一、Broker Failover过程
1. Controller对Broker failure的处理过程
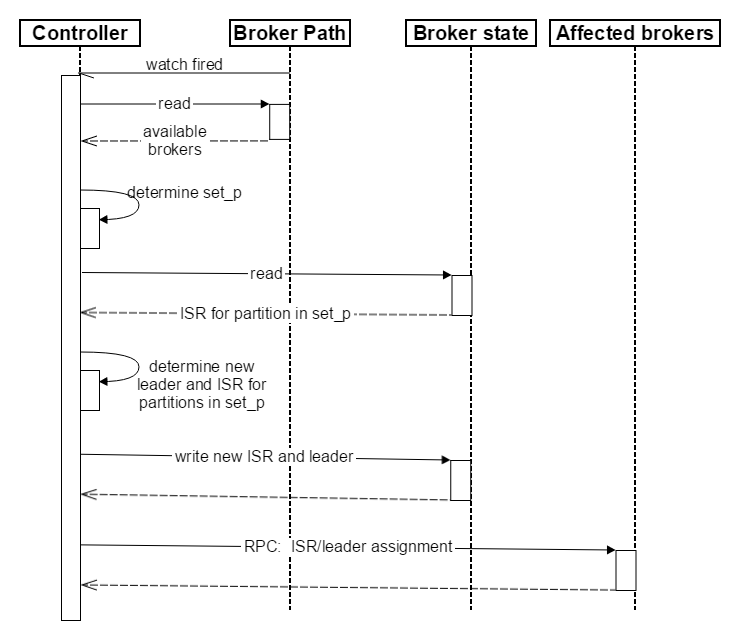
(1)Controller在Zookeeper的/brokers/ids节点上注册Watch。一旦有Broker宕机(本文用宕机代表任何让Kafka认为其Broker die的情景,包括但不限于机器断电,网络不可用,GC导致的Stop The World,进程crash等),其在Zookeeper对应的Znode会自动被删除,Zookeeper会fire Controller注册的Watch,Controller即可获取最新的幸存的Broker列表。
(2)Controller决定set_p,该集合包含了宕机的所有Broker上的所有Partition。
(3)对set_p中的每一个Partition:
(3.1)从/brokers/topics/[topic]/partitions/[partition]/state读取该Partition当前的ISR。
(3.2)决定该Partition的新Leader。如果当前ISR中有至少一个Replica还幸存,则选择其中一个作为新Leader,新的ISR则包含当前ISR中所有幸存的Replica。否则选择该Partition中任意一个幸存的Replica作为新的Leader以及ISR(该场景下可能会有潜在的数据丢失)。如果该Partition的所有Replica都宕机了,则将新的Leader设置为-1。
(3.3) 将新的Leader,ISR和新的leader_epoch及controller_epoch写入/brokers/topics/[topic]/partitions/[partition]/state。注意,该操作只有Controller版本在3.1至3.3的过程中无变化时才会执行,否则跳转到3.1。
(4)直接通过RPC向set_p相关的Broker发送LeaderAndISRRequest命令。Controller可以在一个RPC操作中发送多个命令从而提高效率。
Broker failover顺序图如下所示。
LeaderAndIsrRequest结构如下
case class LeaderAndIsrRequest (versionId: Short, correlationId: Int, clientId: String, controllerId: Int, controllerEpoch: Int, partitionStateInfos: Map[(String, Int), PartitionStateInfo], leaders: Set[Broker]) extends RequestOrResponse(Some(RequestKeys.LeaderAndIsrKey)) {
LeaderAndIsrResponse结构如下
case class LeaderAndIsrResponse(correlationId: Int, responseMap: Map[(String, Int), Short], errorCode: Short = ErrorMapping.NoError)
2. 创建/删除Topic
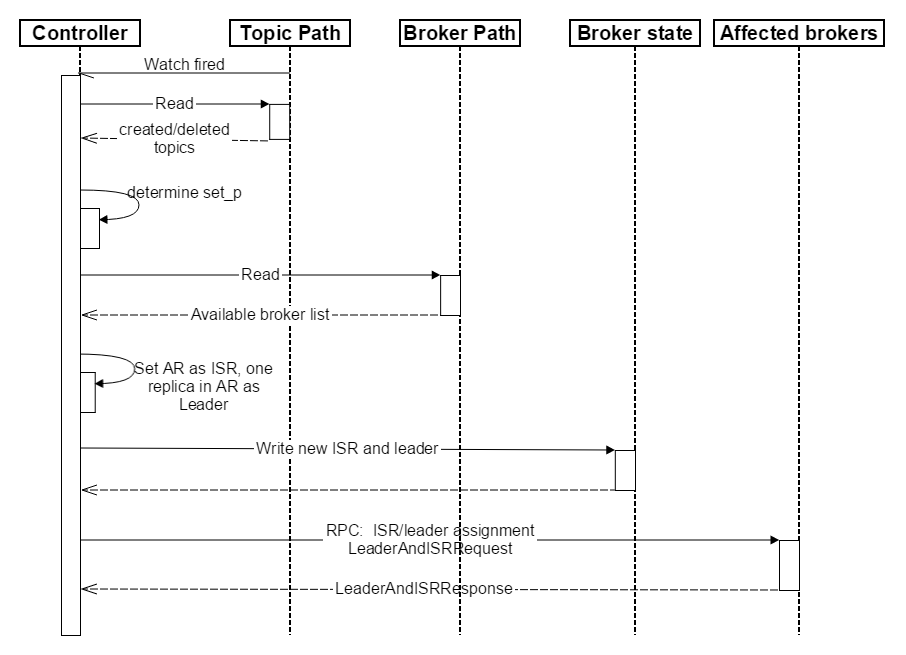
(1)Controller在Zookeeper的/brokers/topics节点上注册Watch,一旦某个Topic被创建或删除,则Controller会通过Watch得到新创建/删除的Topic的Partition/Replica分配。
(2)对于删除Topic操作,Topic工具会将该Topic名字存于/admin/delete_topics。若delete.topic.enable为true,则Controller注册在/admin/delete_topics上的Watch被fire,Controller通过回调向对应的Broker发送StopReplicaRequest;若为false则Controller不会在/admin/delete_topics上注册Watch,也就不会对该事件作出反应,此时Topic操作只被记录而不会被执行。
(3)对于创建Topic操作,Controller从/brokers/ids读取当前所有可用的Broker列表,对于set_p中的每一个Partition:
(3.1)从分配给该Partition的所有Replica(称为AR)中任选一个可用的Broker作为新的Leader,并将AR设置为新的ISR(因为该Topic是新创建的,所以AR中所有的Replica都没有数据,可认为它们都是同步的,也即都在ISR中,任意一个Replica都可作为Leader)
(3.2)将新的Leader和ISR写入/brokers/topics/[topic]/partitions/[partition]
(4)直接通过RPC向相关的Broker发送LeaderAndISRRequest。
创建Topic顺序图如下所示
3. Broker响应请求流程
Broker通过kafka.network.SocketServer及相关模块接受各种请求并作出响应。整个网络通信模块基于Java NIO开发,并采用Reactor模式,其中包含1个Acceptor负责接受客户请求,N个Processor负责读写数据,M个Handler处理业务逻辑。
Acceptor的主要职责是监听并接受客户端(请求发起方,包括但不限于Producer,Consumer,Controller,Admin Tool)的连接请求,并建立和客户端的数据传输通道,然后为该客户端指定一个Processor,至此它对该客户端该次请求的任务就结束了,它可以去响应下一个客户端的连接请求了。其核心代码如下。
serverChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); startupComplete() var currentProcessor = 0 while(isRunning) { val ready = selector.select(500) if(ready > 0) { val keys = selector.selectedKeys() val iter = keys.iterator() while(iter.hasNext && isRunning) { var key: SelectionKey = null try { key = iter.next iter.remove() if(key.isAcceptable) accept(key, processors(currentProcessor)) else throw new IllegalStateException("Unrecognized key state for acceptor thread.") // round robin to the next processor thread currentProcessor = (currentProcessor + 1) % processors.length } catch { case e: Throwable => error("Error while accepting connection", e) } } } }
Processor主要负责从客户端读取数据并将响应返回给客户端,它本身并不处理具体的业务逻辑,并且其内部维护了一个队列来保存分配给它的所有SocketChannel。Processor的run方法会循环从队列中取出新的SocketChannel并将其SelectionKey.OP_READ注册到selector上,然后循环处理已就绪的读(请求)和写(响应)。Processor读取完数据后,将其封装成Request对象并将其交给RequestChannel。
RequestChannel是Processor和KafkaRequestHandler交换数据的地方,它包含一个队列requestQueue用来存放Processor加入的Request,KafkaRequestHandler会从里面取出Request来处理;同时它还包含一个respondQueue,用来存放KafkaRequestHandler处理完Request后返还给客户端的Response。
Processor会通过processNewResponses方法依次将requestChannel中responseQueue保存的Response取出,并将对应的SelectionKey.OP_WRITE事件注册到selector上。当selector的select方法返回时,对检测到的可写通道,调用write方法将Response返回给客户端。
KafkaRequestHandler循环从RequestChannel中取Request并交给kafka.server.KafkaApis处理具体的业务逻辑。
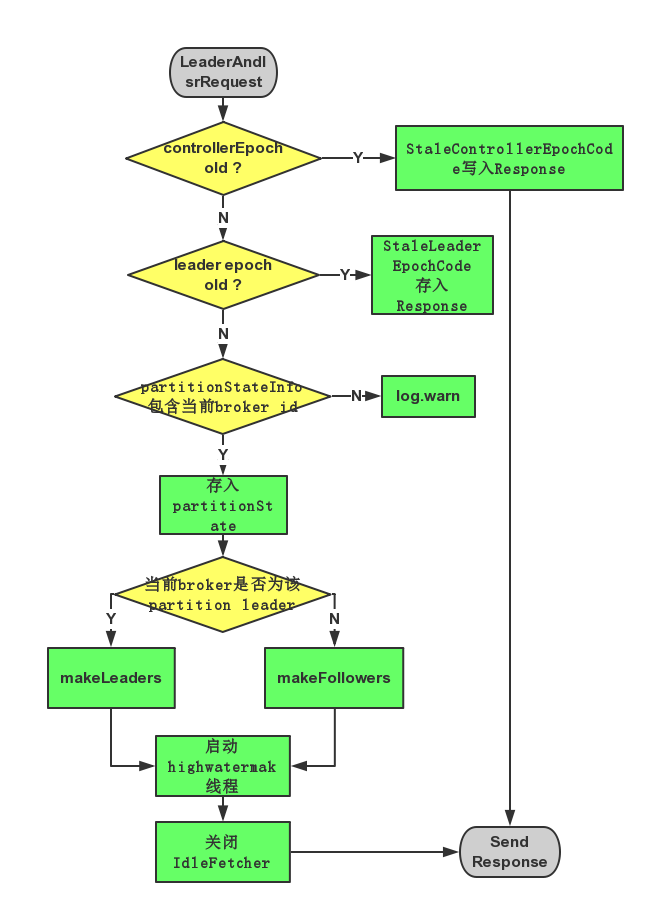
4. LeaderAndIsrRequest响应过程
对于收到的LeaderAndIsrRequest,Broker主要通过ReplicaManager的becomeLeaderOrFollower处理,流程如下:
(1)若请求中controllerEpoch小于当前最新的controllerEpoch,则直接返回ErrorMapping.StaleControllerEpochCode。
(2)对于请求中partitionStateInfos中的每一个元素,即((topic, partitionId), partitionStateInfo):
(2.1) 若partitionStateInfo中的leader epoch大于当前ReplicManager中存储的(topic, partitionId)对应的partition的leader epoch,则:
(2.1.1) 若当前brokerid(或者说replica id)在partitionStateInfo中,则将该partition及partitionStateInfo存入一个名为partitionState的HashMap中
(2.1.2)否则说明该Broker不在该Partition分配的Replica list中,将该信息记录于log中
(2.2)否则将相应的Error code(ErrorMapping.StaleLeaderEpochCode)存入Response中
(3)筛选出partitionState中Leader与当前Broker ID相等的所有记录存入partitionsTobeLeader中,其它记录存入partitionsToBeFollower中。
(4)若partitionsTobeLeader不为空,则对其执行makeLeaders方。
(5)若partitionsToBeFollower不为空,则对其执行makeFollowers方法。
(6)若highwatermak线程还未启动,则将其启动,并将hwThreadInitialized设为true。
(7)关闭所有Idle状态的Fetcher。
LeaderAndIsrRequest处理过程如下图所示
5. Broker启动过程
Broker启动后首先根据其ID在Zookeeper的/brokers/ids zonde下创建临时子节点(Ephemeral node),创建成功后Controller的ReplicaStateMachine注册其上的Broker Change Watch会被fire,从而通过回调KafkaController.onBrokerStartup方法完成以下步骤:
(1)向所有新启动的Broker发送UpdateMetadataRequest,其定义如下。
case class UpdateMetadataRequest (versionId: Short, correlationId: Int, clientId: String, controllerId: Int, controllerEpoch: Int, partitionStateInfos: Map[TopicAndPartition, PartitionStateInfo], aliveBrokers: Set[Broker]) extends RequestOrResponse(Some(RequestKeys.UpdateMetadataKey))
(2)将新启动的Broker上的所有Replica设置为OnlineReplica状态,同时这些Broker会为这些Partition启动high watermark线程。
(3)通过partitionStateMachine触发OnlinePartitionStateChange。
6. Controller Failover
Controller也需要Failover。每个Broker都会在Controller Path (/controller)上注册一个Watch。当前Controller失败时,对应的Controller Path会自动消失(因为它是Ephemeral Node),此时该Watch被fire,所有“活”着的Broker都会去竞选成为新的Controller(创建新的Controller Path),但是只会有一个竞选成功(这点由Zookeeper保证)。竞选成功者即为新的Leader,竞选失败者则重新在新的Controller Path上注册Watch。因为Zookeeper的Watch是一次性的,被fire一次之后即失效,所以需要重新注册。
Broker成功竞选为新Controller后会触发KafkaController.onControllerFailover方法,并在该方法中完成如下操作:
(1)读取并增加Controller Epoch。
(2)在ReassignedPartitions Path(/admin/reassign_partitions)上注册Watch。
(3)在PreferredReplicaElection Path(/admin/preferred_replica_election)上注册Watch。
(4)通过partitionStateMachine在Broker Topics Patch(/brokers/topics)上注册Watch。
(5)若delete.topic.enable设置为true(默认值是false),则partitionStateMachine在Delete Topic Patch(/admin/delete_topics)上注册Watch。
(6)通过replicaStateMachine在Broker Ids Patch(/brokers/ids)上注册Watch。
(7)初始化ControllerContext对象,设置当前所有Topic,“活”着的Broker列表,所有Partition的Leader及ISR等。
(8)启动replicaStateMachine和partitionStateMachine。
(9)将brokerState状态设置为RunningAsController。
(10)将每个Partition的Leadership信息发送给所有“活”着的Broker。
(11)若auto.leader.rebalance.enable配置为true(默认值是true),则启动partition-rebalance线程。
(12)若delete.topic.enable设置为true且Delete Topic Patch(/admin/delete_topics)中有值,则删除相应的Topic。
7. Partition重新分配
管理工具发出重新分配Partition请求后,会将相应信息写到/admin/reassign_partitions上,而该操作会触发ReassignedPartitionsIsrChangeListener,从而通过执行回调函数KafkaController.onPartitionReassignment来完成以下操作:
(1)将Zookeeper中的AR(Current Assigned Replicas)更新为OAR(Original list of replicas for partition) + RAR(Reassigned replicas)。
(2)强制更新Zookeeper中的leader epoch,向AR中的每个Replica发送LeaderAndIsrRequest。
(3)将RAR - OAR中的Replica设置为NewReplica状态。
(4)等待直到RAR中所有的Replica都与其Leader同步。
(5)将RAR中所有的Replica都设置为OnlineReplica状态。
(6)将Cache中的AR设置为RAR。
(7)若Leader不在RAR中,则从RAR中重新选举出一个新的Leader并发送LeaderAndIsrRequest。若新的Leader不是从RAR中选举而出,则还要增加Zookeeper中的leader epoch。
(8)将OAR - RAR中的所有Replica设置为OfflineReplica状态,该过程包含两部分。第一,将Zookeeper上ISR中的OAR - RAR移除并向Leader发送LeaderAndIsrRequest从而通知这些Replica已经从ISR中移除;第二,向OAR - RAR中的Replica发送StopReplicaRequest从而停止不再分配给该Partition的Replica。
(9)将OAR - RAR中的所有Replica设置为NonExistentReplica状态从而将其从磁盘上删除。
(10)将Zookeeper中的AR设置为RAR。
(11)删除/admin/reassign_partition。
注意:最后一步才将Zookeeper中的AR更新,因为这是唯一一个持久存储AR的地方,如果Controller在这一步之前crash,新的Controller仍然能够继续完成该过程。
以下是Partition重新分配的案例,OAR = {1,2,3},RAR = {4,5,6},Partition重新分配过程中Zookeeper中的AR和Leader/ISR路径如下
| AR | leader/isr | Step |
|---|---|---|
| {1,2,3} | 1/{1,2,3} | (initial state) |
| {1,2,3,4,5,6} | 1/{1,2,3} | (step 2) |
| {1,2,3,4,5,6} | 1/{1,2,3,4,5,6} | (step 4) |
| {1,2,3,4,5,6} | 4/{1,2,3,4,5,6} | (step 7) |
| {1,2,3,4,5,6} | 4/{4,5,6} | (step 8) |
| {4,5,6} | 4/{4,5,6} | (step 10) |
8. Follower从Leader Fetch数据
Follower通过向Leader发送FetchRequest获取消息,FetchRequest结构如下
case class FetchRequest(versionId: Short = FetchRequest.CurrentVersion, correlationId: Int = FetchRequest.DefaultCorrelationId, clientId: String = ConsumerConfig.DefaultClientId, replicaId: Int = Request.OrdinaryConsumerId, maxWait: Int = FetchRequest.DefaultMaxWait, minBytes: Int = FetchRequest.DefaultMinBytes, requestInfo: Map[TopicAndPartition, PartitionFetchInfo]) extends RequestOrResponse(Some(RequestKeys.FetchKey))
从FetchRequest的结构可以看出,每个Fetch请求都要指定最大等待时间和最小获取字节数,以及由TopicAndPartition和PartitionFetchInfo构成的Map。实际上,Follower从Leader Fetch数据和Consumer从Broker Fetch数据,都是通过FetchRequest请求完成,所以在FetchRequest结构中,其中一个字段是clientID,并且其默认值是ConsumerConfig.DefaultClientId。
Leader收到Fetch请求后,Kafka通过KafkaApis.handleFetchRequest响应该请求,响应过程如下:
(1)replicaManager根据请求读出数据存入dataRead中。
(2)如果该请求来自Follower则更新其相应的LEO(log end offset)以及相应Partition的High Watermark
(3)根据dataRead算出可读消息长度(单位为字节)并存入bytesReadable中。
(4)满足下面4个条件中的1个,则立即将相应的数据返回
- Fetch请求不希望等待,即fetchRequest.macWait <= 0
- Fetch请求不要求一定能取到消息,即fetchRequest.numPartitions <= 0,也即requestInfo为空
- 有足够的数据可供返回,即bytesReadable >= fetchRequest.minBytes
- 读取数据时发生异常
(5)若不满足以上4个条件,FetchRequest将不会立即返回,并将该请求封装成DelayedFetch。检查该DeplayedFetch是否满足,若满足则返回请求,否则将该请求加入Watch列表
Leader通过以FetchResponse的形式将消息返回给Follower,FetchResponse结构如下
case class FetchResponse(correlationId: Int, data: Map[TopicAndPartition, FetchResponsePartitionData]) extends RequestOrResponse()
#Replication工具
9. Topic Tool
$KAFKA_HOME/bin/kafka-topics.sh,该工具可用于创建、删除、修改、查看某个Topic,也可用于列出所有Topic。另外,该工具还可修改以下配置。
unclean.leader.election.enable
delete.retention.ms
segment.jitter.ms
retention.ms
flush.ms
segment.bytes
flush.messages
segment.ms
retention.bytes
cleanup.policy
segment.index.bytes
min.cleanable.dirty.ratio
max.message.bytes
file.delete.delay.ms
min.insync.replicas
index.interval.bytes
10. Replica Verification Tool
$KAFKA_HOME/bin/kafka-replica-verification.sh,该工具用来验证所指定的一个或多个Topic下每个Partition对应的所有Replica是否都同步。可通过topic-white-list这一参数指定所需要验证的所有Topic,支持正则表达式。
11. Preferred Replica Leader Election Tool
用途
有了Replication机制后,每个Partition可能有多个备份。某个Partition的Replica列表叫作AR(Assigned Replicas),AR中的第一个Replica即为“Preferred Replica”。创建一个新的Topic或者给已有Topic增加Partition时,Kafka保证Preferred Replica被均匀分布到集群中的所有Broker上。理想情况下,Preferred Replica会被选为Leader。以上两点保证了所有Partition的Leader被均匀分布到了集群当中,这一点非常重要,因为所有的读写操作都由Leader完成,若Leader分布过于集中,会造成集群负载不均衡。但是,随着集群的运行,该平衡可能会因为Broker的宕机而被打破,该工具就是用来帮助恢复Leader分配的平衡。
事实上,每个Topic从失败中恢复过来后,它默认会被设置为Follower角色,除非某个Partition的Replica全部宕机,而当前Broker是该Partition的AR中第一个恢复回来的Replica。因此,某个Partition的Leader(Preferred Replica)宕机并恢复后,它很可能不再是该Partition的Leader,但仍然是Preferred Replica。
原理
- 在Zookeeper上创建/admin/preferred_replica_election节点,并存入需要调整Preferred Replica的Partition信息。
- Controller一直Watch该节点,一旦该节点被创建,Controller会收到通知,并获取该内容。
- Controller读取Preferred Replica,如果发现该Replica当前并非是Leader并且它在该Partition的ISR中,Controller向该Replica发送LeaderAndIsrRequest,使该Replica成为Leader。如果该Replica当前并非是Leader,且不在ISR中,Controller为了保证没有数据丢失,并不会将其设置为Leader。
用法
$KAFKA_HOME/bin/kafka-preferred-replica-election.sh --zookeeper localhost:2181
在包含8个Broker的Kafka集群上,创建1个名为topic1,replication-factor为3,Partition数为8的Topic,使用如下命令查看其Partition/Replica分布。
$KAFKA_HOME/bin/kafka-topics.sh --describe --topic topic1 --zookeeper localhost:2181
查询结果如下图所示,从图中可以看到,Kafka将所有Replica均匀分布到了整个集群,并且Leader也均匀分布。
Topic:iteblog PartitionCount:8 ReplicationFactor:1 Configs: Topic: iteblog Partition: 0 Leader: 1 Replicas: 1,3,4 Isr: 4,1,3 Topic: iteblog Partition: 1 Leader: 2 Replicas: 2,4,5 Isr: 5,2,4 Topic: iteblog Partition: 2 Leader: 3 Replicas: 3,5,6 Isr: 5,3,6 Topic: iteblog Partition: 3 Leader: 4 Replicas: 4,6,7 Isr: 4,7,6 Topic: iteblog Partition: 4 Leader: 5 Replicas: 5,7,0 Isr: 5,7,0 Topic: iteblog Partition: 5 Leader: 6 Replicas: 6,0,1 Isr: 0,6,1 Topic: iteblog Partition: 6 Leader: 7 Replicas: 7,1,2 Isr: 7,1,2 Topic: iteblog Partition: 7 Leader: 0 Replicas: 0,2,3 Isr: 0,2,3
手动停止部分Broker,topic1的Partition/Replica分布如下图所示。从图中可以看到,由于Broker 1/2/4都被停止,Partition 0的Leader由原来的1变为3,Partition 1的Leader由原来的2变为5,Partition 2的Leader由原来的3变为6,Partition 3的Leader由原来的4变为7。
Topic:iteblog PartitionCount:8 ReplicationFactor:1 Configs: Topic: iteblog Partition: 0 Leader: 3 Replicas: 1,3,4 Isr: 3 Topic: iteblog Partition: 1 Leader: 5 Replicas: 2,4,5 Isr: 5 Topic: iteblog Partition: 2 Leader: 6 Replicas: 3,5,6 Isr: 5,3,6 Topic: iteblog Partition: 3 Leader: 7 Replicas: 4,6,7 Isr: 7,6 Topic: iteblog Partition: 4 Leader: 5 Replicas: 5,7,0 Isr: 5,7,0 Topic: iteblog Partition: 5 Leader: 6 Replicas: 6,0,1 Isr: 0,6 Topic: iteblog Partition: 6 Leader: 7 Replicas: 7,1,2 Isr: 7 Topic: iteblog Partition: 7 Leader: 0 Replicas: 0,2,3 Isr: 0,3
再重新启动ID为1的Broker,topic1的Partition/Replica分布如下。可以看到,虽然Broker 1已经启动(Partition 0和Partition5的ISR中有1),但是1并不是任何一个Parititon的Leader,而Broker 5/6/7都是2个Partition的Leader,即Leader的分布不均衡——一个Broker最多是2个Partition的Leader,而最少是0个Partition的Leader。
Topic:iteblog PartitionCount:8 ReplicationFactor:1 Configs: Topic: iteblog Partition: 0 Leader: 3 Replicas: 1,3,4 Isr: 3,1 Topic: iteblog Partition: 1 Leader: 5 Replicas: 2,4,5 Isr: 5 Topic: iteblog Partition: 2 Leader: 6 Replicas: 3,5,6 Isr: 5,3,6 Topic: iteblog Partition: 3 Leader: 7 Replicas: 4,6,7 Isr: 7,6 Topic: iteblog Partition: 4 Leader: 5 Replicas: 5,7,0 Isr: 5,7,0 Topic: iteblog Partition: 5 Leader: 6 Replicas: 6,0,1 Isr: 0,6,1 Topic: iteblog Partition: 6 Leader: 7 Replicas: 7,1,2 Isr: 7,1 Topic: iteblog Partition: 7 Leader: 0 Replicas: 0,2,3 Isr: 0,3
运行该工具后,topic1的Partition/Replica分布如下图所示。由图可见,除了Partition 1和Partition 3由于Broker 2和Broker 4还未启动,所以其Leader不是其Preferred Repliac外,其它所有Partition的Leader都是其Preferred Replica。同时,与运行该工具前相比,Leader的分配更均匀——一个Broker最多是2个Parittion的Leader,最少是1个Partition的Leader。
Topic:iteblog PartitionCount:8 ReplicationFactor:1 Configs: Topic: iteblog Partition: 0 Leader: 1 Replicas: 1,3,4 Isr: 3,1 Topic: iteblog Partition: 1 Leader: 5 Replicas: 2,4,5 Isr: 5 Topic: iteblog Partition: 2 Leader: 3 Replicas: 3,5,6 Isr: 5,3,6 Topic: iteblog Partition: 3 Leader: 7 Replicas: 4,6,7 Isr: 7,6 Topic: iteblog Partition: 4 Leader: 5 Replicas: 5,7,0 Isr: 5,7,0 Topic: iteblog Partition: 5 Leader: 6 Replicas: 6,0,1 Isr: 0,6,1 Topic: iteblog Partition: 6 Leader: 7 Replicas: 7,1,2 Isr: 7,1 Topic: iteblog Partition: 7 Leader: 0 Replicas: 0,2,3 Isr: 0,3
启动Broker 2和Broker 4,Leader分布与上一步相比并未变化,如下图所示。
Topic:iteblog PartitionCount:8 ReplicationFactor:1 Configs: Topic: iteblog Partition: 0 Leader: 1 Replicas: 1,3,4 Isr: 3,1,4 Topic: iteblog Partition: 1 Leader: 5 Replicas: 2,4,5 Isr: 5,2,4 Topic: iteblog Partition: 2 Leader: 3 Replicas: 3,5,6 Isr: 5,3,6 Topic: iteblog Partition: 3 Leader: 7 Replicas: 4,6,7 Isr: 7,6,4 Topic: iteblog Partition: 4 Leader: 5 Replicas: 5,7,0 Isr: 5,7,0 Topic: iteblog Partition: 5 Leader: 6 Replicas: 6,0,1 Isr: 0,6,1 Topic: iteblog Partition: 6 Leader: 7 Replicas: 7,1,2 Isr: 7,1,2 Topic: iteblog Partition: 7 Leader: 0 Replicas: 0,2,3 Isr: 0,3,2
再次运行该工具,所有Partition的Leader都由其Preferred Replica承担,Leader分布更均匀——每个Broker承担1个Partition的Leader角色。
除了手动运行该工具使Leader分配均匀外,Kafka还提供了自动平衡Leader分配的功能,该功能可通过将auto.leader.rebalance.enable设置为true开启,它将周期性检查Leader分配是否平衡,若不平衡度超过一定阈值则自动由Controller尝试将各Partition的Leader设置为其Preferred Replica。检查周期由leader.imbalance.check.interval.seconds指定,不平衡度阈值由leader.imbalance.per.broker.percentage指定。
12. Kafka Reassign Partitions Tool
用途
该工具的设计目标与Preferred Replica Leader Election Tool有些类似,都旨在促进Kafka集群的负载均衡。不同的是,Preferred Replica Leader Election只能在Partition的AR范围内调整其Leader,使Leader分布均匀,而该工具还可以调整Partition的AR。
Follower需要从Leader Fetch数据以保持与Leader同步,所以仅仅保持Leader分布的平衡对整个集群的负载均衡来说是不够的。另外,生产环境下,随着负载的增大,可能需要给Kafka集群扩容。向Kafka集群中增加Broker非常简单方便,但是对于已有的Topic,并不会自动将其Partition迁移到新加入的Broker上,此时可用该工具达到此目的。某些场景下,实际负载可能远小于最初预期负载,此时可用该工具将分布在整个集群上的Partition重装分配到某些机器上,然后可以停止不需要的Broker从而实现节约资源的目的。
需要说明的是,该工具不仅可以调整Partition的AR位置,还可调整其AR数量,即改变该Topic的replication factor。
原理
该工具只负责将所需信息存入Zookeeper中相应节点,然后退出,不负责相关的具体操作,所有调整都由Controller完成。
(1)在Zookeeper上创建/admin/reassign_partitions节点,并存入目标Partition列表及其对应的目标AR列表。
(2)Controller注册在/admin/reassign_partitions上的Watch被fire,Controller获取该列表。
(3)对列表中的所有Partition,Controller会做如下操作:
- 启动
RAR - AR中的Replica,即新分配的Replica。(RAR = Reassigned Replicas, AR = Assigned Replicas) - 等待新的Replica与Leader同步
- 如果Leader不在RAR中,从RAR中选出新的Leader
- 停止并删除
AR - RAR中的Replica,即不再需要的Replica - 删除/admin/reassign_partitions节点
用法
该工具有三种使用模式
- generate模式,给定需要重新分配的Topic,自动生成reassign plan(并不执行)
- execute模式,根据指定的reassign plan重新分配Partition
- verify模式,验证重新分配Partition是否成功
下面这个例子将使用该工具将Topic的所有Partition重新分配到Broker 4/5/6/7上,步骤如下:
(1)使用generate模式,生成reassign plan。指定需要重新分配的Topic ({“topics”:[{“topic”:”topic1”}],”version”:1}),并存入/tmp/topics-to-move.json文件中,然后执行
$KAFKA_HOME/bin/kafka-reassign-partitions.sh --zookeeper localhost:2181 --topics-to-move-json-file /tmp/topics-to-move.json --broker-list "4,5,6,7" --generate
结果如下图所示
Current partition replica assignment {"version":1,"partitions":[{"topic":"iteblog","partition":2,"replicas":[3]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":6,"replicas":[1]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":7,"replicas":[2]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":0,"replicas":[1]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":8,"replicas":[3]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":5,"replicas":[3]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":4,"replicas":[2]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":3,"replicas":[1]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":1,"replicas":[2]}]} Proposed partition reassignment configuration {"version":1,"partitions":[{"topic":"iteblog","partition":6,"replicas":[3]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":2,"replicas":[3]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":7,"replicas":[2]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":0,"replicas":[3]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":8,"replicas":[3]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":5,"replicas":[2]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":4,"replicas":[3]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":1,"replicas":[2]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":3,"replicas":[2]}]}
(2)使用execute模式,执行reassign plan
将上一步生成的reassignment plan存入/tmp/reassign-plan.json文件中,并执行
$KAFKA_HOME/bin/kafka-reassign-partitions.sh
--zookeeper localhost:2181
--reassignment-json-file /tmp/reassign-plan.json --execute
Current partition replica assignment {"version":1,"partitions":[{"topic":"iteblog","partition":2,"replicas":[3]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":6,"replicas":[1]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":7,"replicas":[2]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":0,"replicas":[1]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":8,"replicas":[3]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":5,"replicas":[3]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":4,"replicas":[2]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":3,"replicas":[1]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":1,"replicas":[2]}]} Save this to use as the --reassignment-json-file option during rollback Successfully started reassignment of partitions {"version":1,"partitions":[{"topic":"iteblog","partition":2,"replicas":[3]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":6,"replicas":[3]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":7,"replicas":[2]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":0,"replicas":[3]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":8,"replicas":[3]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":4,"replicas":[3]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":5,"replicas":[2]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":3,"replicas":[2]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":1,"replicas":[2]}]}
此时,Zookeeper上/admin/reassign_partitions节点被创建,且其值与/tmp/reassign-plan.json文件的内容一致。
[zk: www.xxx.com:2181(CONNECTED) 12] get /admin/reassign_partitions
{"version":1,"partitions":[{"topic":"iteblog","partition":2,"replicas":[3]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":6,"replicas":[3]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":7,"replicas":[2]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":0,"replicas":[3]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":8,"replicas":[3]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":4,"replicas":[3]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":5,"replicas":[2]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":3,"replicas":[2]},{"topic":"iteblog","partition":1,"replicas":[2]}]}
(3)使用verify模式,验证reassign是否完成。执行verify命令
$KAFKA_HOME/bin/kafka-reassign-partitions.sh --zookeeper localhost:2181 --verify --reassignment-json-file /tmp/reassign-plan.json
Status of partition reassignment: Reassignment of partition [iteblog,4] completed successfully Reassignment of partition [iteblog,0] completed successfully Reassignment of partition [iteblog,2] completed successfully Reassignment of partition [iteblog,6] completed successfully Reassignment of partition [iteblog,7] completed successfully Reassignment of partition [iteblog,5] completed successfully Reassignment of partition [iteblog,3] completed successfully Reassignment of partition [iteblog,8] completed successfully Reassignment of partition [iteblog,1] completed successfully
接下来用Topic Tool再次验证。
bin/kafka-topics.sh --zookeeper localhost:2181 --describe --topic topic1
结果如下图所示,从图中可看出topic1的所有Partition都被重新分配到Broker 4/5/6/7,且每个Partition的AR与reassign plan一致。
Topic:iteblog PartitionCount:9 ReplicationFactor:1 Configs: Topic: iteblog Partition: 0 Leader: 3 Replicas: 3 Isr: 3 Topic: iteblog Partition: 1 Leader: 2 Replicas: 2 Isr: 2 Topic: iteblog Partition: 2 Leader: 3 Replicas: 3 Isr: 3 Topic: iteblog Partition: 3 Leader: 2 Replicas: 2 Isr: 2 Topic: iteblog Partition: 4 Leader: 3 Replicas: 3 Isr: 3 Topic: iteblog Partition: 5 Leader: 2 Replicas: 2 Isr: 2 Topic: iteblog Partition: 6 Leader: 3 Replicas: 3 Isr: 3 Topic: iteblog Partition: 7 Leader: 2 Replicas: 2 Isr: 2 Topic: iteblog Partition: 8 Leader: 3 Replicas: 3 Isr: 3
需要说明的是,在使用execute之前,并不一定要使用generate模式自动生成reassign plan,使用generate模式只是为了方便。事实上,某些场景下,generate模式生成的reassign plan并不一定能满足需求,此时用户可以自己设置reassign plan。
13. State Change Log Merge Tool
用途
该工具旨在从整个集群的Broker上收集状态改变日志,并生成一个集中的格式化的日志以帮助诊断状态改变相关的故障。每个Broker都会将其收到的状态改变相关的的指令存于名为state-change.log的日志文件中。某些情况下,Partition的Leader Election可能会出现问题,此时我们需要对整个集群的状态改变有个全局的了解从而诊断故障并解决问题。该工具将集群中相关的state-change.log日志按时间顺序合并,同时支持用户输入时间范围和目标Topic及Partition作为过滤条件,最终将格式化的结果输出。
用法
bin/kafka-run-class.sh kafka.tools.StateChangeLogMerger --logs /opt/kafka_2.11-0.8.2.1/logs/state-change.log --topic topic1 --partitions 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7