一、使用NIO实现非阻塞Socket通信
可以参考另一篇博客:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42762133/article/details/100040141
讲得很细致
1.1 前言
从JDK1.4以来,Java提供了NIO API来开发高性能的网络服务,但是在JDK1.4之前,网络通信程序是基于阻塞式API的——即当程序执行输入,输出操作后,在这些操作返回之前会一直阻塞该线程,所以服务器必须为每个客户端都提供一个独立线程进行处理,当服务器端需要同时处理大量客户端时,这种做法会导致性能下降。使用NIO API则可以让服务器端使用一个或有限几个线程来同时处理链接到服务器端的所有程序
1.2 非阻塞式Socket通信的几个特殊类
1.2.1 Selector类
1.Selector:它是SelectableChannel对象的多路复用器,所有希望采用非阻塞方式进行通信的Channel都应该注册到Selector对象。可以通过调用此类的open()静态方法来创建Selector实例,该方法将使用系统默认的Selector来返回新的Selector.
Selector可以同时监控多个SelectableChannel的IO状态,是非阻塞IO的核心。一个Selector实例有三个SelectionKey集合。
1).所有的SelectionKey集合:代表了注册在该Selector上的Channel,这个集合可以通过keys()方法返回。
2).被选择的SelectionKey集合:代表了所有可通过select()方法获取的,需要进行IO处理的Channel,这个集合可以通过selectedKeys()返回。
3).被取消的SelectionKey集合:代表了所有被取消注册关系的Channel,在下一次执行select()方法时,这些Channel对应的SelectionKey会被彻底解除,程序通常无需直接访问该集合。
2、Selector还提供了一系列和select()相关的方法,如下所示。
1).int select():监控所有注册的Channel,当他们中间有需要处理的IO操作时,该方法返回,并将对应的SelectionKey加入到被选择的SelectionKey集合中,该方法返回这些Channel的数量。
2).int select(long timeout):可以设置超时时长的select()操作。
3).int selectNow():执行一个立即返回的select()操作,相对于无参数的select()方法而言,该方法不会阻塞线程。
4).Selector wakeup():使一个还未返回的select()方法立即返回。
1.2.2 SelectableChannel类
SelectableChannel:它代表可以支持非阻塞IO操作的Channel对象,它可被注册到Selector上,这种注册关系由SelectionKey实例表示。Selector对象提供了一个select()方法,该方法允许应用程序同时监控多个IO Channel。
应用程序可调用SelectableChannel的register()方法将其注册到指定Selector上,当该Selector上的某些SelectableChannel上有需要处理的IO操作时,程序可以调用Selector实例的select()方法获取它们的数量,并可以通过selectredKeys()方法返回它们对应的SelectionKey集合——通过该集合就可以获取所有需要进行IO处理的SelectableChannel集。
SelectableChannel对象支持阻塞和非阻塞两种模式(所有的Channel默认都是阻塞模式),必须使用非阻塞模式才可以利用非阻塞IO操作
SelectableChannel提供了如下两个方法来设置和返回该Channel的模式状态。
1). SelectableChannel configureBloking(boolean blok):设置是否采用阻塞模式。
2). boolean isBlocking():返回该Channel是否是阻塞模式。
不同的SelectableChannel所支持的操作不一样。例如ServerSocketChannel代表一个ServerSocket,它就只支持OP_ACCEPT操作。SelectableChannel提供了如下方法返回它支持的所有操作。
3). int validOps():返回一个整数值,表示这个Channel所支持的IO操作。
提示:在SelectionKey中,用静态常量定义了4中IO操作:OP_READ(1)、OP_WRITE(4)、OP_CONNECT(8)、OP_ACCEPT(16),这里任意2个、3个、4个进行按位或的结果和相加的结果相等,而且任意2个、3个、4个相加的结果总是互不相同,所以系统可以根据validOps()方法返回值确定该SelectableChannel支持的操作,例如返回5,即可知道它支持(1)和(4).
除此之外,SelectableChannel还提供了如下几个方法来获取它的注册状态。
1).boolean isRegistered():返回该Channel是否已注册在一个或多个Selector上。
2).SelectionKey keyFor(Selector sel):返回该Channel和sel Selector之间的注册关系,如果不存在注册关系,则返回null.
