Redux 版本:3.7.2
Redux 是 JavaScript 状态容器,提供可预测化的状态管理。
说白了Redux就是声明了一个对象,提供了这个对象的读取,修改,订阅等方法。
- getState: getter(读取)
- dispatch: setter(修改)
- subscribe: 订阅
Redux 提供了五个方法
接下来我们来一一解析。
createStore
创建一个 Redux store 来以存放应用中所有的 state。应用中应有且仅有一个 store。
参数:
- reducer (Function): 接收两个参数,分别是当前的 state 树和要处理的 action,返回新的 state 树。
- [ reloadedState ] (any):初始时的 state。
- enhancer (Function):后面再讲。
返回值:
- getState:获取store方法
- dispatch:修改store方法
- subscribe:订阅store变化方法
- replaceReducer:重置reducer方法
先来写一个基础的 createStore 如下:
function createStore() {
function getState() { } // 取
function dispatch() { } // 存
function subscribe() { } // 订阅
function replaceReducer() { } // 重置reducer
return { getState, dispatch, subscribe, replaceReducer }
}
getState
getState 实现很简单,直接返回 currentState。
function createStore() {
let currentState = {}; // 数据
function getState() { // 取
return currentState;
}
function dispatch() { } // 存
function subscribe() { } // 订阅
function replaceReducer() { } // 重置reducer
return { getState, dispatch, subscribe, replaceReducer }
}
dispatch
dispatch 传入 action,通过 action.type 区别操作。
function createStore() {
let currentState = {};
function getState() { // 取
return currentState;
}
function dispatch(action) { // 存
switch (action.type) {
case 'PLUS':
currentState = {
...currentState,
count: currentState.count + 1,
};
}
return action;
}
function subscribe() { } // 订阅
function replaceReducer() { } // 重置reducer
return { getState, dispatch, subscribe, replaceReducer }
}
因为 Redux 要通用,所以 dispatch 内和业务相关的代码要提取出来,Redux 给它起了个名字,叫 reducer。
提取reducer,
const initialState = {
count: 0,
}
export default (state = initialState, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'PLUS':
return {
...state,
count: state.count + 1,
}
case 'MINUS':
return {
...state,
count: state.count - 1,
}
default:
return state
}
}
给 createStore 添加两个参数 reducer, preloadedState。
preloadedState非必传,如果不传,currentState 默认值就是 undefined。
在 createStore 中添加初始化方法 dispatch({ type: '@@redux/INIT' }) ; 初始化的 action.type 必须是 reducer 中没有使用过的,Redux 源码中使用了 '@@redux/INIT'。初始化方法会执行一次 dispatch。
初始化时,如果 currentState 是 undefined, 那么在 reducer 中, state = initialState 会把 initialState 赋值给 state,然后通过 default return 出去, 最后修改 currentState。相当于 currentState = initialState。
最后 createStore 如下
function createStore(reducer, preloadedState) {
let currentState = preloadedState;
function getState() { // 取
return currentState;
}
function dispatch(action) { // 存
currentState = reducer(currentState, action);
return action;
}
function subscribe() { } // 订阅
function replaceReducer() { } // 重置reducer
dispatch({ type: '@@redux/INIT' }); // 初始化
return { getState, dispatch, subscribe, replaceReducer }
}
根据代码可以看出,reducer 和 action 都是开发者自定义的,Redux 只是把 reducer 返回的 state 赋值给了 currentState,那么开发者自定义其他格式的action ,并且在 reducer 中作出对应的解析,然后返回 state,当然也是完全可以的。只是 Redux 统一了这种写法,降低了个性化带来的开发成本。
实际上 createStore 还有第三个参数 enhancer,目前用不到,后面再讲。
subscribe
subscribe 有一个参数 listener (Function): 每当 dispatch action 的时候都会执行的回调。
subscribe 使用了设计模式中的 发布-订阅模式,又叫 观察者模式。
实现:
- 在 createStore 中添加一个储存 变化监听器 的数组 currentListeners;
- subscribe 将 变化监听器 放入 currentListeners;
- 每次 dispatch 时, 循环执行 currentListeners 中的 变化监听器。
