Given a reference of a node in a connected undirected graph, return a deep copy (clone) of the graph. Each node in the graph contains a val (int) and a list (List[Node]) of its neighbors.
Example:
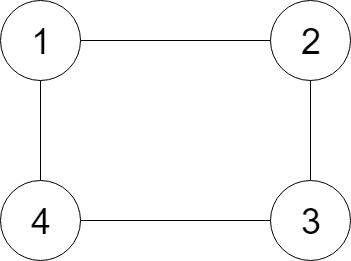
Input:
{"$id":"1","neighbors":[{"$id":"2","neighbors":[{"$ref":"1"},{"$id":"3","neighbors":[{"$ref":"2"},{"$id":"4","neighbors":[{"$ref":"3"},{"$ref":"1"}],"val":4}],"val":3}],"val":2},{"$ref":"4"}],"val":1}
Explanation:
Node 1's value is 1, and it has two neighbors: Node 2 and 4.
Node 2's value is 2, and it has two neighbors: Node 1 and 3.
Node 3's value is 3, and it has two neighbors: Node 2 and 4.
Node 4's value is 4, and it has two neighbors: Node 1 and 3.
Note:
- The number of nodes will be between 1 and 100.
- The undirected graph is a simple graph, which means no repeated edges and no self-loops in the graph.
- Since the graph is undirected, if node p has node q as neighbor, then node q must have node p as neighbor too.
- You must return the copy of the given node as a reference to the cloned graph.
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node { public int val; public List<Node> neighbors; public Node() {} public Node(int _val,List<Node> _neighbors) { val = _val; neighbors = _neighbors; } }; */ class Solution { public Node cloneGraph(Node node) { if (node == null) { return null; } return cloneHelper(node); } public static Map<Node, Node> newNodesMap = new HashMap<>(); public static Node cloneHelper(Node node) { if (!newNodesMap.containsKey(node)) { Node newNode = new Node(node.val, new ArrayList<>()); newNodesMap.put(node, newNode); } else { return newNodesMap.get(node); } for (Node temp : node.neighbors) { Node neighbour = cloneHelper(temp); newNodesMap.get(node).neighbors.add(neighbour); } return newNodesMap.get(node); } }
复杂DFS