1.2.3 SelectorKey、ServerSocketChannel和SocketChannel
1、SelectorKey:该对象代表SelectableChannel和Selector之间的注册关系
2、ServerSocketChannel:支持非阻塞操作,对应于java.net.ServerSocket这个类,只支持OP_ACCEPT操作。该类也提供了accept()方法,功能相当于ServerSocket提供的accept()方法。
3、SocketChannel:支持非阻塞操作,对应于java.net.Socket这个类,支持OP_CONNECT,OP_READ和OP_WRITE操作。这个类还实现了ByteChannel接口,ScatteringByteChannel接口和GatheringByteChannel接口,所以可以直接通过SocketChannel来读写ByteBuffer对象。
1.3 非阻塞式服务器示意图
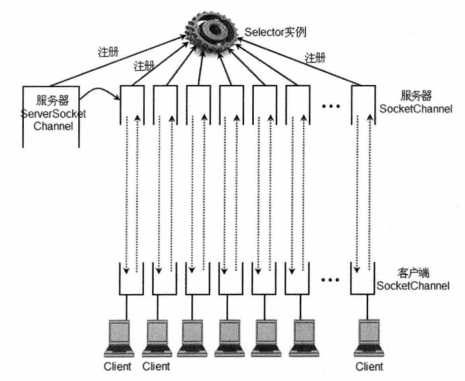
从图中可以看出,服务器上的所有Channel(包括ServerSocketChannel和SocketChannel)都需要向Selector注册,而该Selector则负责监视这些Socket的IO状态,当其中任意一个或多个Channel具有可用的IO操作时,该Selector的select()方法将会返回大于0的整数,该整数值就表示该Selector上有多少个Channel具有可用的IO操作,并提供了selectedKeys()方法来返回这些Channel对应的SelectionKey集合。正是通过Selector,使得服务器端只需要不断地调用Selector实例的select()方法,即可知道当前的所有Channel是否有需要处理的IO操作。
提示:当Selector上注册的所有Channel都没有需要处理的IO操作时,select()方法将会阻塞,调用该方法的线程被阻塞。
本示例程序使用NIO实现了多人聊天室功能,服务器使用循环不断地获取Selector的select()方法的返回值,当该返回值大于0时就处理该Selector上被选择的SelectionKey所对应的Channel。
服务器需要使用ServerSocket Channel来监听客户端的连接请求,Java对该类的设计比较难用:它不像ServerSocket可以直接指定监听某个端口;而且不能使用已有的ServerSocket的getChannel()来获取ServerSocket Channel实例。程序必须先调用它的open()静态方法返回一个返回一个ServerSocketChannel实例,再使用它的bind()方法指定它在某个端口监听。创建一个可用的ServerSocketChannel需要采用如下代码片段:
//通过一个open()方法打开一个未绑定的ServerSocketChannel实例
ServerSocketChannel server=ServerSocketChannel.open();
var isa=new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",30000);
//将该ServerSocketChannel绑定到指定IP地址
server.bind(isa);
如果需要使用非阻塞方式来处理该ServerSocketChannel,还应该设置它的非阻塞模式,并将其注册到指定的Selector。代码片段如下所示:
//设置ServerSocket以非阻塞方式工作
server.configureBlocking(false);
//将server注册到指定的Selector对象
server.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
经过上面的步骤,该ServerSocketChannel可以接受客户端的连接请求,还需要调用Selector的select()方法来监听所有Channel上的IO操作。
package NIO_NET;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.*;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
public class NServer
{
//用于检测所有channel状态的Selector——SelectableChannel对象的多路复用器
private Selector selector=null;
static final int PORT=30000;
//定义编码、解码的字符集对象
private Charset charset=Charset.forName("utf-8");
public void init() throws IOException
{
//通过Selector类的open()静态方法来创建Selector实例
selector=Selector.open();
//通过open方法打开一个未绑定的ServerSocketChannel实例
ServerSocketChannel server=ServerSocketChannel.open();
var isa=new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",PORT);
//将ServerSocketChannel绑定到指定IP地址
server.bind(isa);
//设置ServerSocketChannel以非阻塞式工作
server.configureBlocking(false);
//将server注册到指定的Selector对象
server.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while(selector.select()>0)