function createStore(reducer, preloadedState) {
let currentState = preloadedState;
let currentListeners = [];
function getState() { // 取
return currentState;
}
function dispatch(action) { // 存
currentState = reducer(currentState, action);
currentListeners.forEach(fn => fn());
return action;
}
function subscribe(listener) { // 订阅
currentListeners.push(listener);
}
function replaceReducer() { } // 重置reducer
dispatch({ type: '@@redux/INIT' }); // 初始化
return { getState, dispatch, subscribe, replaceReducer }
}
replaceReducer
重置 reducer, 并不会重置 currentState。
实现:
- 添加变量 currentReducer;
- dispatch 使用 currentReducer;
- replaceReducer 方法将 nextReducer 赋值给 replaceReducer, 然后执行
dispatch({ type: '@@redux/INIT' })。
注意:实际上,replaceReducer 中的 dispatch({ type: '@@redux/INIT' }),只有此时 currentState 是 undefined 时,才有作用,会把新的 initialState 赋值给 currentState。
function createStore(reducer, preloadedState) {
let currentReducer = reducer
let currentState = preloadedState;
let currentListeners = [];
function getState() { // 取
return currentState;
}
function dispatch(action) { // 存
currentState = currentReducer(currentState, action);
currentListeners.forEach(fn => fn());
return action;
}
function subscribe(listener) { // 发布订阅
currentListeners.push(listener);
}
function replaceReducer(nextReducer) { // 重置reducer
currentReducer = nextReducer;
dispatch({ type: '@@redux/INIT' }); // 重置
}
dispatch({ type: '@@redux/INIT' }); // 初始化
return { getState, dispatch, subscribe, replaceReducer }
}
createStore 的实现到这里已经完成,Redux 源码除此之外还做了大量的错误校验。
combineReducers
随着项目越来越大,把 reducer 放在一个文件里写会越来越臃肿,于是 Redux 提供了 combineReducers 方法。
先来看下如何使用
rootReducer = combineReducers({potato: potatoReducer, tomato: tomatoReducer})
// rootReducer 将返回如下的 state 对象
{
potato: {
// ... potatoes, 和一些其他由 potatoReducer 管理的 state 对象 ...
},
tomato: {
// ... tomatoes, 和一些其他由 tomatoReducer 管理的 state 对象,比如说 sauce 属性 ...
}
}
combineReducers 参数是 reducers 对象,返回一个合成后的 reducer。
实现逻辑比较简单,循环把 reducers 里的每一个 reducer 都执行, 执行结果放在 nextState 里,如果数据改变了就返回 nextState,如果数据没有改变就返回传入的 state。
注意:如果数据没有改变,返回的是传入的 state,虽然此时和 nextState 数据是一样的,但是实际地址并不一样。为了区分,Redux 特意用了 hasChanged 变量来记录。
function combineReducers(reducers) {
const reducerKeys = Object.keys(reducers); // key[]
return function combination(state = {}, action) {
let hasChanged = false; // state 是否改变
const nextState = {}; // 改变后的 state
// 循环 reducers
reducerKeys.forEach(key => {
const reducer = reducers[key]; // 当前 reducer
const previousStateForKey = state[key]; // 当前 state
const nextStateForKey = reducer(previousStateForKey, action); // 如果 没有匹配到action.type,会在 reducer 中的 switch default 返回传入的 state,即 previousStateForKey
nextState[key] = nextStateForKey;
hasChanged = hasChanged || nextStateForKey !== previousStateForKey;
})
return hasChanged ? nextState : state;
}
}
bindActionCreators
bindActionCreators(actionCreators, dispatch) 把一个 value 为不同 action creator 的对象,转成拥有同名 key 的对象。
action 生成器名字叫做叫 action creator, 如下
function addTodo(text) {
return {
type: 'ADD_TODO',
text,
};
}
修改数据需要这样写
dispatch(addTodo('Use Redux'))
如果我们多个 action creator,写起来会比较繁琐,
dispatch(addTodo('Use Redux'))
