; 94 } catch (NoSuchElementException exc) { 95 throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index); 96 } 97 } 98 99 /** 100 * Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list 101 * (optional operation). Shifts the element currently at that position 102 * (if any) and any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their 103 * indices). 104 * 105 * <p>This implementation first gets a list iterator pointing to the 106 * indexed element (with <tt>listIterator(index)</tt>). Then, it 107 * inserts the specified element with <tt>ListIterator.add</tt>. 108 * 109 * <p>Note that this implementation will throw an 110 * <tt>UnsupportedOperationException</tt> if the list iterator does not 111 * implement the <tt>add</tt> operation. 112 * 113 * @throws UnsupportedOperationException {@inheritDoc} 114 * @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc} 115 * @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc} 116 * @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc} 117 * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} 118 */ 119 public void add(int index, E element) { 120 try { 121 listIterator(index).add(element); 122 } catch (NoSuchElementException exc) { 123 throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index); 124 } 125 } 126 127 /** 128 * Removes the element at the specified position in this list (optional 129 * operation). Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one 130 * from their indices). Returns the element that was removed from the 131 * list. 132 * 133 * <p>This implementation first gets a list iterator pointing to the 134 * indexed element (with <tt>listIterator(index)</tt>). Then, it removes 135 * the element with <tt>ListIterator.remove</tt>. 136 * 137 * <p>Note that this implementation will throw an 138 * <tt>UnsupportedOperationException</tt> if the list iterator does not 139 * implement the <tt>remove</tt> operation. 140 * 141 * @throws UnsupportedOperationException {@inheritDoc} 142 * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} 143 */ 144 public E remove(int index) { 145 try { 146 ListIterator<E> e = listIterator(index); 147 E outCast = e.next(); 148 e.remove(); 149 return outCast; 150 } catch (NoSuchElementException exc) { 151 throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index); 152 } 153 } 154 155 156 // Bulk Operations 157 158 /** 159 * Inserts all of the elements in the specified collection into this 160 * list at the specified position (optional operation). Shifts the 161 * element currently at that position (if any) and any subsequent 162 * elements to the right (increases their indices). The new elements 163 * will appear in this list in the order that they are returned by the 164 * specified collection's iterator. The behavior of this operation is 165 * undefined if the specified collection is modified while the 166 * operation is in progress. (Note that this will occur if the specified 167 * collection is this list, and it's nonempty.) 168 * 169 * <p>This implementation gets an iterator over the specified collection and 170 * a list iterator over this list pointing to the indexed element (with 171 * <tt>listIterator(index)</tt>). Then, it iterates over the specified 172 * collection, inserting the elements obtained from the iterator into this 173 * list, one at a time, using <tt>ListIterator.add</tt> followed by 174 * <tt>ListIterator.next</tt> (to skip over the added element). 175 * 176 * <p>Note that this implementation will throw an 177 * <tt>UnsupportedOperationException</tt> if the list iterator returned by 178 * the <tt>listIterator</tt> method does not implement the <tt>add</tt> 179 * operation. 180 * 181 * @throws UnsupportedOperationException {@inheritDoc} 182 * @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc} 183 * @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc} 184 * @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc} 185 * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} 186 */ 187 public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { 188 try { 189 boolean modified = false; 190 ListIterator<E> e1 = listIterator(index); 191 Iterator<? extends E> e2 = c.iterator(); 192 while (e2.hasNext()) { 193 e1.add(e2.next()); 194 modified = true; 195 } 196 return modified; 197 } catch (NoSuchElementException exc) { 198 throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index); 199 } 200 } 201 202 203 // Iterators 204 205 /** 206 * Returns an iterator over the elements in this list (in proper 207 * sequence).<p> 208 * 209 * This implementation merely returns a list iterator over the list. 210 * 211 * @return an iterator over the elements in this list (in proper sequence) 212 */ 213 public Iterator<E> iterator() { 214 return listIterator(); 215 } 216 217 /** 218 * Returns a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper 219 * sequence). 220 * 221 * @param index index of first element to be returned from the list 222 * iterator (by a call to the <code>next</code> method) 223 * @return a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper 224 * sequence) 225 * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} 226 */ 227 public abstract ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index); 228 }