{
//依次处理selector上每个已选择的selectionKey
for(SelectionKey sk:selector.selectedKeys())
{
//从selector上的已选择的SelectionKey集合中删除正在处理的SelectionKey
selector.selectedKeys().remove(sk);//代码1
//如果sk对应的Channel包含客户端的连接请求
if(sk.isAcceptable())//代码2
{
System.out.println("有新连接连入");
//调用accept()方法接受连接,产生服务器端的SocketChannel
SocketChannel sc=server.accept();
//设置非阻塞模式
sc.configureBlocking(false);
//也将该SocketChannel注册到selector
sc.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
//将sk对应的channel设置成准备接受其它请求
sk.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
}
//如果sk对应的对应的Channel有数据需要读取
if(sk.isReadable())//代码3
{
//获取该SelectionKey对应的Channel,该Channel中有可读的数据
var sc=(SocketChannel)sk.channel();
//定义准备执行读取数据的ByteBuffer
ByteBuffer buff=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
var content="";
//开始读取数据
try
{
while(sc.read(buff)>0)
{
buff.flip();
content+=charset.decode(buff);
}
//打印从该sk对应的Channel里读取的数据
System.out.println("读取的数据:"+content);
//将sk对应的的Channel设置成准备下一次读取
sk.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
//如果捕获到sk对应的Channel出现了异常,即表明该Channel
//对应的Client出现了问题,所以Selector中取消sk的注册
catch (IOException ex)
{
//从Selector中指定删除SelectionKey
sk.cancel();
if(sk.channel()!=null)
{
sk.channel().close();
}
}
//如果content的长度大于0,即聊天信息不为空
if(content.length()>0)
{
//遍历该Selector里注册的所有SelectionKey
for(SelectionKey key:selector.keys())
{
//获取该key对应的Channel
Channel targetChannel=key.channel();
//如果该Channel是SocketChannel对象
if(targetChannel instanceof SocketChannel)
{
//将读到的内容写入该Channel中
var dest=(SocketChannel)targetChannel;
dest.write(charset.encode(sk.hashCode()+"发来消息:"+content));
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
new NServer().init();
}
}
上面程序启动了时创建了一个可监听请求的ServerSocketChannel,并将该Channel注册到指定的selector,接着程序直接采用循环方式不断地监控Selector对象的select()方法返回值,当该返回值大于0时,处理该Selector上所有被选择的SelectionKey。
开始处理指定的SelectionKey之后,立即从该Selector上被选择的SelectionKey集合中删除该SelectionKey,如程序中代码①处所示。
服务器端的Selector仅需要监听两种操作:连接和读数据,所以程序分别处理这两种操作,如程序代码②、代码③所示——处理连接操作时,系统只需要将连接完成后产生的SocketChannel注册到指定的Selector对象即可;处理读数据操作时,系统先从该Socket中读取数据,再将数据写入Selector上注册的所有Channel中。
上路处理流程:
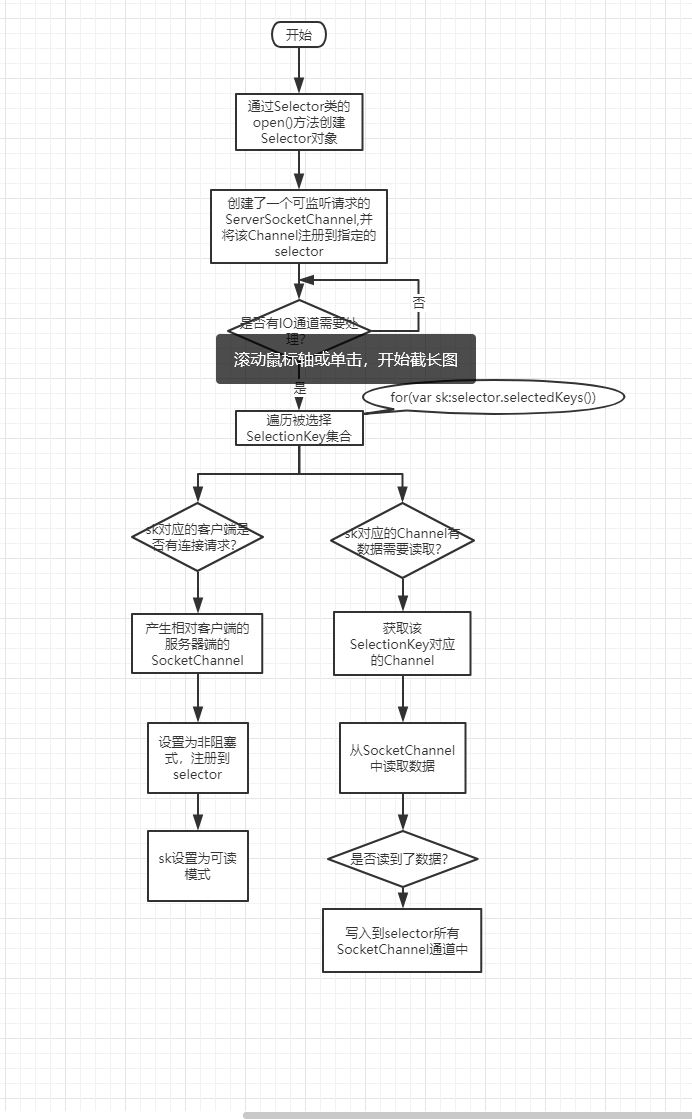
提示:使用NIO来实现服务器端时,无须使用List来保存服务器端所有SocketChannel,因为所有SocketChannel都已注册到指定的Selector对象。除此之外,当客户端关闭时会导致服务器端对应的Channel也抛出异常,而且本程序只有一个线程,因为该异常得不到处理将会导致整个服务器端退出,所以程序捕获了这种异常,并在处理异常时从从Selector删除Channel的注册。
本示例程序的客户端需要两个线程,一个线程负责读取用户键盘的输入,并将输入内容写入SocketChannel;另一个线程则不断查询Selector对象的select()方法,如果方法的返回值大于0,那就说明程序需要对相应的Channel执行IO处理。
package NIO_NET;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class NClient
{
//定义检测SocketChannel的Selector对象
