Given a binary tree, flatten it to a linked list in-place.
For example, given the following tree:
1 / 2 5 / 3 4 6
The flattened tree should look like:
1
2
3
4
5
6
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ class Solution { //要求123456,那么recursion就是654321 //如何遍历得到654321?right->left->root即可 private TreeNode prev = null; public void flatten(TreeNode root) { if(root == null) return; flatten(root.right); flatten(root.left); root.right = prev; root.left = null; prev = root; } }
有意思
https://www.cnblogs.com/springfor/p/3864355.html
2020/7/10,我垃圾,看不懂递归,但能看懂stack做法(在大佬的帮助下
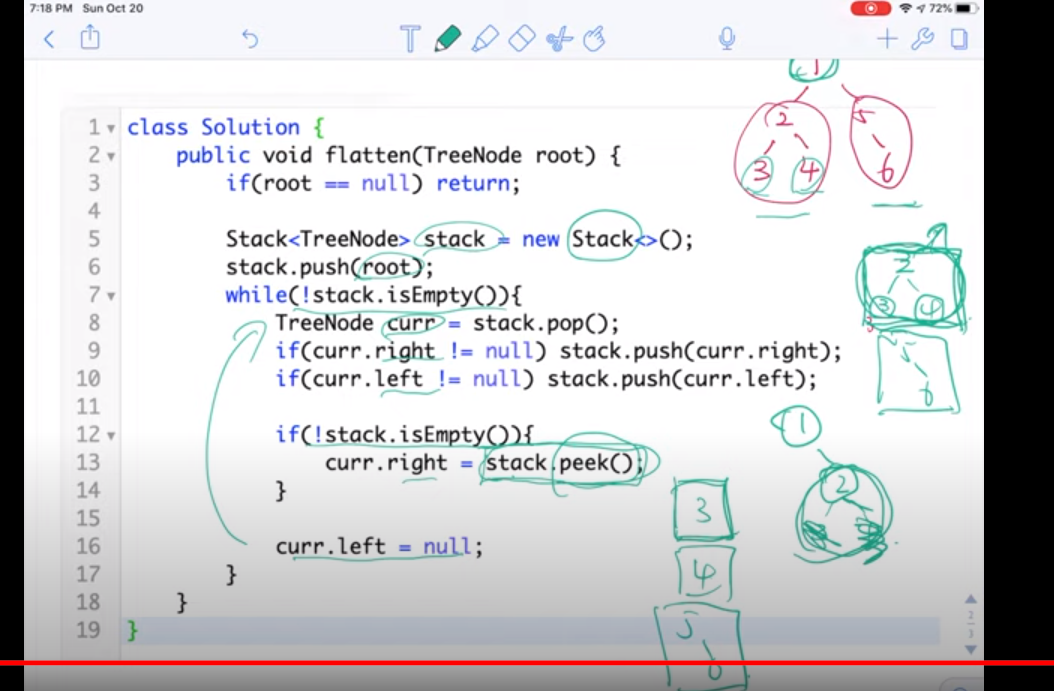
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v2ob-ek9TgE
class Solution { public void flatten(TreeNode root) { if(root == null) return; Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack(); stack.push(root); while(!stack.isEmpty()){ TreeNode cur = stack.pop(); if(cur.right != null) stack.push(cur.right); if(cur.left != null) stack.push(cur.left); if(!stack.isEmpty()){ cur.right = stack.peek(); } cur.left = null; } } }
用stack来保证永远优先处理left node,先把rootpush进去,然后在循环里pop栈顶,加入right再加入left,因为用的时候先用left。
如果栈不为空的话,就让cur.right = stack.peek(),这样就能让cur优先指向left node了
然后继续循环直到结束