匈牙利算法简介
个人认为这个算法是一种贪心+暴力的算法,对于二分图的两部X和Y,记x为X部一点,y为Y部一点,我们枚举X的每个点x,如果Y部存在匹配的点y并且y没有被其他的x匹配,那就直接匹配;如果Y中已经没有可以和x匹配的点(包括可以匹配的点已经被其他的x匹配),那就让已经匹配的y的原配x'寻找其他可以匹配的y’,并将y和x匹配,最后,统计出匹配的对数
(详细了解的话,可以看看这位的博客:https://blog.csdn.net/sunny_hun/article/details/80627351)
题意
在一个n*n的网格中,存在一些墙壁,用'X‘表示,我们需要摆放blockhouse,由于每个blockhouse会向四周发射子弹,所以任意两个blockhouse不能在一条直线上,除非他们之间有墙壁分隔,问在给定的网格中,最多可以摆放多少个blockhouse
解题思路
(一开始我想用深搜暴力写的,过了样例,但是WA了,觉得自己的暴力写法没什么问题的,但是一直过不了,就只能放弃暴力了)
注意到如果我们在每个点放置了blockhouse,那么这个blockhouse向四个方向延申至墙壁或者边界,这个blockhouse可以视作是由一段连续的横区间和纵区间的交点,如下图所示:
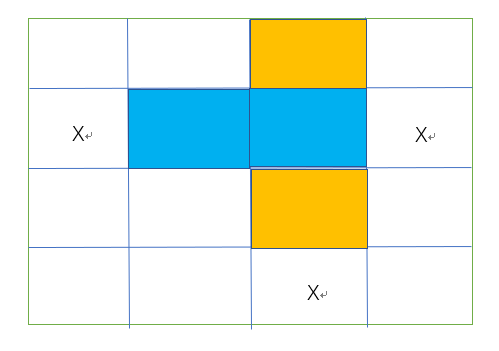
因此,我们发现,连续的纵横区间的交点形成一个blockhouse,并使得这两个区间都无法放置其他的blockhouse,由此看出这是一个求二分图最大匹配的问题
我们将连续的纵区间当作一个点,作为X部,将练习的横区间当作一个点,作为Y部,对于相交的横纵区间,我们由纵区间代表的点向横坐标代表的点建边,构建二分图
随后我们可以通过将二分图转化使用最大流求解,也可以用匈牙利算法求解,由于Dinic算法代码量冗长,这里就采用了匈牙利算法求解
代码区

#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #include<cstring> #include<queue> #include<string> #include<fstream> #include<vector> #include<stack> #include <map> #include <iomanip> #define bug cout << "**********" << endl #define show(x, y) cout<<"["<<x<<","<<y<<"] " #define LOCAL = 1; using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int inf = 1e7 + 10; const ll mod = 1e9 + 7; const int Max = 1e6 + 10; const int Max2 = 3e2 + 10; int n; char mp[5][5]; int row_id[5][5], col_id[5][5], cnt_row, cnt_col; //记录每个点所处的行、列编号 bool edge[20][20], vis[20]; //代表是否配对以及是否已经占用 int match[20]; bool dfs(int x) { for (int i = 0; i < cnt_col; i++) { if (edge[x][i] && !vis[i]) //used表示曾试图改变i的匹配对象,但是没有成功的话(used[i]= true),所以就无需继续 { vis[i] = true; if (match[i] == -1 || dfs(match[i])) //i没有匹配对象,或者i原来的匹配对象还可以和其他的匹配 { match[i] = x; return true; } } } return false; } int solve() { int res = 0; memset(match, -1, sizeof(match)); for (int i = 0; i < cnt_row; i++) { memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis)); if (dfs(i)) res++; } return res; } int main() { #ifdef LOCAL // freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin); // freopen("output.txt", "w", stdout); #endif while (scanf("%d", &n) != EOF && n) { cnt_row = cnt_col = 0; memset(edge, 0, sizeof(edge)); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { scanf("%s", mp[i] + 1); } for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) { if (mp[i][j] == '.') { int u = 0, v = 0; if (j == 1 || mp[i][j - 1] == 'X') u = cnt_row++; else u = row_id[i][j - 1]; if (i == 1 || mp[i - 1][j] == 'X') v = cnt_col++; else v = col_id[i - 1][j]; edge[u][v] = true; row_id[i][j] = u; col_id[i][j] = v; } } } printf("%d ", solve()); } return 0; }
题外延申
匈牙利算法复杂度O(VE)
最小点覆盖=最大匹配数
最小边覆盖=左右点数-最大匹配数
最小路径覆盖=点数-最大匹配数
最大独立集=点数-最大匹配数