dispatch(plusTodo())
dispatch(setDataTodo({ id: 1 }))
所以 Redux 提供了 bindActionCreators 函数,传入 action creators 和 dispatch, 返回绑定了 dispatch 的 action creators。
实现也很简单,遍历 actionCreators, 把每个元素用 dispatch 处理后生成新的函数,返回新函数的集合。
actionCreators 参数是 action creator 的集合对象,如 { addTodo, addTodo1 }。实现代码如下:
function bindActionCreators(actionCreators, dispatch) {
const boundActionCreators = {};
Object.keys(actionCreators).forEach(key => {
const actionCreator = actionCreators[key];
if (typeof actionCreator === 'function') {
boundActionCreators[key] = (...args) => dispatch(actionCreator(...args));
}
})
return boundActionCreators;
}
使用 bindActionCreators 写起来就会方便很多
const boundActionCreators = bindActionCreators({
addTodo,
plusTodo,
setDataTodo,
}, dispatch);
// 写入数据
boundActionCreators.addTodo('Use Redux')
boundActionCreators.plusTodo()
boundActionCreators.addTodo({ id: 1 })
Redux 支持 actionCreators 是一个单个 action creator 的函数,所以提取公共方法。改造如下:
function bindActionCreator(actionCreator, dispatch) {
return (...args) => dispatch(actionCreator(...args));
}
function bindActionCreators(actionCreators, dispatch) {
if (typeof actionCreators === 'function') {
return bindActionCreator(actionCreators, dispatch)
}
const boundActionCreators = {};
Object.keys(actionCreators).forEach(key => {
const actionCreator = actionCreators[key];
if (typeof actionCreator === 'function') {
boundActionCreators[key] = bindActionCreator(actionCreator, dispatch);
}
})
return boundActionCreators;
}
compose
从右到左来组合多个函数。
先来看看源码:
function compose(...funcs) {
if (funcs.length === 0) {
return arg => arg
}
if (funcs.length === 1) {
return funcs[0]
}
return funcs.reduce((a, b) => (...args) => a(b(...args)))
}
最后一行很难理解,把它换成function写法如下
funcs.reduce(function (a, b) {
return function (...args) {
return a(b(...args))
}
})
先看下reduce方法
reduce(callbackfn: (previousValue: T, currentValue: T, currentIndex: number, array: T[]) => T): T;
reduce(callbackfn: (previousValue: T, currentValue: T, currentIndex: number, array: T[]) => T, initialValue: T): T;
// 从左到右为每个数组元素执行一次回调函数,并把上次回调函数的返回值放在一个暂存器中传给下次回调函数,并返回最后一次回调函数的返回值。
previousValue 上次循环的返回值
currentValue 当前循环item
所以第二次循环过程如下
// 第一次循环返回值为
function (...args) {
return a(b(...args))
}
// 第二次循环时,第一个参数为:第一次循环的返回值,第二个参数为:funcs 内第三个元素,用c来表示
// 第二次循环返回值为
function (...args) {
return (function (...args) {
return a(b(...args))
})(c(...args))
}
// 整理后
function (...args) {
return a(b(c(...args)))
}
所以 [a, b, c, d, e] 的执行结果是 (...args) => a(b(c(d(e(...args)))))。
所以能看出来,funcs 内函数需要满足 函数参数和函数返回值结构一致。
applyMiddleware
applyMiddleware 是把 dispatch 一层一层包装。洋葱圈模型。
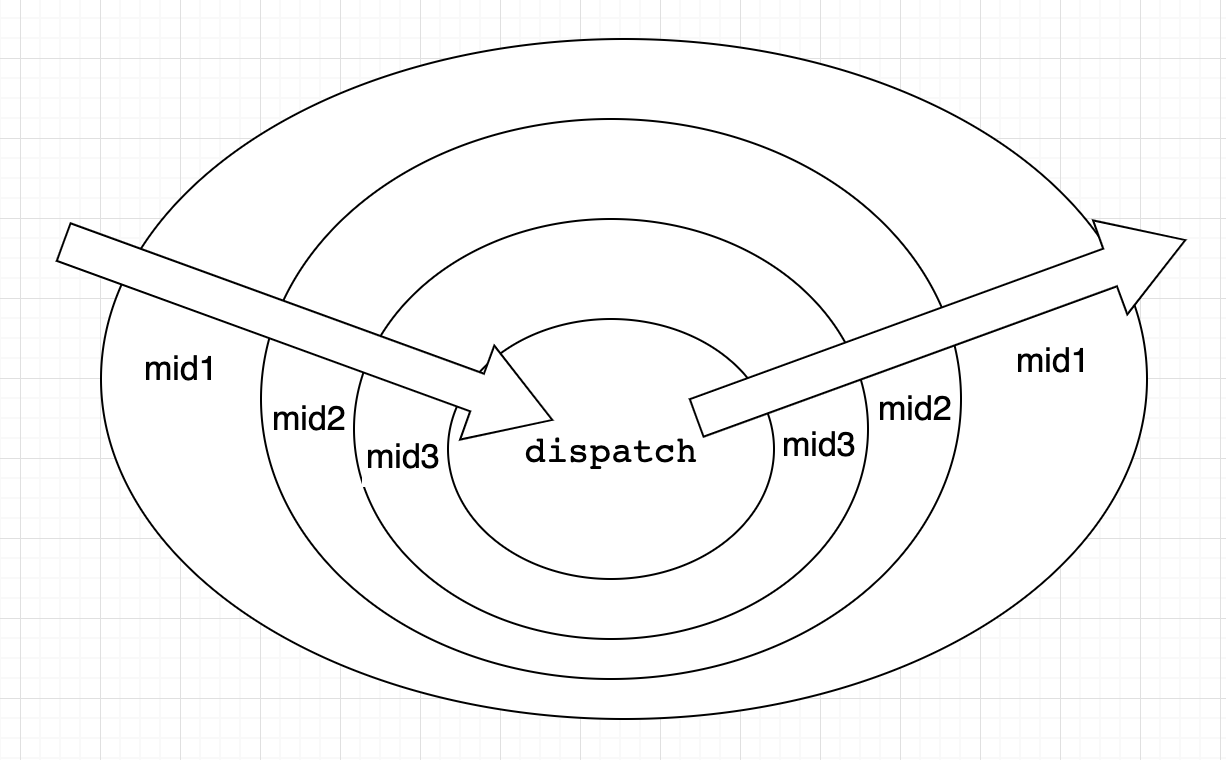
先看看 createStore 的第三个参数 enhancer
function createStore(reducer, preloadedState, enhancer) {
// 实现了 preloadedState 参数可以省略
if (typeof preloadedState === 'function' && typeof enhancer === 'undefined') {
enhancer = preloadedState
preloadedState = undefined
}
if (typeof enhancer !== 'undefined') {
// 看起来 enhancer 是个高阶函数,返回值还是 store creator
// 可以看出 enhancer 的大概结构为
// (createStore) => (reducer, preloadedState) => createStore(educer, preloadedState)
return enhancer(createStore)(reducer, preloadedState)
}
// 这里是其他代码
// ...
}
再看看官网给的 applyMiddleware 使用例子
let store = createStore(
todos,
[ 'Use Redux' ],
applyMiddleware(logger)
)
所以 applyMiddleware 的结构应该是
(...middlewares) => (createStore) => (reducer, preloadedState) => createStore(educer, preloadedState)
所以猜出来了 applyMiddleware 的参数是函数,返回值执行多次后还是 createStore(educer, preloadedState)。
所以再来看官方定义就比较好理解
Middleware 可以让你包装 store 的 dispatch 方法来达到你想要的目的。同时, middleware 还拥有“可组合”这一关键特性。多个 middleware 可以被组合到一起使用,形成 middleware 链。其中,每个 middleware 都不需要关心链中它前后的 middleware 的任何信息。
来看 applyMiddleware 看源码, 跟着 序号看会稍微清晰点:
applyMiddleware(...middlewares) {
return (createStore) => (reducer, preloadedState, enhancer) => {
const store = createStore(reducer, preloadedState, enhancer)
let dispatch = store.dispatch
let chain = []
const middlewareAPI = {
getState: store.getState,
dispatch: (action) => dispatch(action)
}
// 2、chain内元素结构为 (store.dispatch) => store.dispatch
// 所以 middleware(middlewareAPI) 结果为 (store.dispatch) => store.dispatch
// 所以 middleware 结构为 (middlewareAPI) => (store.dispatch) => store.dispatch
// 即 参数 middlewares 内元素结构为 (middlewareAPI) => (store.dispatch) => store.dispatch
chain = middlewares.map(middleware => middleware(middlewareAPI))
// 1、上面解释过 compose 的返回值是 (...arg) => a(b(c(...arg))),
// 所以下面 dispatch = ((...arg) => a(b(c(...arg))))(store.dispatch)
// 即 dispatch = a(b(c(store.dispatch)))
// 所以 a、b、c 即 chain内元素 的结构需要为 (store.dispatch) => store.dispatch
dispatch = compose(...chain)(store.dispatch)
return {
...store,
dispatch // 这里可以看出,applyMiddleware 只包装替换了 createStore 的 dispatch
}
}
}
现在我们知道了 applyMiddleware 的参数结构是 (middlewareAPI) => (store.dispatch) => store.dispatch,然后我们来写个简单的 middleware
// 原始长这个样子
function logger(middlewareAPI) {
return (dispatch) => dispatch;
}
// 然后 给 dispatch 包装以下,并且换个名字叫 next
function logger(middlewareAPI) {
return (next) => (action) => {
let value = next(action);
return value;
};
}
// 然后 加入功能
function logger(middlewareAPI) {
return (next) => (action) => {
// 这里的 dispatch 是 createStore 创建的。一般不用。
const { getState, dispatch } = middlewareAPI;
console.log('will dispatch', action);
let value = next(action);
console.log('state after dispatch', getState());
// createStore 里实现的 dispatch 返回 action,
// 一般会是 action 本身,除非
// 后面的 middleware 修改了它。
return value;
};
}
最后再来回味下 applyMiddleware 的这几个结构
// compose
([a, b, c, d, e]) => (...args) => a(b(c(d(e(...args)))))
// applyMiddleware
(...middlewares) => (createStore) => (reducer, preloadedState) => createStore(educer, preloadedState)
// middleware
(middlewareAPI) => (dispatch) => dispatch