1.基本概念
dll(dynamic-link library),动态链接库,是微软实现共享函数库的一种方式。动态链接,就是把一些常用的函数代码制作成dll文件,当某个程序调用到dll中的某个函数的时候,windows系统才把dll加载到内存中。也就是说当程序需要的时候才链接dll,所以是动态链接。
动态链接的好处是磁盘和内存的消耗减少,这也是dll的最初目的。同时dll也提供了模块化的函数库。不过,dll也有缺点,就是版本冲突,比如不同的应用程序共享同一个dll,而它们需求的是不同的版本,这就会出现矛盾,解决的方法是把不同版本的dll放在不同的文件夹中。
2.dll文件的编写(使用vs2013)
首先新建一个dll项目:
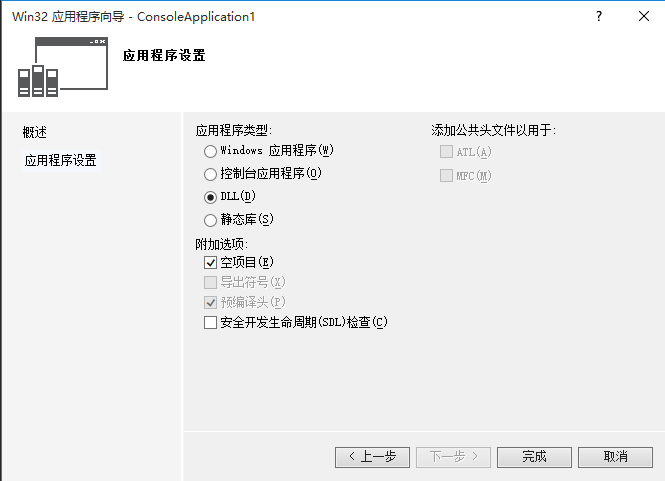
然后添加一个头文件和一个源文件(mydll.h / mydll.cpp)
编写头文件,如下:
#ifndef _MYDLL_H_ #define _MYDLL_H_ #define EXPORT_DLL _declspec(dllexport) extern "C" EXPORT_DLL int add(int a, int b); // 即 int add(int a,int b) #endif
编写源文件:
#include "mydll.h" int add(int a, int b) { return (a + b); }
编译链接完成后会生成 mydll.dll和mydll.lib,这是最后的目标文件
源文件的编写正常,区别是头文件的编写,要加上 _declspec(dllexport),这样就省去了编写.def文件 ,也可以加上 extern "C" 这样通用性更强,因为C++和C的函数名转换不一样,详细见末尾链接。
3.dll文件的使用
dll文件的使用有两种方法,加载时动态链接和运行时动态链接
3.1.加载时动态链接:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; #pragma comment(lib,"mydll.lib") extern "C" _declspec(dllimport) int add(int a, int b); int main() { cout << add(1, 2) << endl; }
3.2.运行时动态链接(主要使用 LoadLibrary和GetProcAddress):
#include <iostream> #include <Windows.h> using namespace std; typedef int(*addfun)(int a, int b); int main() { HMODULE hdll = LoadLibrary(LPCWSTR("mydll.dll")); if (hdll != NULL) { addfun add = (addfun)GetProcAddress(hdll, "add"); if (add != NULL) { cout << add(1, 2) << endl; } FreeLibrary(hdll); } }
4.在python中使用dll
需要安装ctypes
使用方法:

推荐链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/cswuyg/archive/2011/09/30/dll.html