private Selector selector=null;
static final int PORT=30000;
//定义编码器和解码器的字符集
private Charset charset= Charset.forName(String.valueOf(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
//客户端的SocketChannel
private SocketChannel sc=null;
public void init() throws IOException
{
selector=Selector.open();
var isa=new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",PORT);
//调用Open()静态方法连接到主机
sc=SocketChannel.open(isa);
//设置该sc以非阻塞方式工作
sc.configureBlocking(false);
//将socketChannel注册到指定的Selector
sc.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
//启动读取服务器的线程
new ClientThread().start();
//创建键盘输入流
var scan=new Scanner(System.in);
while(scan.hasNextLine())
{
//读取键盘输入
String line=scan.nextLine();
//将键盘输入内容写入到SocketChannel中
sc.write(charset.encode(line));
}
}
//定义读取服务器端数据的线程
private class ClientThread extends Thread
{
public void run()
{
try
{
while(selector.select()>0)//①
{
//遍历每个又可用的IO操作的Channel对应的SelectionKey
for(var sk:selector.selectedKeys())
{
//删除正在处理的SelectionKey
selector.selectedKeys().remove(sk);
//如果该SelectionKey对应的Channel有数据可读
if(sk.isReadable())
{
//使用NIO读取Channel中的数据
SocketChannel sc=(SocketChannel)sk.channel();
ByteBuffer buff=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
String content="";
while (sc.read(buff)>0)
{
buff.flip();
content+=charset.decode(buff);
}
//打印读取的内容
System.out.println(content);
//为下一次读取数据做好准备
sk.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
}
}
}
catch (IOException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
throws IOException
{
new NClient().init();
}
}
运行结果:
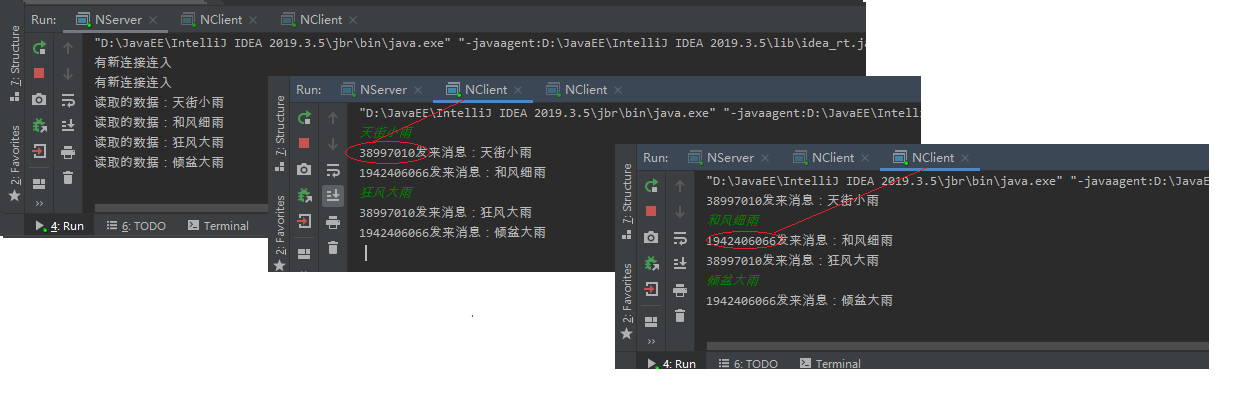
相比之下客户端的程序要简单多了,客户端只有一个SocketChannel,将SocketChannel注册到指定的Selector后,程序启动另外一个线程来监听该Selector即可。如果程序监听到Selector的select()方法返回值大于0,表明该Selecotr上有需要进行IO处理的Channel,接着程序取出该Channel,并使用NIO读取该Channel中的数据。
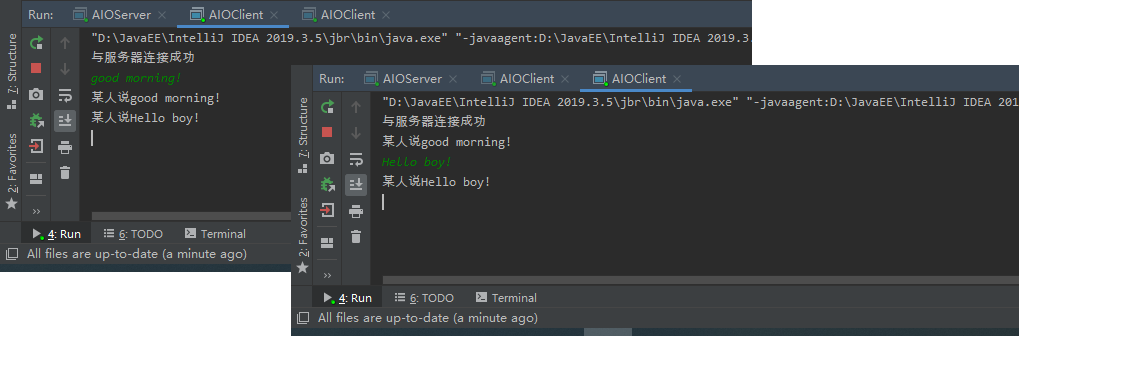
二、使用AIO实现非阻塞通信
Java 7的NIO.2提供了异步Channel支持,这种异步Channel可以提供更高效的IO,这种基于异步的Channel的IO也被称为异步IO(Asychronous IO).
2.1 同步IO和异步IO
按照POSIX的标准来划分IO,可以把IO分为两类:同步IO和异步IO
对于IO的操作可以分为两步:①程序发出IO请求;②完成实际的IO操作
阻塞式IO和非阻塞IO都是针对第一步来进行划分的,如果程序发出IO请求会阻塞线程,这就是阻塞IO;如果发出的IO请求没有阻塞线程,就是非阻塞式IO。
同步IO和异步IO的区别在于第二步——如果实际的IO的操作由操作系统完成,再将结果返回给应用程序,这就是异步IO;
如果实际的IO操作需要应用程序本身去执行,会阻塞线程,那就是同步IO。
2.2 AIO的接口和实现类
NIO.2提供了一系列以Asynchronous开头的Channel接口和类,如图所示:
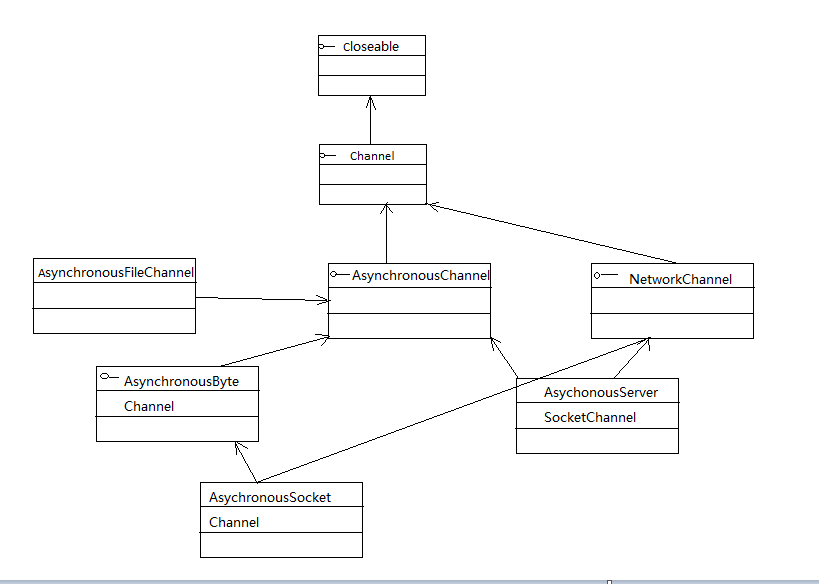
其中AsychronousSocketChannel、AsynchronousServerSocketChannel是支持TCP通信的异步Channel,也是本节介绍的重点。
2.3 AsynchronousServerSocketChannel类
2.3.1 创建AsynchronousServerSocketChannel实例
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel是一个负责监听的Channel,与ServerSocketChannel相似,创建可以的AsynchronousServerSocketChannel需要两步:
