servlet(2)
ServletContext
servlet的上下文
每个jvm的虚拟机中的每个web工程都只有一个ServletContext工程,即在一个web工程中,无论写了多少个Java类只要获取该类对象,那么得到的该类对象都是同一个。
如何获取该类对象
ServletContext context = getServletContext();
通过servlet类的getServletContext()方法。
作用
1.获取全局配置参数
2.获取web工程中的资源
3.存取数据,servlet间共享数据,域对象
获取全局参数
public String getInitParameter(String name):返回包含指定上下文范围初始化参数值的 String
,如果参数不存在,则返回 null。
获取的内容为:通过web.xml中的< context >元素中的的name值去获取中的value。其中< context >元素独立于 元素存在。
<context-param>
<param-name>gxwf</param-name>
<param-value>18</param-value>
</context-param>
<servlet>
<description></description>
<display-name>t1</display-name>
<servlet-name>t1</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>wf.t1</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>t1</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/t1</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
获取方式
ServletContext sc = this.getServletContext();
String s = sc.getInitParameter("gxwf");
System.out.println("name-gx = "+s);
out:
name-gx = 18
获取web应用中的properties配置文件中的信息
properties配置文件中的数据以 键 = 值
的方式存在,而Properties类会将文件解析为Java中的键值对形式
想要获取properties配置文件中的信息,先通过Properties获取该类对象
Properties p = new Properties();
再通过该对象载入properties配置文件的流对象。然后通过Properties类的getProperty()方法通过指定的键获取对应的值。
以下给出获取流对象的三种方法。
1.通过获取资源在tomcat里面的绝对路径
1.当我们要获取资源时需要先获取其绝对路径
public String getRealPath(String path):为给定虚拟路径返回包含实际路径的 String。例如,
可以通过对 "http://host/contextPath/index.html" 的请求使路径 "/index.html" 返回服务器
文件系统上的绝对文件路径,其中 contextPath 是此 ServletContext 的上下文路径。
该方法在输入path为空字符串的情况下返回工程在tomcat里面的目录(E:javaapache-tomcat-7.0.52wtpwebappsservletcontesttest(servletcontesttest是项目名称))。而输入path为相对路径的情况下会返回工程目录 + 相对路径(E:javaapache-tomcat-7.0.52wtpwebappsservletcontesttest file es.properties ),由此看看出该方法的作用是:先获取web工程在tomcat下的绝对路径,然后再拼接上资源的相对路径,然后在将该字符串返回。
ServletContext sc = this.getServletContext();
Properties p = new Properties();
String s = sc.getRealPath("");
System.out.println("t1-path = "+s);
//E:javaapache-tomcat-7.0.52wtpwebappsservletcontesttest
String path = sc.getRealPath("file/res.properties");
System.out.println("real-path = "+path);
//E:javaapache-tomcat-7.0.52wtpwebappsservletcontesttestfile
es.properties
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(path);
2.通过(InputStream in = new FileInputStream(path);)new出一个流对象。
2.getResourceAsStream 获取资源 流对象
public java.io.InputStream getResourceAsStream(String path)
以 InputStream 对象的形式返回位于指定路径上的资源
该方法类似于1中两方法的相加。
ServletContext sc = this.getServletContext();
InputStream in2 = sc.getResourceAsStream("file/res.properties");
p.load(in2);
String s2 = p.getProperty("gx");
System.out.println(s2);
3.通过classloader去获取web工程下的资源
InputStream in3 = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("../../file/res.properties");
通过class方法调用类加载器中的getResourceAsStream()该方法同2中getResourceAsStream 方法相同是由一个内得到配置文件路径的getResource(name)和得到流对象的方法组合而成
public InputStream getResourceAsStream(String name) {
URL url = getResource(name);
try {
return url != null ? url.openStream() : null;
} catch (IOException e) {
return null;
}
}
getResource(name)方法得到的是(/E:/java/apache-tomcat-7.0.52/wtpwebapps/servletcontesttest/WEB-INF/classes/)是tomcat下项目的WEB-INF/classes目录,而我们要得到(E:javaapache-tomcat-7.0.52wtpwebappsservletcontesttestfile es.properties)所以在使用时要先回到,项目的根目录。
InputStream in3 = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("../../file/res.properties");
完整的获取web应用中的properties配置文件中的信息代码
preperties文件内容
gx=18
代码
ServletContext sc = this.getServletContext();
Properties p = new Properties();
//方法1
// String s = sc.getRealPath("");
// System.out.println("t1-path = "+s);
// //E:javaapache-tomcat-7.0.52wtpwebappsservletcontesttest
// String path = sc.getRealPath("file/res.properties");
// System.out.println("real-path = "+path);
// //E:javaapache-tomcat-7.0.52wtpwebappsservletcontesttestfile
es.properties
// InputStream in = new FileInputStream(path);
// p.load(in);
// String s1 = p.getProperty("gx");
// System.out.println(s1);
//方法2
// InputStream in2 = sc.getResourceAsStream("file/res.properties");
// p.load(in2);
// String s2 = p.getProperty("gx");
// System.out.println(s2);
//方法3
URL s3 = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource("");
//file:/E:/java/apache-tomcat-7.0.52/wtpwebapps/servletcontesttest/WEB-INF/classes/
System.out.println(s3);
InputStream in3 = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("../../file/res.properties");
p.load(in3);
String s4 = p.getProperty("gx");
System.out.println(s4);
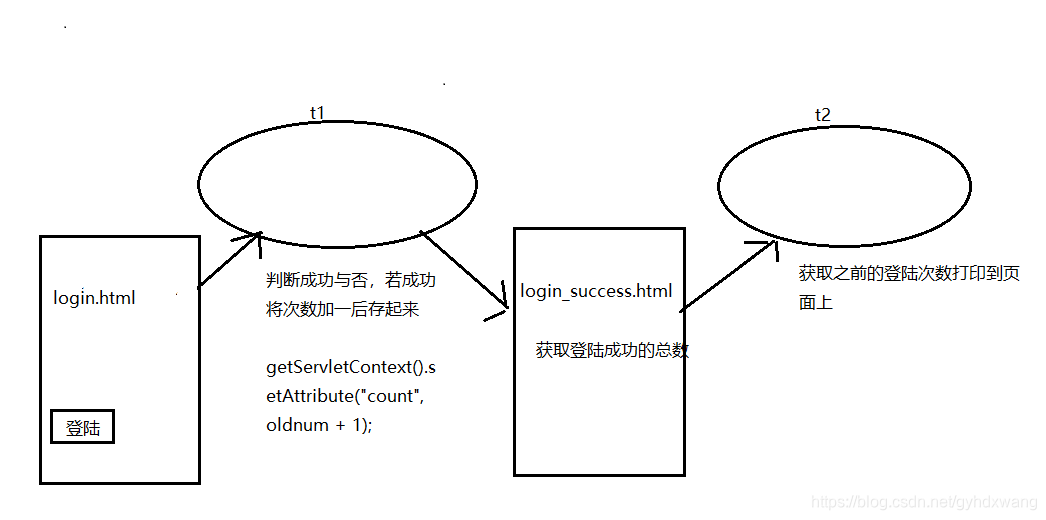
使用ServletContext存取数据。
1.定义一个html页面定义一个form表单,命名login.html
form表单中的action表示了该页面信息传入的位置(即信息传入了哪一个servlet,此处为传入t1)
注意:此处的t1不是表示下面的servlet名称t1,而是在web.xml文件配置中url-pattern中的名称
<servlet> <description></description> <display-name>t1</display-name> <servlet-name>t1</servlet-name> <servlet-class>wf1.t1</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>t1</servlet-name> <!--目标位置--> <url-pattern>/t1</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <servlet>
<body>
<h2>请输入账号与密码</h2>
<form action="t1" method = "get">
账号:<input type="text" name = "username"/><br>
密码:<input type="text" name = "password"/><br>
<input type="submit" name = "登陆"/><br>
</form>
</body>
2.定义一个servlet,名为t1
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
/*
* HttpServletRequest request:请求对象,包含从浏览器传入的信息
* HttpServletResponse response:响应对象,通过该对象返回信息给浏览器
*/
String username = request.getParameter("username");
String password = request.getParameter("password");
System.out.println("username = "+username);
System.out.println("password = "+password);
//response.getWriter()创建一个流对象,通过该对象可以向浏览器打印字符串
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
//做判断,看传入的值是否为我们想要的
if("admin".equals(username)&& "123".equals(password)) {
//在控制台打印
// System.out.println("登陆成功");
//在浏览器端打印(此处的字符串应为英文,若输入中文会产生乱码,该问题后面解决)打印的东西会覆盖以前的信息
// out.write("login success...");
//此处为计算该servlet被访问的次数
//getServletContext().getAttribute("count");该类返回一个object对象。如果对应count的值不存在,则返回null。
Object obj = getServletContext().getAttribute("count");
int oldnum = 0;
//判断obj是否为null,为null就说明该servlet第一次被访问oldnum值不变,不为null就把obj转为int并赋值给oldnum
if(obj != null) {
oldnum = (int)obj;
}
System.out.println("网站访问次数 = "+oldnum);
//将新的count与对应的值oldnum + 1设置到文件中

//通过响应一个状态码303,使网页跳转到新的页面。login_success.html
response.setStatus(303);
response.setHeader("Location", "login_success.html");
}else {
// System.out.println("登录失败");
out.write("login filed...");
}
}
3.编写新的html页面显示成功后的网页, 命名login_success.html
将跳转页面设置为t2
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>登陆成功</h2>
<a href = "t2">查看网站登陆次数</a>
</body>
</html>
4.再编写一个servlet命名t2对成功后操作
public class log_success extends HttpServlet {
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//向网页打印访问次数
Integer a = (int) getServletContext().getAttribute("count");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
//System.out.println("登陆次数 : "+a);
out.write(a.toString() +"--" + 4);
out.write(99);
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request, response);
}
}
ServletContext存取值分析
细节:
<!--
A路径: Servlet的路径
http://localhost:8080/Demo4/login
B路径: 当前这个html的路径:
http://localhost:8080/Demo4/login.html -->
<form action="login" method="get">
账号:<input type="text" name="username"/><br>
密码:<input type="text" name="password"/><br>
<input type="submit" value="登录"/>
</form>
ServletContext的创建和销毁时期
创建:服务器在启动时,会为托管的每一个web应用程序,创建一个ServletContext对象
销毁:从服务器中移除托管,或关闭web应用程序所在的服务器
servletContext的作用范围
只要在同一个项目中都可以使用。