Given a binary tree with the following rules:
root.val == 0- If
treeNode.val == xandtreeNode.left != null, thentreeNode.left.val == 2 * x + 1 - If
treeNode.val == xandtreeNode.right != null, thentreeNode.right.val == 2 * x + 2
Now the binary tree is contaminated, which means all treeNode.val have been changed to -1.
You need to first recover the binary tree and then implement the FindElements class:
FindElements(TreeNode* root)Initializes the object with a contamined binary tree, you need to recover it first.bool find(int target)Return if thetargetvalue exists in the recovered binary tree.
Example 1:
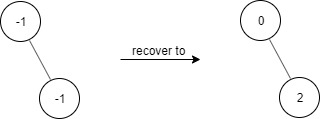
Input ["FindElements","find","find"] [[[-1,null,-1]],[1],[2]] Output [null,false,true] Explanation FindElements findElements = new FindElements([-1,null,-1]); findElements.find(1); // return False findElements.find(2); // return True
Example 2:
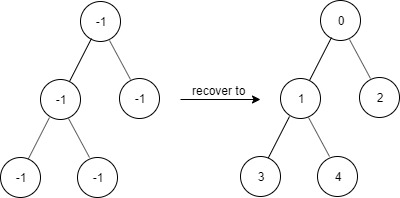
Input ["FindElements","find","find","find"] [[[-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]],[1],[3],[5]] Output [null,true,true,false] Explanation FindElements findElements = new FindElements([-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]); findElements.find(1); // return True findElements.find(3); // return True findElements.find(5); // return False
Example 3:
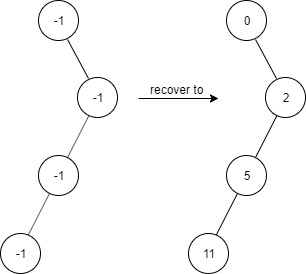
Input ["FindElements","find","find","find","find"] [[[-1,null,-1,-1,null,-1]],[2],[3],[4],[5]] Output [null,true,false,false,true] Explanation FindElements findElements = new FindElements([-1,null,-1,-1,null,-1]); findElements.find(2); // return True findElements.find(3); // return False findElements.find(4); // return False findElements.find(5); // return True
Constraints:
TreeNode.val == -1- The height of the binary tree is less than or equal to
20 - The total number of nodes is between
[1, 10^4] - Total calls of
find()is between[1, 10^4] 0 <= target <= 10^6
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ class FindElements { TreeNode t3; public FindElements(TreeNode root) { TreeNode t = new TreeNode(0);
t3 = t; F(root, t); } public void F(TreeNode root, TreeNode t){ if(root == null) return; if(root.left != null){ TreeNode t1 = new TreeNode(t.val * 2 + 1); t.left = t1; F(root.left, t.left); } if(root.right != null){ TreeNode t2 = new TreeNode(t.val * 2 + 2); t.right = t2; F(root.right, t.right); } } public boolean find(int target) { return find1(t3, target); //return false; } public boolean find1(TreeNode x, int target){ if(x == null) return false; if(x.val == target) return true; return find1(x.left, target) || find1(x.right, target); } } /** * Your FindElements object will be instantiated and called as such: * FindElements obj = new FindElements(root); * boolean param_1 = obj.find(target); */
这题巩固了几个知识点:
1. 克隆tree,写两个方法,一个初始化根的value,另一个void方法不停的call复制树和被复制树.也是如果null就return,不然就判断left和right是否为空,不空就新建node,连接,然后recursively call
2.查找tree的元素,如果null就false,如果相等就true,否则查找左右子树。
class FindElements { Set<Integer> set; /** * Build the tree using dfs, put all values to the set. Then for find use set for lookups */ public FindElements(TreeNode root) { set = new HashSet(); dfs(root, 0); } void dfs(TreeNode n, int val) { if (n == null) return; set.add(val); dfs(n.left, 2*val + 1); dfs(n.right, 2*val + 2); } public boolean find(int target) { return set.contains(target); } }
大佬的方法,用set存value,屌
class FindElements { TreeNode t3; Set<Integer> set; public FindElements(TreeNode root) { TreeNode t = new TreeNode(0); set = new HashSet(); set.add(0); t3 = t; F(root, t); } public void F(TreeNode root, TreeNode t){ if(root == null) return; if(root.left != null){ TreeNode t1 = new TreeNode(t.val * 2 + 1); set.add(t.val * 2 + 1); t.left = t1; F(root.left, t.left); } if(root.right != null){ TreeNode t2 = new TreeNode(t.val * 2 + 2); set.add(t.val * 2 + 2); t.right = t2; F(root.right, t.right); } } public boolean find(int target) { return set.contains(target); } }
再修改一下我的。