.NET是一门多语言平台,这是我们所众所周知的,其实现原理在于因为了MSIL(微软中间语言)的一种代码指令平台。所以.NET语言的编译就分为了两部分,从语言到MSIL的编译(我喜欢称为预编译),和运行时的从MSIL到本地指令,即时编译(JIT)。JIT编译分为经济编译器和普通编译器,在这里就不多说了,不是本文的重点。本文主要讨论下预编译过程中我们能做的改变编译情况,改变生成的IL,从编译前后看看微软C#3.0一些语法糖,PostSharp的静态注入等等。
1:我们先来看看最简单的var:
C#:
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
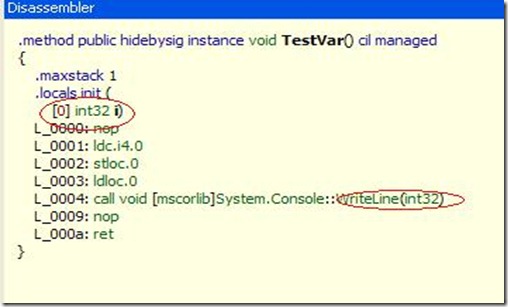
使用Reflector查看生成
IL:
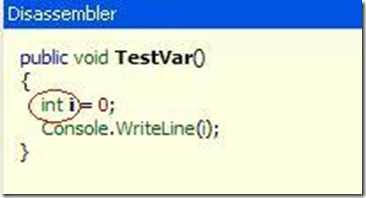
反编译后的C#:
这里VS在编译的时候将var为我们转变为了int类型。
2:Action<int>:
C#:
{
var i = 1;
Func<int,int> f = t => t+1;
i=10;
f(i);
}
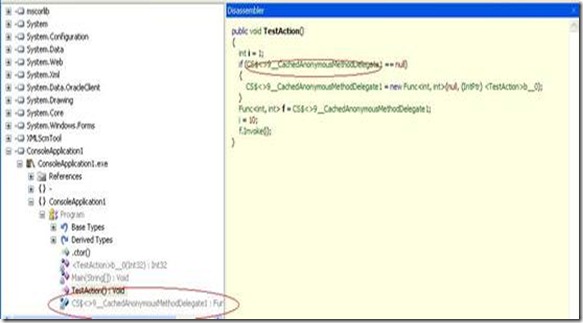
反编译后C#:
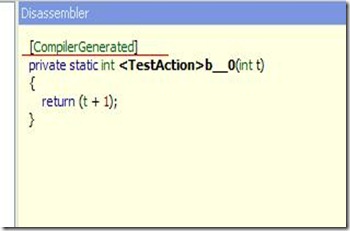
编译器为我们在这里生成了代理方法。
总结:
关于lambda表达式的编译规则:
当一个lambda expression被赋值给一个delegate类型,例如Action<T>或者Func<T, TResult>等,这个lambda expression会被编译器直接编译为
1) 当lambda expression没有使用闭包内的非局部引用也没有使用到this时,编译为一个私有静态方法;
2) 当lambda expression没有使用闭包内的非局部引用,但用到了this时,编译为一个私有成员方法;
3) 当lambda expression中引用到非局部变量,则编译为一个私有的内部类,将引用到的非局部变量提升为内部类的。
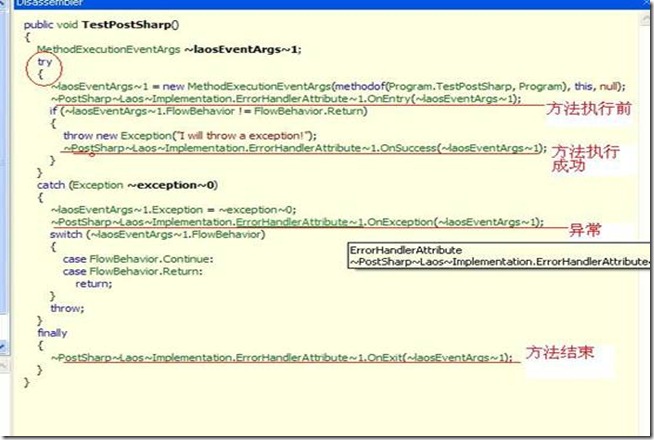
3:PostSharp:
PostSharp是结合了 MSBuild Task 和 MSIL Injection 技术,编译时静态注入实现 AOP 编程。在编译时候改变VS的编译行为。更详细的信息,请访问 PostSharp 网站
原c#:
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
new Program().TestPostSharp();
}
[ErrorHandler()]
public void TestPostSharp()
{
throw new Exception("I will throw a exception!");
}
}
[Serializable]
public class ErrorHandlerAttribute : PostSharp.Laos.OnMethodBoundaryAspect
{
public override void OnException(PostSharp.Laos.MethodExecutionEventArgs eventArgs)
{
//do some AOP operation!
Console.WriteLine(eventArgs.Method+":" +eventArgs.Exception.Message);
eventArgs.FlowBehavior = PostSharp.Laos.FlowBehavior.Continue;
}
}
}
反编译后:
今天就到此为至,只是简单的了解下IL注入实例,在后面会利用MSBuild Task+Mono Cecil 和PostSharp实现一些简单的注入实例.