(1)调用它的open()静态方法创建一个未监听端口的AsynchronousServerSocketChannel。
(2)调用AsynchronousServerSocketChannel的bind()方法指定该Channel在指定地址、指定端口监听。
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel的open()方法有两个版本:
(1)open():创建一个默认的AsynchronousServerSocketChannel
(2)open(AsynchronousChannelGroup group):使用指定的AsynchronousChannelGroup来创建AsynchronousServerSocketChannel。
AsynchronousChannelGroup是异步channel的分组管理器,它会实现资源共享。创建AsynchronousChannelGroup时需要传入一个ExecutorService,也即是说,他会绑定一个线程池,该线程池负责两个任务:处理IO事件和触发CompletionHandler.
AIO中的AsychronousSocketChannel、AsynchronousServerSocketChannel都允许使用线程池来进行管理,因此创建AsynchronousSocketChannel时也可以传入一个AsynchronousChannelGroup对象进行分组管理。
实际应用:
直接创建AsynchronousServerSocketChannel的代码片段:
//以指定的线程池来创建一个AsynchronousServerSocketChannel
serverChannel=AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open().bind(new InetSocketAddress(PORT));
使用AsychronousChannelGroup创建AsynchronousServerSocketChannel的代码片段:
//创建线程池
ExecutorService executor=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(80);
//以指定线程池来创建一个AsychronousChannelGroup
AsychronousChannelGroup channelGroup=AsynchronousChannelGroup.withThreadPool(executor);
//以指定的线程池来创建一个AsynchronousServerSocketChannel
serverChannel=AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open(channelGroup).bind(new InetSocketAddress(PORT));
2.3.2 AsynchronousServerSocketChannel执行监听accept()
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel创建成功后,接下来就调用它的accept()方法来接受来自客户端的连接请求,由于异步IO的实际IO操作交给系统来完成,因此程序并不知道异步IO操作什么时候完成——也就是说,程序调用AsynchronousServerSocketChannel的accept()方法之后,当前线程会阻塞,程序不知道什么时候accept()方法会接收到客户端的请求。为了解决这个问题,AIO为accept()方法提供了如下两个版本:
(1)Future<AsynchronousSocketChannel> accept():接受客户端的请求。
如果程序需要获得连接成功后返回AsynchronousSocketChannel,
该应该调用该方法返回的Futrue对象的get()方法——get()方法会阻塞线程,
因此这种方式依然会阻塞当前线程。
(2)<A> void accept(A attachment,CompletionHandler<AsynchronousSocketChannel,? super A> handler):
接受来自客户端的请求,连接成功或失败都会触发CompletionHandler对象里相应的方法。
其中AsynchronousSocketChannel就代表连接成功后返回AsynchronousSocketChannel。
CompletionHandler是一个接口,该接口里定义了两个方法:
(1)completed(V result,A attachment):当IO操作完成时触发该操作。该方法的第一个参数代表IO操作所返回的对象;第二个参数代表发起IO操作时传入的附加参数。
(2)failed(Throwable exc,A aatachment):当IO操作失败时触发该方法。该方法的第一个参数代表IO操作失败时引发的异常或错误;第二个参数代表发起IO操作时传入的附加参数。
2.3.3 总结:创建AsynchronousServerSocketChannel的步骤
1、调用open()静态方法创建AsynchronousServerSocketChannel;
2、调用AsynchronousServerSocketChannel的bind()方法让它在指定IP地址、端口监听;
3、调用AsynchronousServerSocketChannel的accept()方法接受连接请求。
下面使用最简单、最少的步骤来实现一个基于AsynchronousServerSocketChannel的服务器端
