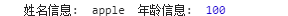JavaScript的this关键字非常灵活!
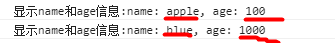
1 var o1={ 2 name:'apple', 3 age:100, 4 msg:function(){ 5 return '显示name和age信息:'+'name: '+this.name+', age: '+this.age; 6 } 7 }; 8 //针对msg中的this进行研究: 9 console.log(o1.msg());//this 指向当前对象o1 10 var o2={ 11 name:'blue', 12 age:1000 13 }; 14 o2.msg=o1.msg; 15 console.log(o2.msg());//this 指向当前对象o2
当o1.msg()时,this指向o1;而o2.msg()时,this指向o2。也就是this指向的是“当前”环境运行时所在的对象。
运行结果:
将函数提出来,更形象的表示:
1 console.log('---'); 2 function f(){ 3 console.log(this.name1); 4 } 5 var o3={ 6 name1:'alice', 7 info:f 8 }; 9 var o4={ 10 name1:'boy', 11 info:f 12 }; 13 f();//undefined 14 o3.info();//alice 15 o4.info();//boy
f():this指向顶层对象window;o3.info():this指向的是o3;o4.info():this指向的是o4。即this总是指向“当前”运行时所在的对象。
运行结果:

如果我们在全局环境中,将对象中的方法赋值给变量。以本文最上面代码o1.msg示例:
1 var name='abc'; 2 var age=1; 3 var test1=o1.msg; 4 console.log(test1());//此时this指向顶层对象window
此时test1():this指向的是window
运行结果:

由上面的这些例子,我们可以“粗略”的认为:每个函数中都存在着this,它总是指向当前运行环境的对象。
全局环境下的this:指向顶层对象window
1 function test2(){ 2 if(this === window){ 3 console.log('此时this 指向顶层对象window'); 4 } 5 } 6 test2();
运行结果:

1 function Test3(num){ 2 this.num=num; 3 } 4 var t3=new Test3(100); 5 console.log(t3.num);//this 指向t3 6 7 Test3.prototype.m=function (){//所有由Test3构造函数生成的实例化对象都共享m方法 8 return this.num; 9 }; 10 console.log(t3.m());//this 指向t3
运行结果:

注意下面这种情况:
1 var o5={ 2 name:'application', 3 send:function(){ 4 console.log(this 5 ); 6 } 7 }; 8 o5.send();//o5 9 (o5.send=o5.send)();//window 10 /** 11 * 相当于 12 * (o5.send=function(){ 13 * console.log(this); 14 * }) 15 */ 16 (false||o5.send)();//window 17 /** 18 * 相当于 19 * (false || function(){ 20 * console.log(this); 21 * }) 22 */ 23 (1,o5.send)();//window 24 /** 25 * 相当于 26 * (1,function(){ 27 * console.log(this); 28 * }) 29 */
即:除非直接使用o5.send(),结果返回当前对象;否则均返回顶层对象window
运行结果:

如果方法位于多层对象的内部,那么this指向当前对象层,不会继承更上面的层:
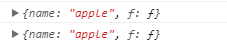
1 var o6={ 2 name:'cat', 3 f:{ 4 f1:function (){ 5 console.log(this.name); 6 console.log(this==o6.f);//其实this指向的是o6.f 7 } 8 } 9 }; 10 o6.f.f1();//undefined 11 //因为此时this指向的是f
上面代码中o6对象中f属性对应的值,是一个对象。该对象里面又存在着一个函数,此时函数里面的this指向o6.f,而不是o6
运行结果:

