

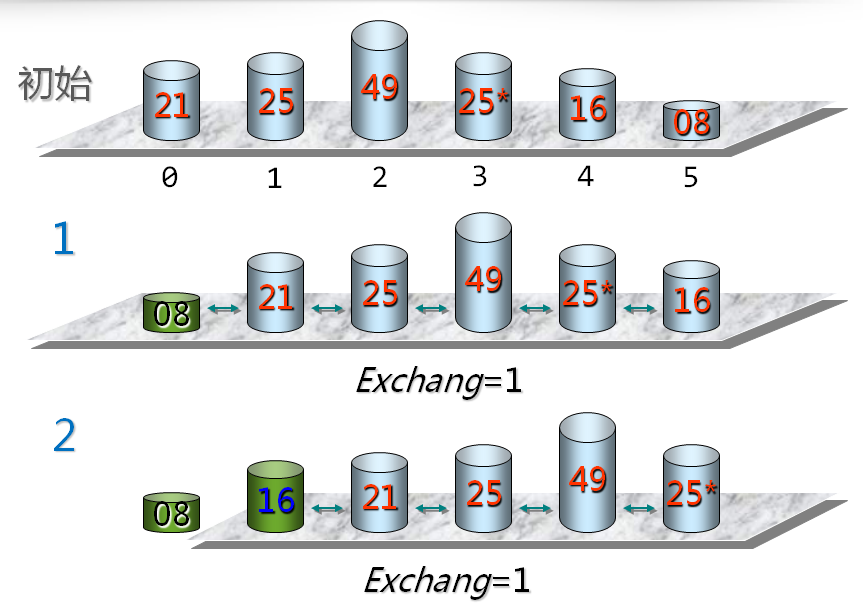
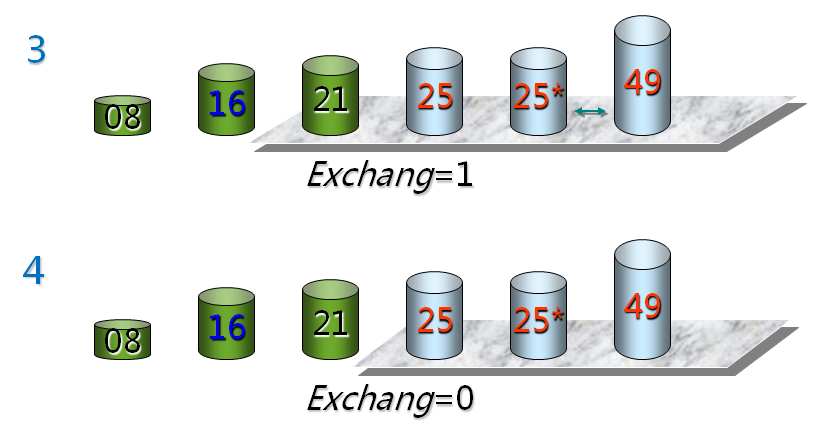
Exchang是一个标记,比较一遍的时候如果没有发生任何交换就可以结束了。
冒泡排序就是模拟泡泡从湖底到湖面的过程。
添加冒泡排序:
1 #ifndef SORT_H 2 #define SORT_H 3 4 #include "Object.h" 5 6 namespace DTLib 7 { 8 9 class Sort : public Object 10 { 11 private: 12 Sort(); 13 Sort(const Sort&); 14 Sort& operator = (const Sort&); 15 16 template <typename T> 17 static void Swap(T& a, T& b) 18 { 19 T c(a); 20 a = b; 21 b = c; 22 } 23 24 public: 25 template < typename T > 26 static void Select(T array[], int len, bool min2max=true) 27 { 28 for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) 29 { 30 int min = i; 31 for(int j = i + 1; j < len; j++) 32 { 33 if( min2max ? (array[min] > array[j]) : (array[min] < array[j]) ) 34 { 35 min = j; 36 } 37 } 38 39 if( min != i) 40 { 41 Swap(array[i], array[min]); 42 } 43 } 44 } 45 46 template < typename T > 47 static void Insert(T array[], int len, bool min2max=true) 48 { 49 for(int i=1; i < len; i++) //从1开始,第0个元素没有必要插入操作 50 { 51 int k = i; 52 T e = array[i]; 53 54 for(int j=i-1; (j>=0) && (min2max ? (array[j] > e) : (array[j] < e)); j--) 55 { 56 array[j+1] = array[j]; 57 k = j; 58 } 59 60 if( k != i ) //赋值比“比较操作耗时” 61 { 62 array[k] = e; 63 } 64 } 65 } 66 67 template < typename T > 68 static void Bubble(T array[], int len, bool min2max=true) 69 { 70 bool exchange = true; 71 72 for(int i=0; (i<len) && exchange; i++) 73 { 74 exchange = false; 75 76 for(int j=len-1; j>i; j--) 77 { 78 if(min2max ? (array[j] < array[j-1]) : (array[j] > array[j-1])) 79 { 80 Swap(array[j], array[j-1]); 81 exchange = true; 82 } 83 } 84 } 85 } 86 87 88 }; 89 90 } 91 92 #endif // SORT_H
注意:冒泡排序是稳定的

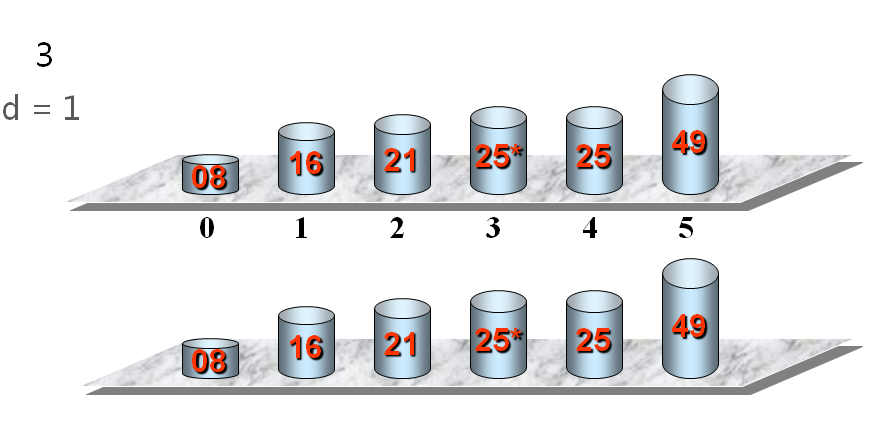
希尔做了这样一个观察:在一个序列基本有序的情况下,插入排序效率非常高。对于冒泡排序,我们做了标记,如果序列已经是基本有序的,冒泡排序效率也会提高。
希尔排序正是用了这样的思想,先让序列基本有序。
希尔思想:
先分组做插入排序,然后做一次整体的插入排序。

红圈部分不叫基本有序,蓝圈的部分才是基本有序,这跟划分分组的策略有关。

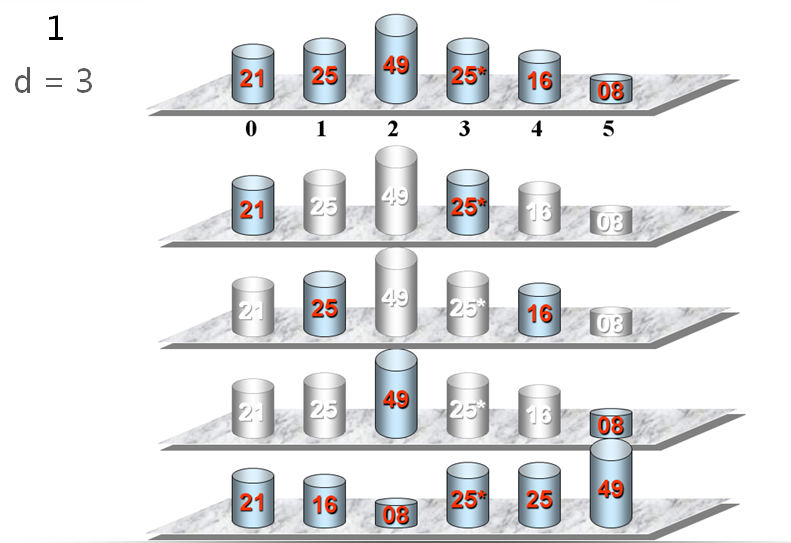
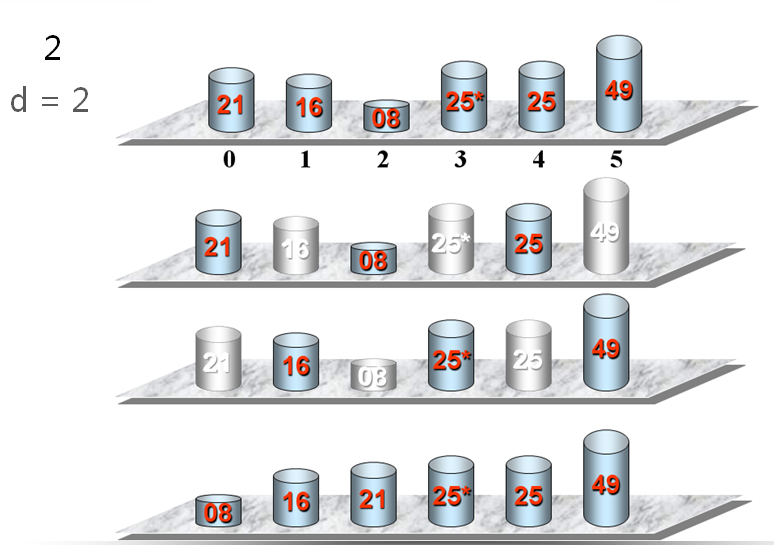
添加希尔排序:
1 #ifndef SORT_H 2 #define SORT_H 3 4 #include "Object.h" 5 6 namespace DTLib 7 { 8 9 class Sort : public Object 10 { 11 private: 12 Sort(); 13 Sort(const Sort&); 14 Sort& operator = (const Sort&); 15 16 template <typename T> 17 static void Swap(T& a, T& b) 18 { 19 T c(a); 20 a = b; 21 b = c; 22 } 23 24 public: 25 template < typename T > 26 static void Select(T array[], int len, bool min2max=true) 27 { 28 for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) 29 { 30 int min = i; 31 for(int j = i + 1; j < len; j++) 32 { 33 if( min2max ? (array[min] > array[j]) : (array[min] < array[j]) ) 34 { 35 min = j; 36 } 37 } 38 39 if( min != i) 40 { 41 Swap(array[i], array[min]); 42 } 43 } 44 } 45 46 template < typename T > 47 static void Insert(T array[], int len, bool min2max=true) 48 { 49 for(int i=1; i < len; i++) //从1开始,第0个元素没有必要插入操作 50 { 51 int k = i; 52 T e = array[i]; 53 54 for(int j=i-1; (j>=0) && (min2max ? (array[j] > e) : (array[j] < e)); j--) 55 { 56 array[j+1] = array[j]; 57 k = j; 58 } 59 60 if( k != i ) //赋值比“比较操作耗时” 61 { 62 array[k] = e; 63 } 64 } 65 } 66 67 template < typename T > 68 static void Bubble(T array[], int len, bool min2max=true) 69 { 70 bool exchange = true; 71 72 for(int i=0; (i<len) && exchange; i++) 73 { 74 exchange = false; 75 76 for(int j=len-1; j>i; j--) 77 { 78 if(min2max ? (array[j] < array[j-1]) : (array[j] > array[j-1])) 79 { 80 Swap(array[j], array[j-1]); 81 exchange = true; 82 } 83 } 84 } 85 } 86 87 template < typename T > 88 static void Shell(T array[], int len, bool min2max=true) 89 { 90 int d = len; 91 do 92 { 93 d = d / 3 + 1; //d的减小方式(实践证明这样做效果比较好) 94 95 for(int i = d; i < len; i+=d) 96 { 97 int k = i; 98 T e = array[i]; 99 100 for(int j=i-d; (j>=0) && (min2max ? (array[j] > e) : (array[j] < e)); j-=d) 101 { 102 array[j+d] = array[j]; 103 k = j; 104 } 105 106 if( k != i ) //赋值比“比较操作耗时” 107 { 108 array[k] = e; 109 } 110 } 111 112 }while( d > 1 ); 113 } 114 }; 115 116 } 117 118 #endif // SORT_H
注意:希尔排序是不稳定的
希尔排序使用了插入排序作为基本的排序法。
划分分组后,也可以使用冒泡排序作为基本的排序。
小结:
