1. Shrinkage(缩减) Methods
当特征比样本点还多时(n>m),输入的数据矩阵X不是满秩矩阵,在求解(XTX)-1时会出现错误。接下来主要介绍岭回归(ridge regression)和前向逐步回归(Foward Stagewise Regression)两种方法。
1.1 岭回归(ridge regression)
简单来说,岭回归就是在矩阵XTX上加上一个![]() 从而使得矩阵非奇异,进而能进行求逆。其中矩阵I是一个单位矩阵,
从而使得矩阵非奇异,进而能进行求逆。其中矩阵I是一个单位矩阵,![]() 是一个调节参数。
是一个调节参数。
岭回归的回归系数计算公式为:
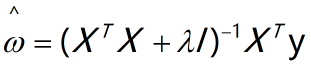
岭回归最先用来处理特征数多于样本的情况,现在也用于在估计中加入偏差,来得到更好的估计。当![]() =0时,岭回归和普通线性回归一样,当
=0时,岭回归和普通线性回归一样,当![]() 趋近于正无穷时,回归系数接近于0。可以通过交叉验证的方式得到使测试结果最好的
趋近于正无穷时,回归系数接近于0。可以通过交叉验证的方式得到使测试结果最好的![]() 值。
值。
岭回归代码:
1 # encoding: utf-8 2 ''' 3 @Author: shuhan Wei 4 @File: ridgeRegression.py 5 @Time: 2018/8/24 11:16 6 ''' 7 import numpy as np 8 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 9 10 def loadDataSet(fileName): 11 numFeat = len(open(fileName).readline().split('\t')) - 1 12 dataMat = []; labelMat = [] 13 fr = open(fileName) 14 for line in fr.readlines(): 15 lineArr = [] 16 curLine = line.strip().split('\t') 17 for i in range(numFeat): 18 lineArr.append(float(curLine[i])) 19 dataMat.append(lineArr) 20 labelMat.append(float(curLine[-1])) 21 return dataMat, labelMat 22 23 24 """ 25 函数说明:岭回归函数 w=(XT*X+lamI)-1 * XT*y 26 Parameters: 27 xMat - x数据集 28 yMat - y数据集 29 lam - 用户自定义参数 30 Returns: 31 ws - 回归系数 32 """ 33 def ridgeRegres(xMat, yMat, lam=0.2): 34 xTx = xMat.T * xMat 35 denom = xTx + np.eye(np.shape(xMat)[1]) * lam 36 if np.linalg.det(denom) == 0.0: 37 print("The matrix is singular, cannot do inverse") 38 return 39 ws = denom.I * (xMat.T * yMat) 40 return ws 41 42 43 """ 44 函数说明:测试岭回归 45 Parameter: 46 xArr - x数据集矩阵 47 yArr - y数据集矩阵 48 Returns: 49 wMat - 回归系数矩阵,30组系数 50 """ 51 def ridgeTest(xArr, yArr): 52 xMat = np.mat(xArr); yMat = np.mat(yArr).T 53 #对数据进行标准化处理 54 yMean = np.mean(yMat, 0) 55 yVar = np.var(yMat,0) 56 yMat = yMat - yMean 57 xMeans = np.mean(xMat,0) #行操作 58 xVar = np.var(xMat, 0) 59 xMat = (xMat - xMeans) / xVar 60 numTestPts = 30 # 在30个不同lambda值下 61 wMat = np.zeros((numTestPts, np.shape(xMat)[1])) #系数矩阵 62 for i in range(numTestPts): 63 ws = ridgeRegres(xMat, yMat, np.exp(i-10)) 64 wMat[i,:] = ws.T 65 return wMat 66 67 """ 68 函数说明:绘制回归系数与lambda关系曲线 69 """ 70 def plotLambda(ridgeWeights): 71 plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] 72 plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False 73 fig = plt.figure() 74 ax = fig.add_subplot(111) 75 ax.plot(ridgeWeights) 76 ax_title_text = ax.set_title(u'log(lambada)与回归系数的关系') 77 ax_xlabel_text = ax.set_xlabel(u'log(lambada)') 78 ax_ylabel_text = ax.set_ylabel(u'回归系数') 79 plt.setp(ax_title_text, size=20, weight='bold', color='red') 80 plt.setp(ax_xlabel_text, size=10, weight='bold', color='black') 81 plt.setp(ax_ylabel_text, size=10, weight='bold', color='black') 82 plt.show() 83 84 85 if __name__ == '__main__': 86 abX, abY = loadDataSet('abalone.txt') 87 ridgeWeights = ridgeTest(abX, abY) 88 plotLambda(ridgeWeights)
1.2 前向逐步回归(Foward Stagewise Regression)
前向逐步回归算法属于一种贪心算法,即每一步都尽可能减少误差,一开始所有的权重都设置为1,然后每一步对权重增加或减少一个很小的值。
算法是伪代码如下:
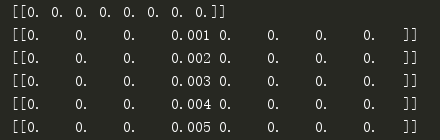
数据标准化,使其分布满足0均值和单位方差 在每轮迭代过程中: 设置当前最小误差lowestError为正无穷 对每个特征: 增大或缩小: 改变一个系数得到一个新的W 计算新W下的误差 如果误差Error小于lowestError,设置wbest = 当前W 将W设置为新的wbest
代码如下:
1 # encoding: utf-8 2 ''' 3 @Author: shuhan Wei 4 @File: stageWise.py 5 @Time: 2018/8/24 13:10 6 ''' 7 import numpy as np 8 import regression 9 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 10 11 12 def regularize(xMat):#regularize by columns 13 inMat = xMat.copy() 14 inMeans = np.mean(inMat,0) #calc mean then subtract it off 15 inVar = np.var(inMat,0) #calc variance of Xi then divide by it 16 inMat = (inMat - inMeans)/inVar 17 return inMat 18 19 20 def rssError(yArr,yHatArr): #yArr and yHatArr both need to be arrays 21 return ((yArr-yHatArr)**2).sum() 22 23 24 """ 25 函数说明:向前逐步回归算法 26 Parameters: 27 xArr - x数据集 28 yArr - y数据集 29 eps - 每次迭代步长 30 numIt - 迭代次数 31 Returns: 32 系数矩阵 33 """ 34 def stageWise(xArr, yArr, eps=0.01, numIt = 100): 35 xMat = np.mat(xArr) 36 yMat = np.mat(yArr).T 37 yMean = np.mean(yMat, 0) 38 yMat = yMat - yMean 39 xMat = regularize(xMat) 40 m, n = np.shape(xMat) 41 returnMat = np.zeros((numIt, n)) # testing code remove 42 ws = np.zeros((n, 1));wsTest = ws.copy();wsMax = ws.copy() 43 for i in range(numIt): # could change this to while loop 44 print(ws.T) 45 lowestError = np.inf; #初始化最小误差为正无穷 46 for j in range(n): #遍历每个特征 47 for sign in [-1, 1]: 48 wsTest = ws.copy() 49 wsTest[j] += eps * sign 50 yTest = xMat * wsTest 51 rssE = rssError(yMat.A, yTest.A) 52 if rssE < lowestError: 53 lowestError = rssE 54 wsMax = wsTest 55 ws = wsMax.copy() 56 returnMat[i, :] = ws.T 57 return returnMat 58 59 60 def plot(weights): 61 plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] 62 plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False 63 fig = plt.figure() 64 ax = fig.add_subplot(111) 65 ax.plot(weights) 66 ax_title_text = ax.set_title(u'回归系数与迭代次数的关系') 67 ax_xlabel_text = ax.set_xlabel(u'迭代次数') 68 ax_ylabel_text = ax.set_ylabel(u'回归系数') 69 plt.setp(ax_title_text, size=20, weight='bold', color='red') 70 plt.setp(ax_xlabel_text, size=10, weight='bold', color='black') 71 plt.setp(ax_ylabel_text, size=10, weight='bold', color='black') 72 plt.show() 73 74 75 if __name__ == '__main__': 76 abX, abY = regression.loadDataSet('abalone.txt') 77 weights = stageWise(abX, abY, 0.001, 5000) 78 plot(weights)
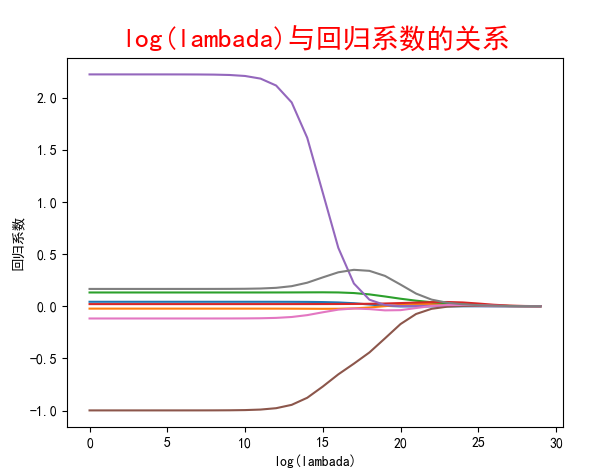
结果:
中间省略
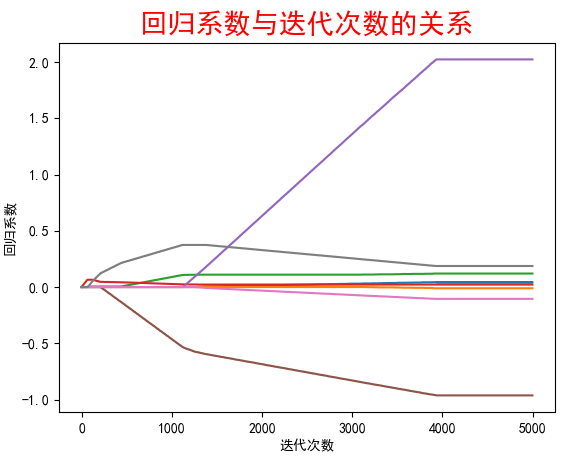
当迭代次数很大时,接近于普通最小二乘回归
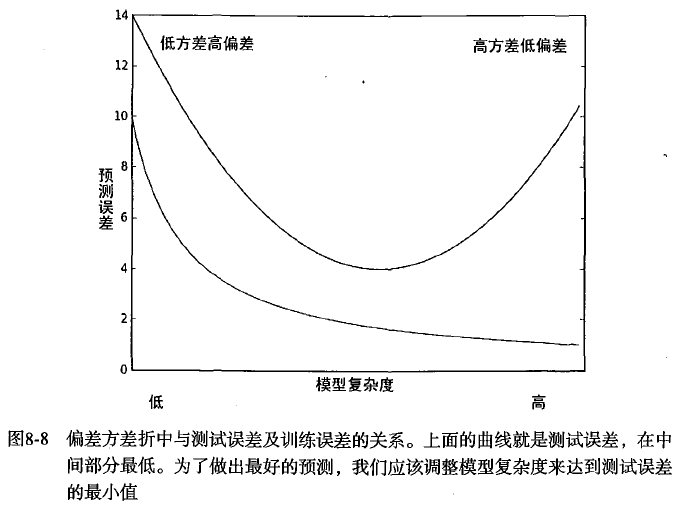
小结:当使用缩减方法时,把一些系数的回归系数缩减到0,减少了模型的复杂度,增加了模型的偏差,同时减小了方差
权衡偏差和方差
1.3 实例:预测乐高玩具价格
在交叉验证中使用90%数据集作为训练数据,10%做为测试数据,通过10次迭代之后,求30个不同lambda下的误差均值,再选择最小的误差,从而获取最优回归系数。
使用岭回归时需要对x数据集进行标准化,对y数据集进行中心化。最后需要对计算的回归系数进行还原,同时截距等于![]()
# encoding: utf-8 ''' @Author: shuhan Wei @File: legao.py @Time: 2018/8/24 16:16 ''' #BeautifulSoup是一个可以从HTML或XML文件中提取数据的Python库 import random from bs4 import BeautifulSoup import numpy as np import regression import ridgeRegression def rssError(yArr,yHatArr): #yArr and yHatArr both need to be arrays return ((yArr-yHatArr)**2).sum() def scrapePage(inFile, outFile, yr, numPce, origPrc): # 打开并读取HTML文件 with open(inFile, encoding='utf-8') as fr: html = fr.read() fw = open(outFile, 'a') # a是追加模式 soup = BeautifulSoup(html) i = 1 currentRow = soup.findAll('table', r="%d" % i) while (len(currentRow) != 0): currentRow = soup.findAll('table', r="%d" % i) title = currentRow[0].findAll('a')[1].text lwrTitle = title.lower() print(lwrTitle) if (lwrTitle.find('new') > -1) or (lwrTitle.find('nisb') > -1): newFlag = 1.0 #全新 else: newFlag = 0.0 #不是全新 soldUnicde = currentRow[0].findAll('td')[3].findAll('span') if len(soldUnicde) == 0: print "item #%d did not sell" % i else: soldPrice = currentRow[0].findAll('td')[4] priceStr = soldPrice.text priceStr = priceStr.replace('$', '') # strips out $ priceStr = priceStr.replace(',', '') # strips out , if len(soldPrice) > 1: priceStr = priceStr.replace('Free shipping', '') # strips out Free Shipping print "%s\t%d\t%s" % (priceStr, newFlag, title) fw.write("%d\t%d\t%d\t%f\t%s\n" % (yr, numPce, newFlag, origPrc, priceStr)) i += 1 currentRow = soup.findAll('table', r="%d" % i) fw.close() def setDataCollect(): scrapePage('setHtml/lego8288.html', 'out.txt', 2006, 800, 49.99) #2006年出品,部件数目800,原价49.99 scrapePage('setHtml/lego10030.html', 'out.txt', 2002, 3096, 269.99) scrapePage('setHtml/lego10179.html', 'out.txt', 2007, 5195, 499.99) scrapePage('setHtml/lego10181.html', 'out.txt', 2007, 3428, 199.99) scrapePage('setHtml/lego10189.html', 'out.txt', 2008, 5922, 299.99) scrapePage('setHtml/lego10196.html', 'out.txt', 2009, 3263, 249.99) """ 函数说明:交叉验证测试岭回归 Parameters: xArr - x数据集 yArr - y数据集 numVal - 交叉验证的次数 """ def