如果想达到预期的效果:
1 var o6={ 2 name:'cat', 3 f:{ 4 f1:function(){ 5 console.log(this.name); 6 }, 7 name:'cat' 8 } 9 } 10 o6.f.f1();//cat
继续进行变通:
1 //将o6.f.f1赋值给变量 2 var v=o6.f.f1; 3 /** 4 * 相当于 5 * var v=function (){ 6 * console.log(this.name); 7 * } 8 */ 9 v();//this指向的对象又指向了顶层对象window 10 //将o6.f赋值给变量 11 var v1=o6.f; 12 v1.f1();//此时返回的结果为'cat' 13 /** 14 * 相当于 15 * var v1={ 16 * f1:function(){ 17 * console.log(this.name);}, 18 * name:'cat' 19 * }; 20 */
同时应尽量避免在函数中使用多层this:
1 //尽量避免在函数中使用多层this 2 var o7={ 3 name:'apple', 4 f:function(){ 5 console.log(this);//this指向当前运行环境对象,即o7 6 var f1=function(){ 7 console.log(this);//this指向顶层对象,即window 8 }();//IIFE;这是立即调用的函数表达式 9 } 10 }; 11 o7.f();
运行结果:

为了让f1中的this也指向该对象:添加一个临时变量作为辅助:固定this。
1 var o8={ 2 name:'apple', 3 f:function(){ 4 console.log(this);//this指向o8 5 var that=this;//使用变量固定this 6 var f1=function(){ 7 console.log(that);//此时that指向o8 8 }(); 9 } 10 }; 11 o8.f();
运行结果:
当然如果采用严格模式,那么函数内部this不能指向顶层对象window!
call():调用函数,指定this指向的对象;第一个参数是this指向的对象,第二个、第三个等是函数调用的参数
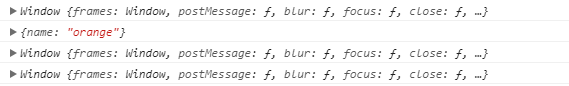
1 var o9={ 2 name:'orange' 3 }; 4 function test4(){ 5 console.log(this); 6 } 7 test4(); 8 test4.call(o9);//指定this的指向 9 //call方法中如果参数为空、nullundefined,那么默认指向全局对象window 10 test4(null); 11 test4(undefined); 12 //call方法第一个参数是this指向的对象,后面的参数是函数调用时用到的参数
运行结果:
call的一个应用:调用对象原生方法,即使该方法被覆盖
1 var o10={}; 2 console.log(o10.hasOwnProperty('toString')); 3 o10.hasOwnProperty=function(){ 4 return true; 5 }; 6 console.log(o10.hasOwnProperty('toString')); 7 //this指向o10,这样方法被覆盖,依然能够调用对象的原生方法 8 console.log(Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(o10,'toString'));
运行结果:

apply():作用与call()类似,第一个参数也是this指向的对象;不同的是函数调用的参数以数组形式传入
1 //apply与call作用类似,只是apply传入的参数是以数组形式传入 2 //同理,第一个参数是this指向的对象,空或null或undefined,默认是全局对象window 3 function test6(a,b){ 4 console.log(a+b); 5 } 6 test6.call(null,1,10);//test6(1,10) 7 test6.apply(null,[10,100]);//test6(10,100) 8 var arr=[1,2,3,4,5]; 9 console.log(Math.max.apply(null,arr));//this指向window,arr调用Math.max方法 10 console.log(Array.prototype.slice.apply({0:1,1:100,length:2}));//类似数组的对象调用方法变为数组
运行结果:

bind():将this绑定到某个对象,返回一个新函数(相较于call,apply的函数立即执行)
1 //bind将this绑定到某个对象,并返回一个函数 2 var o10={ 3 fruit:'apple', 4 f:function(){ 5 console.log(this.fruit); 6 } 7 }; 8 o10.f();//正常取值 9 console.log('---'); 10 var a=o10; 11 a.f();//这样也能正确取值 12 var b=o10.f; 13 b();//这样取值就不行了;undefined 14 /** 15 * 此时this指向全局对象window,上面相当于 16 * var b=function (){ 17 * console.log(this.fruit);//this指向window 18 * } 19 */ 20 21 //绑定this指向o10 22 var c=o10.f.bind(o10); 23 c();//此时能够正确取值
运行结果:

bind还能绑定函数的参数:
1 //bind还可以绑定函数的参数 2 var o10={ 3 name:'apple', 4 age:100 5 }; 6 function test7(x,y){ 7 console.log(x,this.name,y,this.age) ; 8 } 9 var t5= test7.bind(o10,'姓名信息: ');//绑定第一个参数,返回t5这个新函数 10 t5(' 年龄信息: ');
运行结果: