handlerThread产生背景:
开启Thread子线程进行耗时操作,多次创建和销毁线程是很耗系统资源的。
handlerThread是什么?
handler + thread + looper
它其实也是一个线程,只是跟Thread是有区别的,它是一个thread内部有looper,
handlerThread的特点:
- 它本质上是一个线程,它继承了Thread。
- 它有自己的内部Looper对象,可以进行looper循环。
- 通过获取HandlerThread的looper对象传递给Handler对象,可以在handleMessage方法中执行异步任务。
- 优点是不会阻塞,减少了对性能的损耗,缺点是不能同时进行多任务的处理,需要等待进行处理,处理效率较低。
- 与线程池注重并发不同,HandlerThread是一个串行队列【也就是任务必须一个个执行,只有一个执行完了才会执行下一个】,HandlerThread背后只有一个线程。
handlerThread源码解析:
先贴一下它的完整源码:
/** * Handy class for starting a new thread that has a looper. The looper can then be * used to create handler classes. Note that start() must still be called. */ public class HandlerThread extends Thread { int mPriority; int mTid = -1; Looper mLooper; public HandlerThread(String name) { super(name); mPriority = Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_DEFAULT; } /** * Constructs a HandlerThread. * @param name * @param priority The priority to run the thread at. The value supplied must be from * {@link android.os.Process} and not from java.lang.Thread. */ public HandlerThread(String name, int priority) { super(name); mPriority = priority; } /** * Call back method that can be explicitly overridden if needed to execute some * setup before Looper loops. */ protected void onLooperPrepared() { } @Override public void run() { mTid = Process.myTid(); Looper.prepare(); synchronized (this) { mLooper = Looper.myLooper(); notifyAll(); } Process.setThreadPriority(mPriority); onLooperPrepared(); Looper.loop(); mTid = -1; } /** * This method returns the Looper associated with this thread. If this thread not been started * or for any reason is isAlive() returns false, this method will return null. If this thread * has been started, this method will block until the looper has been initialized. * @return The looper. */ public Looper getLooper() { if (!isAlive()) { return null; } // If the thread has been started, wait until the looper has been created. synchronized (this) { while (isAlive() && mLooper == null) { try { wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } } return mLooper; } /** * Quits the handler thread's looper. * <p> * Causes the handler thread's looper to terminate without processing any * more messages in the message queue. * </p><p> * Any attempt to post messages to the queue after the looper is asked to quit will fail. * For example, the {@link Handler#sendMessage(Message)} method will return false. * </p><p class="note"> * Using this method may be unsafe because some messages may not be delivered * before the looper terminates. Consider using {@link #quitSafely} instead to ensure * that all pending work is completed in an orderly manner. * </p> * * @return True if the looper looper has been asked to quit or false if the * thread had not yet started running. * * @see #quitSafely */ public boolean quit() { Looper looper = getLooper(); if (looper != null) { looper.quit(); return true; } return false; } /** * Quits the handler thread's looper safely. * <p> * Causes the handler thread's looper to terminate as soon as all remaining messages * in the message queue that are already due to be delivered have been handled. * Pending delayed messages with due times in the future will not be delivered. * </p><p> * Any attempt to post messages to the queue after the looper is asked to quit will fail. * For example, the {@link Handler#sendMessage(Message)} method will return false. * </p><p> * If the thread has not been started or has finished (that is if * {@link #getLooper} returns null), then false is returned. * Otherwise the looper is asked to quit and true is returned. * </p> * * @return True if the looper looper has been asked to quit or false if the * thread had not yet started running. */ public boolean quitSafely() { Looper looper = getLooper(); if (looper != null) { looper.quitSafely(); return true; } return false; } /** * Returns the identifier of this thread. See Process.myTid(). */ public int getThreadId() { return mTid; } }
以上就是它的完整源码,挺少的,但是设计很精妙,先来看一下它的类注解:

其中它就是继承Thread,很明显就是一个线程,接着来往下分析:
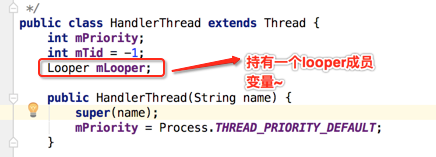

通过下面这句代码就可以知道:
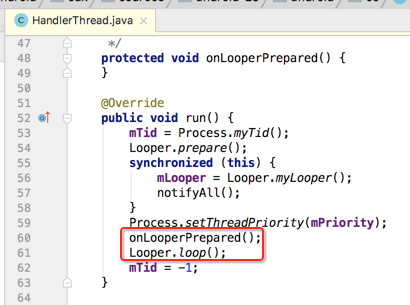
接着看一下线程最核心的run()方法:
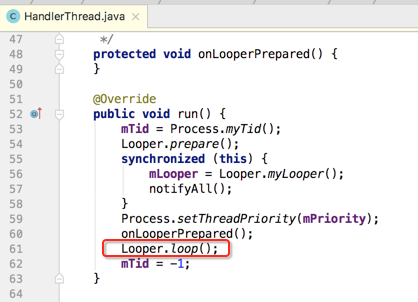
最后执行loop方法:
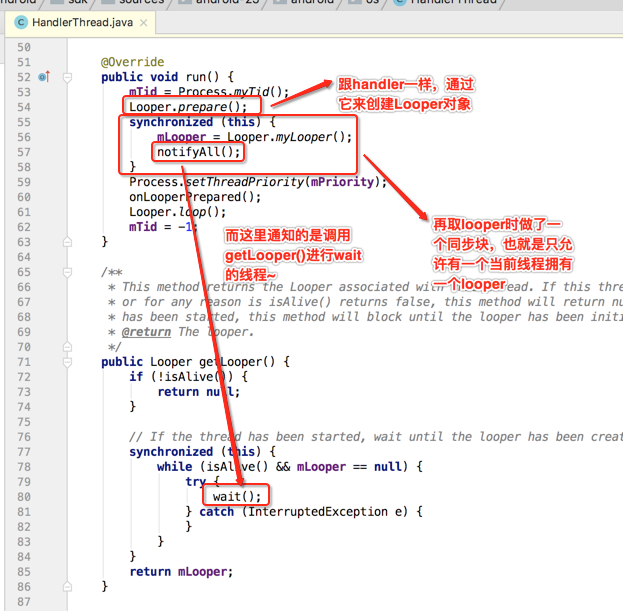
而看一下getLooper()方法:
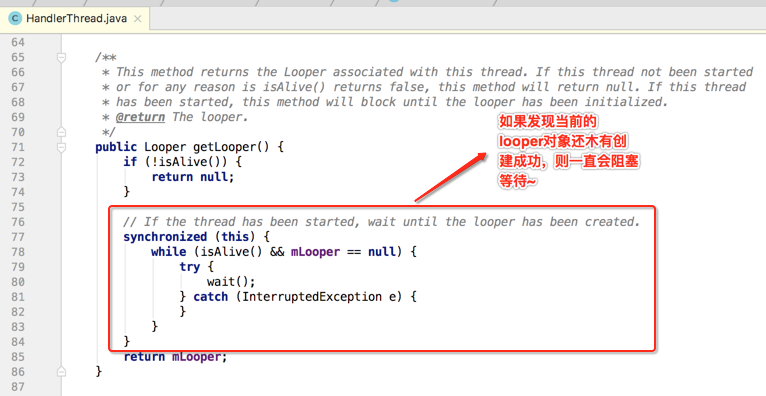
最后再看一下跟退出相关的方法:
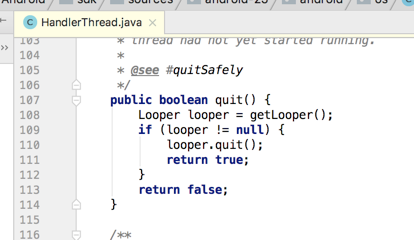

其中安全的退出效率肯定没有直接退出效率高。