crossValidation(xArr,yArr,numVal=10): m = len(yArr) indexList = list(range(m)) #生成索引列表 errorMat = np.zeros((numVal,30))#存放误差值 for i in range(numVal): trainX=[]; trainY=[] testX = []; testY = [] random.shuffle(indexList) #打乱indexList,为了下面随机选取数据 for j in range(m): #使用90%的数据做训练集,10%做测试集 if j < m * 0.9: trainX.append(xArr[indexList[j]]) trainY.append(yArr[indexList[j]]) else: testX.append(xArr[indexList[j]]) testY.append(yArr[indexList[j]]) wMat = ridgeRegression.ridgeTest(trainX,trainY) #使用岭回归获取30组回归系数 print(wMat) for k in range(30):#loop over all of the ridge estimates matTestX = np.mat(testX); matTrainX = np.mat(trainX) meanTrain = np.mean(matTrainX,0) varTrain = np.var(matTrainX,0) matTestX = (matTestX-meanTrain)/varTrain #正规化测试数据 yEst = matTestX * np.mat(wMat[k,:]).T + np.mean(trainY)#计算预测y值 errorMat[i,k] = rssError(yEst.T.A,np.array(testY)) #print errorMat[i,k] meanErrors = np.mean(errorMat,0)#calc avg performance of the different ridge weight vectors minMean = float(min(meanErrors)) #获取最小的误差值 bestWeights = wMat[np.nonzero(meanErrors==minMean)] #can unregularize to get model #when we regularized we wrote Xreg = (x-meanX)/var(x) #we can now write in terms of x not Xreg: x*w/var(x) - meanX/var(x) +meanY xMat = np.mat(xArr); yMat = np.mat(yArr).T meanX = np.mean(xMat,0); varX = np.var(xMat,0) unReg = bestWeights / varX print("the best model from Ridge Regression is:\n",unReg) print("with constant term: ",-1*np.sum(np.multiply(meanX,unReg),1) + np.mean(yMat)) #常数项 if __name__ == '__main__': # setDataCollect() lgX, lgY = regression.loadDataSet('out.txt') #加上X0 lgXMat = np.mat(np.ones((np.shape(lgX)[0],np.shape(lgX)[1]+1))) lgXMat[:,1:5] = np.mat(lgX) print(lgXMat[0]) ws = regression.standRegres(lgXMat,lgY) print(ws) print(lgXMat[0]*ws,lgY[0]) crossValidation(lgX,lgY)
使用最小二乘回归预测结果为:

它对数据拟合得很好,但看上去却没什么道理,从公式看零部件数量越多,反而销售价更低。
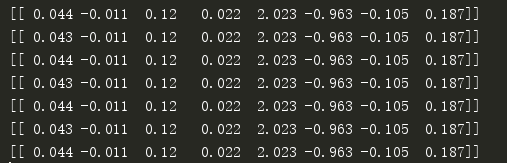
使用岭回归:
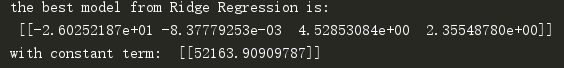

该结果和最小二乘结果没有太大差异,我们本期望找到一个更易于理解的模型,显然没有达到预期效果。为了达到这一点,我们看一下在缩减回归中系数是如何变化的
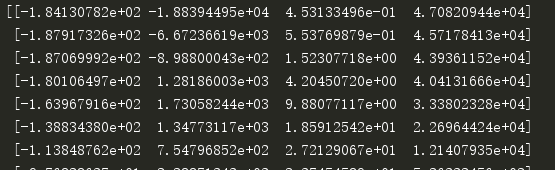
看运行结果的第一行,可以看到最大的是第4项,第二大的是第2项。因此,如果只选择一个特征来做预测的话,我们应该选择第4个特征,也就是原始加个。如果可以选择2个特征的话,应该选择第4个和第2个特征。
这种分析方法使得我们可以挖掘大量数据的内在规律。在仅有4个特征时,该方法的效果也许并不明显;但如果有100个以上的特征,该方法就会变得十分有效:它可以指出哪个特征是关键的,而哪些特征是不重要的。
使用sklearn中的岭回归
def usesklearn(): from sklearn import linear_model reg = linear_model.Ridge(alpha=.5) lgX, lgY = regression.loadDataSet('out.txt') reg.fit(lgX, lgY) print("$%f%f*Year%f*NumPieces+%f*NewOrUsed+%f*original price" % (reg.intercept_, reg.coef_[0], reg.coef_[1], reg.coef_[2], reg.coef_[3],reg.coef[4]))
输出结果: