roi_pooling理解起来比较简单,所以我就先看了一下这部分的代码。
roi_pooling目录下
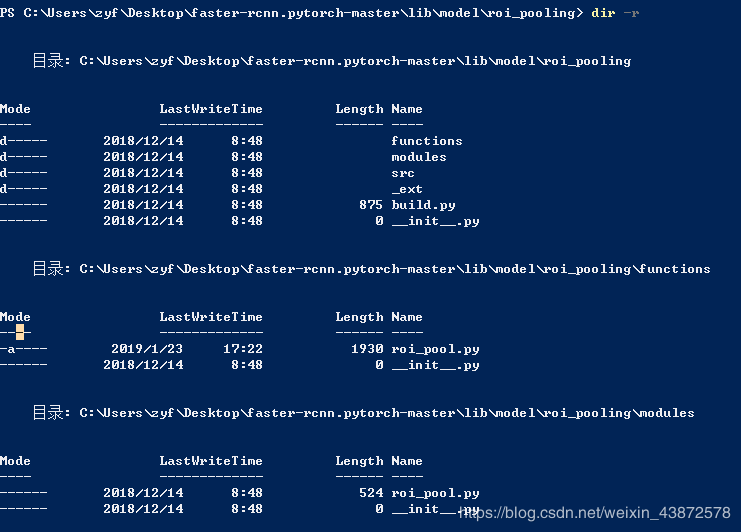

-src文件夹下是c和cuda版本的源码。
-functions文件夹下的roi_pool.py是继承了torch.autograd.Function类,实现RoI层的foward和backward函数。class RoIPoolFunction(Function)。
-modules文件夹下的roi_pool.py是继承了torch.nn.Modules类,实现了对RoI层的封装,此时RoI层就跟ReLU层一样的使用了。class _RoIPooling(Module)。
-_ext文件夹下还有个roi_pooling文件夹,这个文件夹是存储src中c,cuda编译过后的文件的,编译过后就可以被funcitons中的roi_pool.py调用了。
具体代码:
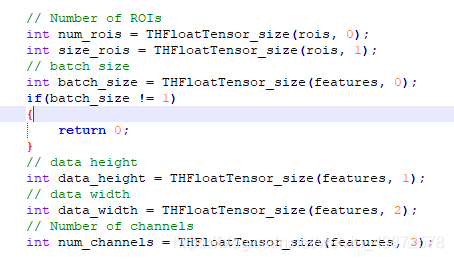
如下图所示:为roi_pooling/src/roi_pooling.c文件中的一段,可以根据该代码了解到各变量包含哪些内容。如果只看py代码,有些地方真不知道包含哪些信息,看起来很费劲,仔细看了下C代码,解决了自己的疑惑。
rois[0] num_rois即roi的个数;
rois[1] size_rois即大小;
features[0] batch_size,批大小;
features[1] data_height,高;
features[2] data_width,宽;
features[3] num_channels,通道数。
细致一点的理解看我的另一篇博客:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43872578/article/details/86628515
functions/roi_pool.py
1 import torch 2 from torch.autograd import Function 3 from .._ext import roi_pooling 4 import pdb 5 6 # 重写函数实现RoI层的正向传播和反向传播 modules中的roi_pool实现层的封装 7 8 class RoIPoolFunction(Function): 9 def __init__(ctx, pooled_height, pooled_width, spatial_scale): 10 #ctx is a context object that can be used to stash information for backward computation 11 #上下文对象,可用于存储信息以进行反向计算 12 ctx.pooled_width = pooled_width 13 ctx.pooled_height = pooled_height 14 ctx.spatial_scale = spatial_scale 15 ctx.feature_size = None 16 17 def forward(ctx, features, rois): 18 ctx.feature_size = features.size() 19 batch_size, num_channels, data_height, data_width = ctx.feature_size 20 num_rois = rois.size(0) 21 output = features.new(num_rois, num_channels, ctx.pooled_height, ctx.pooled_width).zero_() 22 ctx.argmax = features.new(num_rois, num_channels, ctx.pooled_height, ctx.pooled_width).zero_().int() 23 ctx.rois = rois 24 if not features.is_cuda: 25 _features = features.permute(0, 2, 3, 1) 26 roi_pooling.roi_pooling_forward(ctx.pooled_height, ctx.pooled_width, ctx.spatial_scale, 27 _features, rois, output) 28 else: 29 roi_pooling.roi_pooling_forward_cuda(ctx.pooled_height, ctx.pooled_width, ctx.spatial_scale, 30 features, rois, output, ctx.argmax) 31 32 return output 33 34 def backward(ctx, grad_output): 35 assert(ctx.feature_size is not None and grad_output.is_cuda) 36 batch_size, num_channels, data_height, data_width = ctx.feature_size 37 grad_input = grad_output.new(batch_size, num_channels, data_height, data_width).zero_() 38 39 roi_pooling.roi_pooling_backward_cuda(ctx.pooled_height, ctx.pooled_width, ctx.spatial_scale, 40 grad_output, ctx.rois, grad_input, ctx.argmax) 41 42 return grad_input, None
modules/roi_pool.py
1 from torch.nn.modules.module import Module 2 from ..functions.roi_pool import RoIPoolFunction 3 4 # 对roi_pooling层的封装,就是ROI Pooling Layer了 5 6 class _RoIPooling(Module): 7 def __init__(self, pooled_height, pooled_width, spatial_scale): 8 super(_RoIPooling, self).__init__() 9 10 self.pooled_width = int(pooled_width) 11 self.pooled_height = int(pooled_height) 12 self.spatial_scale = float(spatial_scale) 13 14 def forward(self, features, rois): 15 return RoIPoolFunction(self.pooled_height, self.pooled_width, self.spatial_scale)(features, rois) 16 # 直接调用了functions中的函数,此时已经实现了foward,backward操作
剩下的src,_ext文件的代码就可以自己读读了,就是用c,cuda对roi_pooling实现了foward和backward,目的就是为了让python可以调用。
【未完,待更新…】
ref:https://www.jianshu.com/p/d674e16ce896
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43872578/article/details/86616801