package AIO;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousSocketChannel;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
public class SimpleAIOServer
{
static final int PORT=30000;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
try(
//①创建AsynchronousServerSocketChannel对象
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverChannel=
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open();
)
{
//②指定在指定地址、端口监听
serverChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",PORT));
while(true)
{
//③采用循环的方式接受来自客户端的连接
Future<AsynchronousSocketChannel> future=serverChannel.accept();
//获取连接成功后返回的AsynchronousSocketChannel
AsynchronousSocketChannel socketChannel=future.get();
//执行输出,下一小节介绍
socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("欢迎来到AIO的世界".getBytes("UTF-8"))).get();
}
}
}
}
上面程序中的①②③号代码就代表了使用AsynchronousServerSocketChannel的三个基本步骤,由于该程序力求简单,因此程序未使用CompletionHandler监听器。当程序收到来自客户端的连接之后,服务器端就产生一个与客户端相对应的AsynchronousSocketChannel,它就可以执行实际的IO操作了。
2.4 AsynchronousSocketChannel类
2.4.1 创建AsynchronousSocketChannel实例
调用open()静态方法创建AsynchronousSocketChannel实例,同样调用open()方法时同样可以指定一个AsynchronousChannelGroup作为分组管理器。
AsynchronousSocketChannel的open()方法有两个版本:
(1)open():创建一个默认的AsynchronousSocketChannel
(2)open(AsynchronousChannelGroup group):使用指定的AsynchronousChannelGroup来创建AsynchronousServerSocketChannel。
AsynchronousChannelGroup是异步channel的分组管理器,它会实现资源共享。创建AsynchronousChannelGroup时需要传入一个ExecutorService,也即是说,他会绑定一个线程池,该线程池负责两个任务:处理IO事件和触发CompletionHandler.
2.4.2 创建连接
调用AsynchronousSocketChannel的connect()方法连接到指定的IP地址、指定端口的服务器。
2.4.3 进行读写操作
调用AsynchronousChannel的read()、write()方法进行读写。
AsynchronousChannel的connect()、read()、write()方法都有两个版本:一个返回Future对象的版本,一个需要传入CompletionHandler参数的版本。
对于Future对象的版本,必须等到Future对象的get()方法返回时IO操作才真正完成;对于需要传入传入CompletionHandler参数的版本,则可以通过CompletionHandler在IO操作完成时触发相应的方法。
下面先用返回Future对象的read()方法来读取服务器端响应数据
package AIO;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousSocketChannel;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
public class SimpleAIOClient
{
static final int PORT=30000;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
//用于读取数据的ByteBuffer
ByteBuffer buff=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
Charset utf=Charset.forName("utf-8");
try(
//1、创建AsynchronousSocketChannel
AsynchronousSocketChannel clientChannel=AsynchronousSocketChannel.open()
)
{
//2、连接到远程服务器
clientChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",PORT)).get();//4
//3、从clientChannel中读取数据
clientChannel.read(buff).get(); //5
buff.flip();
String content=String.valueOf(utf.decode(buff));
System.out.println("服务器发来的消息:"+content);
