orm的演进过程,jdbc——ibatis——mybatis,jdbc最基础的访问数据库的方式,ibatis基于jdbc进行了封装,程序员
可以直接在xml里面写sql,通过调用dao中的方法执行数据库的操作,mybatis省略了dao的步骤,只需要mapper中的方法与
mapper.xml中的sqlId映射上,就可以直接调用。
1:通过mybatis源码看一下mybatis的实现原理
实现原理就是动态代理,动态代理有两种,jdk代理和cglib代理,jdk代理必须基于接口,在内存中动态生成接口的子类来实现
在上一节中,解析mapper.xml的时候会解析命名空间
public void parse() {
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// 解析sql,生成mapperStatement
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
// 解析命名空间,绑定代理工厂
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingChacheRefs();
parsePendingStatements();
}
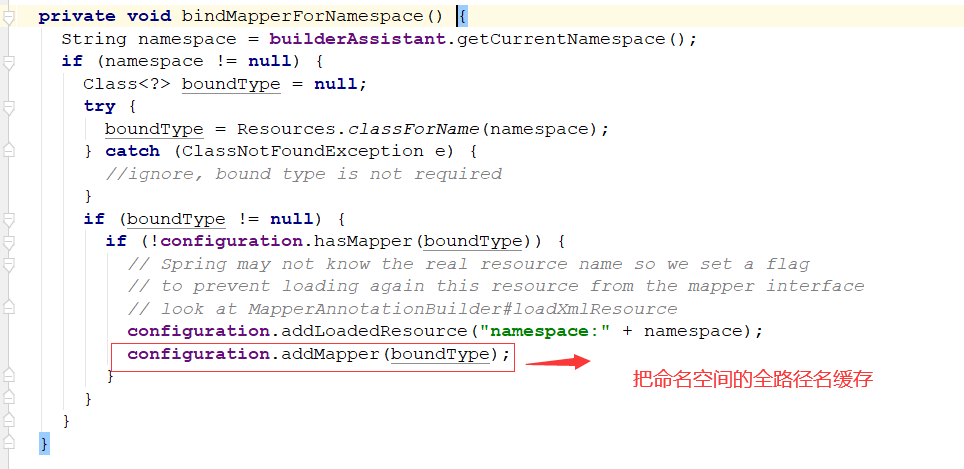
调用configuration的addMapper方法,将命名空间的class对象传入
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
mapperRegistry.addMapper(type);
}
首先判断这个类型是否已经注册,如果已经注册,抛出一个已经绑定的异常,
如果没有注册,则放入knownMappers中缓存,key为类型,value为MapperProxyFactory对象
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<T>(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
下面来看一下这个类:MapperProxyFactory
维护一个mapperInterface的接口,有方法newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession)
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<Method, MapperMethod>();
public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
public Class<T> getMapperInterface() {
return mapperInterface;
}
public Map<Method, MapperMethod> getMethodCache() {
return methodCache;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
}
以上是addMapper的使用,注册了命名空间的类型到内存中。
下面看一下绑定后的使用过程:
从configuration对象中getMapper,实际上是从mapperRegistry中获取,因为在上一节解析命名空间的时候已经注册了
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
return configuration.<T>getMapper(type, this);
}
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}
拿到代理工厂MapperProxyFactory对象,然后调用newInstance方法创建代理
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
最后将代理对象返回,我们得到了UserMapper对象,实际上是一个代理
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
这里可以看到,所谓的动态代理,就是在程序运行过程中生成接口的实现对象,而不是通过代码实现的。

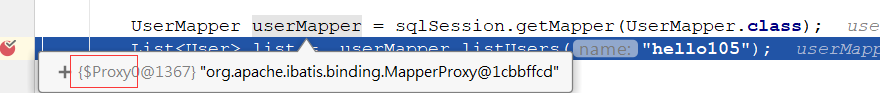
通过debug可以看到proxy 代理对象
所以当我们调用listUsers时,会调到代理的invoke方法
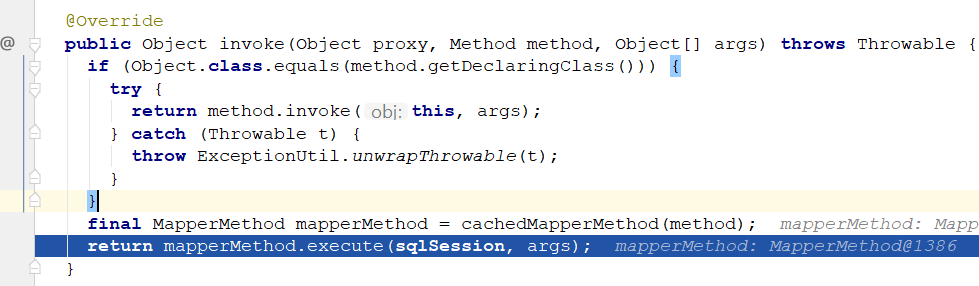
到这里通过代理实现的mybatis的数据绑定就结束了
总结:
两个主要的方法:addMapper、getMapper
addMapper:在解析命名空间的时候会注册到Configuration类中的MapperRegistry中,MapperRegistry类中有个knowMappers的缓存,key为命名空间的Class对象,value为MapperProxyFactory
getMapper:通过SqlSession获取接口实现的时候会调到,然后回到Configuration中的MapperRegistry中拿到MapperProxyFactory对象(根据Class对象),然后生成代理对象,并且返回
当调用方法时,实际上调用的是代理的方法,然后就会调到切面的MapperProxy中的invoke
这一节主要就是分析了一下通过代理实现的数据绑定,这里忽略了最重要的一个类SqlSession,它起到一个承上启下的作用,非常重要,下一点来分析一下SqlSession回话的源码