Consecutive Factors
630 可以分解为 3×5×6×7,其中 5、6、7 是三个连续的数字。
现在给定任意正整数 N,请你找到最大连续因子数,并列出连续因子的最小序列。
思路
固定一个数,然后枚举n连续的因子,记录长度
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
ll n; cin>>n;
ll sq=sqrt(n), mx=0, start=1;
for (int i=2; i<=sq; i++) {
ll j, pro=1;
for (j=i; j<=sq; j++) {
pro*=j;
if (n%pro!=0) break;
}
if (j-i>mx) {
start=i;
mx=j-i;
}
}
if (mx==0) {
cout<<1<<'\n'<<n;
} else {
cout<<mx<<'\n';
int end=start+mx;
for (int i=start; i<end; i++) {
cout<<i;
if (i!=end-1) cout<<'*';
}
}
return 0;
}
Sum of Number Segments
思路
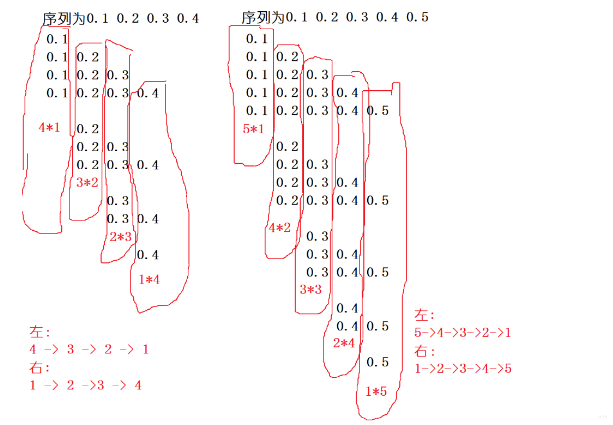
规律是找出来了:笛卡尔积,每个数出现的总次数为:(n-i+1)×i,i∈[1,n]
死活过不去啊,参考别人的做法,将浮点数扩大1000倍,结果等价于最后除以1000(1000是因为需保留两位小数),扩大10000/100倍也不行,这题
盗的图,感觉很清晰,但我不是这样想的,我是干想...
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int main() {
int n; cin>>n;
ll ans=0;
for (int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
double x; scanf("%lf", &x);
ans+=(ll) (x*1000*i*(n-i+1));
}
printf("%.2f", ans/1000.0);
return 0;
}
Prime Factors
N=p1k1*p2k2...pm^km 的格式输出答案。
其中 pi 是质因子,应按照递增顺序排列,ki 是 pi 的指数,如果 ki 为 1,则不必输出。
n在long int范围内,一般32位机,long int就是int
思路
从第一个素数p=2开始枚举,2如果是质因数,则4、6、8...2k 这些因子都会因为不断让n/=p整除被除掉,故不用判断p是否是质数也行
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n, isfirst=true; scanf("%d", &n);
printf("%d=",n);
if (n==1) {
printf("%d",n);
} else {
for (ll p=2; p<=n/p; p++) {
int c=0;
while (n%p==0) {
n/=p, c++;
}
if (c>0) {
if (isfirst) printf("%d", p), isfirst=false;
else printf("*%d", p), isfirst=false;
if (c>1) printf("^%d", c);
}
}
if (n>1){
if (isfirst) printf("%d", n), isfirst=false;
else printf("*%d", n);
}
}
return 0;
}
Are They Equal
如果机器只能保存 3 个有效数字,则将浮点数 12300 和 12358.9 视为相等(多余位数直接舍弃,不进行四舍五入),因为它们都保存为 0.123×105。
现在给定一个机器能够保存的有效数字位数,以及两个浮点数,请你判断两个数在该机器上是否相等
代码即思路
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
string format(string s, int n) {
int p=s.find("."); //.的位置即10^p
if (p==-1) s+=".", p=s.size()-1;
s=s.substr(0,p)+s.substr(p+1);
while (!s.empty() && s[0]=='0') s=s.substr(1), p--; // 前导零
if (s.empty()) p=0; //如果s都是0,
if (s.size()>n) s=s.substr(0,n);
else for (int i=0, d=s.size()-n; i<d; i++) s+="0"; //补0
return "0."+s+"*10^"+to_string(p);
}
int main() {
int n; cin>>n;
string a,b; cin>>a>>b;
a=format(a,n), b=format(b,n);
if (a==b) cout<<"YES"<<' '<<a;
else cout<<"NO"<<' '<<a<< ' '<<b;
return 0;
}
Rational Sum
For each test case, output the sum in the simplest form integer numerator/denominator where integer is the integer part of the sum, numerator < denominator, and the numerator and the denominator have no common factor. You must output only the fractional part if the integer part is 0.
思路
不断通分+约分即可;在pat能过,但有一个样例过不了,不知道是不是溢出还是怎样
4
1/100160063 1/100440259 1/100460273 1/970679
增强了一下代码健壮性:分母为1的情况
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
ll n,up=0ll, dw=1ll; cin>>n;
string s;
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
cin>>s;
if (s[0]=='-') {
up*=-1ll, dw*=-1ll;
}
ll p=s.find("/"), u=stoll(s.substr(0,p)), d=stoll(s.substr(p+1));
up=up*d+u*dw; dw*=d;
ll g=__gcd(up, dw);
up/=g, dw/=g;
}
if (dw<0) {
up*=-1, dw*=-1;
}
if (up/dw<1) {
if (up==0) printf("0");
else {
printf("%lld", up);
if (dw>1) printf("/%lld", dw);
printf("\n");
}
} else {
ll r=up%dw;
printf("%lld", up/dw);
if (r!=0) {
printf(" %lld", r);
if (dw>1) printf("/%lld", dw); //当分母为1时不输出分母
printf("\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
Rational Arithmetic
分别在四行输出两个有理数的和,差,积和商。
每行的格式为 number1 operator number2 = result。
请注意,所有有理数都必须采用最简形式,k a/b,其中 k 是整数部分,而 a/b 是最简分数部分。
如果数字为负,则必须将其包含在一对括号中。
如果除法中除数为 0,则输出 Inf 作为结果。
intput
2/3 -4/2
output
2/3 + (-2) = (-1 1/3)
2/3 - (-2) = 2 2/3
2/3 * (-2) = (-1 1/3)
2/3 / (-2) = (-1/3)
思路
分数的四则运算最终都是可以通过通分进行加减从而约分为一个分数的,下一步就是如何输出答案,无外乎四种情况:
- 有负号(这里-只会出现在分子):直接输出负号,将分子变为正数,这样方便后面的判断
- 分子为0,输出 INF
- 分子≥分母:输出整数部分+小数部分转化为分数
- 分子<分母:直接输出
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
struct node {
ll up, dw;
};
ll gcd(ll A, ll B) {
return A==0ll ? B : gcd(B%A, A);
}
node add(node A, node B) {
return {A.up*B.dw+A.dw*B.up, A.dw*B.dw};
}
node sub(node A, node B) {
return {A.up*B.dw-B.up*A.dw, A.dw*B.dw};
}
node mul(node A, node B) {
return {A.up*B.up, A.dw*B.dw};
}
node div(node A, node B) {
return {A.up*B.dw, A.dw*B.up};
}
node simplify(node f) {
ll g=gcd(f.up, f.dw);
f.up/=g, f.dw/=g;
if (f.dw<0) f.up*=-1, f.dw*=-1;
return f;
}
void output(node f) {
bool has_neg=false;
if (f.up<0) printf("(-"), has_neg=1, f.up*=-1ll;
if (f.dw==0) printf("Inf");
else if (f.dw==1) printf("%lld", f.up);
else if (f.up>f.dw) printf("%lld %lld/%lld", f.up/f.dw, f.up%f.dw, f.dw);
else printf("%lld/%lld", f.up, f.dw);
if (has_neg) printf(")");
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
node A, B;
scanf("%lld/%lld %lld/%lld", &A.up, &A.dw, &B.up, &B.dw);
A=simplify(A), B=simplify(B);
output(A); printf(" + "); output(B); printf(" = "); output(simplify(add(A,B))); printf("\n");
output(A); printf(" - "); output(B); printf(" = "); output(simplify(sub(A,B))); printf("\n");
output(A); printf(" * "); output(B); printf(" = "); output(simplify(mul(A,B))); printf("\n");
output(A); printf(" / "); output(B); printf(" = "); output(simplify(div(A,B)));
return 0;
}
Reversible Primes
N=23,D=2,则 23 是质数,其二进制表示为 10111,反转后得到 11101,转化为十进制后为 29,这也是一个质数,所以 23 在二进制系统中是一个可逆质数。
现在,请你判断所给 N 在 D 进制系统中是否是一个可逆质数。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
// string ten2k(ll n, ll k) {
// string ans;
// while (n) {
// ans+=to_string(n%k);
// n/=k;
// }
// return ans;
// }
// ll k2ten(string s, ll k) {
// ll rate=1, ans=0;
// for (int i=s.size()-1; i>=0; i--) ans=ans+(s[i]-'0')*rate, rate*=k;
// return ans;
// }
//改进后的判断
bool chk(ll n) {
if (n<=1ll) return false;
for (ll i=2; i<=n/i; i++) if (n%i==0)
return false;
return true;
}
bool convert_ans_chk(int n, int k) { //这里一个方法做了两件事:将n转为k进制,然后再将结果翻转后转为10进制
if (!chk(n)) return false;
ll m=0;
while (n) {
m=m*k+n%k;
n/=k;
}
return chk(m);
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
//1.将n转为k进制,得到ans1
//2.将ans1翻转,再转为十进制,得到ans2
//3.判断ans1,ans2
int n,k;
while (cin>>n>>k, n>=1) {
cout<<(convert_ans_chk(n,k) ? "Yes" : "No") <<"\n";
}
return 0;
}
General Palindromic Number
各种是错,总结为几点,n为原数字,m为进制数:
- 当 n=0/n<m 时,转不了m进制,直接输出
- 输出的时候并不是一个字符一个字符的输出,n%m 的数可能是一个多位数,而多位数正常是要输出多位数的
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
vector<int> convert(ll n, ll k) {
vector<int> ans;
while (n) {
ans.insert(ans.begin(), n%k);
n/=k;
}
return ans;
}
bool chk(vector<int>& v) {
int l=0, r=v.size()-1;
while (l<r) {
if (v[l]!=v[r]) return false;
l++, r--;
}
return true;
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
ll n,m; cin>>n>>m;
if (n==0 || n<m) cout<<"Yes\n"<<n; //转不了的话,直接输出
else {
auto v=convert(n,m);
cout<<(chk(v)?"Yes":"No")<<'\n';
for (int i=0; i<v.size(); i++) {
cout<<v[i];
if (i!=v.size()-1)cout<<' ';
}
}
return 0;
}
Mars Numbers
思路
进制转换,13进制,13以下的都是0~12,13以上可以类比10进制的10以上的数字,十进制的11就是 (11/1)*10+(11%1),相应的,13-26,这些都是一个高位为 13,低位为 0~13 组成
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
string lo[14]={"tret","jan", "feb", "mar", "apr", "may", "jun", "jly", "aug", "sep", "oct", "nov", "dec"};
string hi[14]={"tret","tam", "hel", "maa", "huh", "tou", "kes", "hei", "elo", "syy", "lok", "mer", "jou"};
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
string sn; getline(cin, sn);
int n=stoi(sn);
unordered_map<string, int> mp;
for (int i=0; i<13; i++) mp[lo[i]]=i, mp[hi[i]]=13*i;
string s;
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
getline(cin, s);
if (isdigit(s[0])) { //整数转火星
int num=stoi(s), x=num/13, y=num%13; //整数结果是hi,取模结果是lo
if (x!=0) cout<<hi[x];
if (x!=0 && y!=0) cout << " ";
if (x==0 || y!=0) cout<<lo[y];
cout<<'\n';
} else {
int ans=0; //火星转整数
string t;
stringstream ss(s);
while (ss>>t) //得到以空格分隔的子串
ans+=mp[t];
cout << ans << '\n';
}
}
return 0;
}