}
}
}
上面程序中的1、2、3就代表了AsynchronousSocketChannel的三个基本步骤,当程序获得了连接好的AsynchronousSocketChannel之后,就可通过它来执行实际的IO操作了。
先运行服务器端,在运行客户端的运行结果:
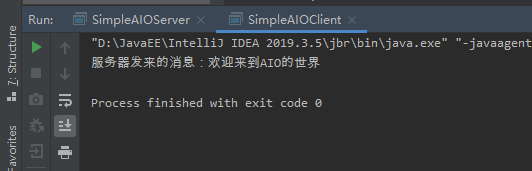
程序中没有用到4、5代码出的get()方法的返回值,但这两个方法必须用到get()方法!因为程序在连接远程服务器、读取服务器端数据时,都没有传入CompletionHandler_因此程序无法通过该监听器在IO操作完成时,触发特定的动作,程序必须调用Future对象的值都get()方法,并等到get()方法完成时才能确定异步IO操作以已经执行完成。
上面代码5处的代码其实可以换成:
Future future=clientChannel.read(buff);
future.get();
这就体现了异步思想,因为程序并不知道读、写、连接在什么时候完成,而且当前线程不会阻塞。为了解决异步的问题,AIO才提供二了两个版本的read()、write()、connect()方法。
2.5 AIO多人通信
服务器端代码
package AIO;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousChannelGroup;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.CompletionHandler;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class AIOServer
{
static final int PORT=30000;
final static String UTF_8="utf-8";
static List<AsynchronousSocketChannel> channelList=new ArrayList<>();
public void startListen() throws InterruptedException,Exception
{
//创建一个线程池
ExecutorService executor= Executors.newFixedThreadPool(20);
//已指定线程池创建一个AsychronousChannelGroup
AsynchronousChannelGroup channelGroup=AsynchronousChannelGroup.withThreadPool(executor);
//以指定的线程池来创建一个AsynchronousServerSocketChannel
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverChannel=AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open()
//指定监听本机的端口
.bind(new InetSocketAddress(PORT));
//使用CompletionHandler接受来自客户端的连接请求
serverChannel.accept(null,new AcceptHandler(serverChannel));//1
Thread.sleep(100000);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
var server=new AIOServer();
server.startListen();
}
}
//实现自己的complementionHandler类
class AcceptHandler implements CompletionHandler<AsynchronousSocketChannel,Object>
{
private AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverChannel;
public AcceptHandler(AsynchronousServerSocketChannel sc)
{
this.serverChannel=sc;
}
//定义一个ByteBuffer准备读取数据
ByteBuffer buff=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//当实际的IO操作完成时触发该方法
@Override
public void completed(final AsynchronousSocketChannel sc, Object attachment)
{
//记录新连接进来的Channel
AIOServer.channelList.add(sc);
//准备接受客户端的下一次连接
serverChannel.accept(null,this);
sc.read(buff, null, new CompletionHandler<Integer, Object>() //2
{
@Override
public void completed(Integer result,Object attachment)
{
buff.flip();
//将buff中的内容转换为字符串
String content= StandardCharsets.UTF_8.decode(buff).toString();
//遍历每个Channel,将受到的信息写入各个Channel中
for(AsynchronousSocketChannel c:AIOServer.channelList)
{
try
{
c.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(content.getBytes(AIOServer.UTF_8))).get();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
buff.clear();
//读取下一次数据
sc.read(buff,null,this);
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable ex,Object attachment)
{
System.out.println("读取数据失败:"+ex);
//从该Channel中读取数据失败,就将该Channel输出
AIOServer.channelList.remove(sc);
}
});
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable throwable, Object o)
{
System.out.println("连接失败");
}
}
上面程序与前一个服务器编程步骤大致相似,但这个程序使用了CompletionHandler监听来自客户端的连接,如代码1所示;当连接成功后,系统会自动触发该监听器的completed()方法——在该方法中,执行IO读操作时,执行读操作时,再次使用了CompletionHandler去读取服务器端的数据,如代码2所示。
本程序的客户端向服务器发送信息,并显示其他用户的聊天信息:
package AIO;
import NIO_NET.NClient;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.CharBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousChannelGroup;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.CompletionHandler;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class AIOClient
{
final static String UTF_8="utf-8";
final static int PORT=30000;
//与服务器端通信的异步Channel
AsynchronousSocketChannel clientChannel;
//向服务器端写数据
public void init() throws IOException
{
//定义一个ByteBuffer准备读取数据
final ByteBuffer buff=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//创建一个线程池
ExecutorService executor= Executors.newFixedThreadPool(80);
//以指定线程池来创建一个AsychronousChannelGroup
AsynchronousChannelGroup group=AsynchronousChannelGroup.withThreadPool(executor);
//以指定的线程池来创建一个AsynchronousSocketChannel
clientChannel=AsynchronousSocketChannel.open(group);
//让AsynchronousSocketChannel连接到指定IP地址、指定端口
clientChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",PORT));
System.out.println("与服务器连接成功");
//启动写入服务器端的线程
new ClientThread().start();
clientChannel.read(buff, null,
new CompletionHandler<Integer, Object>()
{
@Override
public void completed(Integer integer, Object o)
{
buff.flip();
//将buff中的数据转换为字符串
String content= StandardCharsets.UTF_8.decode(buff).toString();
//显示服务器端发来的数据
System.out.println("某人说"+content);
buff.clear();
clientChannel.read(buff,null,this);
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable throwable, Object o)
{
System.out.println("读取数据失败");
}
});
}
private class ClientThread extends Thread
{
public void run()
{
Charset charset=Charset.forName("utf-8");
CharBuffer cbuff=CharBuffer.allocate(1024);
Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in);
while(scan.hasNextLine())
{
cbuff.put(scan.nextLine());
cbuff.flip();
clientChannel.write(charset.encode(cbuff));
cbuff.clear();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
new AIOClient().init();
}
}
运行结果: