类型识别:

为什么引入类型识别呢?因为面向对象中有一个非常重要的原则就是赋值兼容性原则,就是子类对象完全可以当成父类对象使用。
当我们拿到指针p,我们知道它到底指向子类还是父类对象吗?
p的静态类型是Base,本意是期望指向Base对象,但是由于赋值兼容性,指针有可能指向子类对象,子类对象在这里是动态类型。

想要安全的转换就要得到b实际指向的动态类型,我们需要提前判断动态类型是什么。
C++中如何得到动态类型呢?

示例程序:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 class Base 7 { 8 public: 9 virtual string type() 10 { 11 return "Base"; 12 } 13 }; 14 15 class Derived : public Base 16 { 17 public: 18 string type() 19 { 20 return "Derived"; 21 } 22 23 void printf() 24 { 25 cout << "I'm a Derived." << endl; 26 } 27 }; 28 29 class Child : public Base 30 { 31 public: 32 string type() 33 { 34 return "Child"; 35 } 36 }; 37 38 void test(Base* b) 39 { 40 /* 危险的转换方式 */ 41 // Derived* d = static_cast<Derived*>(b); 42 43 if( b->type() == "Derived" ) 44 { 45 Derived* d = static_cast<Derived*>(b); 46 47 d->printf(); 48 } 49 50 // cout << dynamic_cast<Derived*>(b) << endl; 51 } 52 53 54 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 55 { 56 Base b; 57 Derived d; 58 Child c; 59 60 test(&b); 61 test(&d); 62 test(&c); 63 64 return 0; 65 }
运行结果如下:
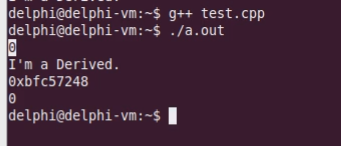
我们不仅需要知道dynamic_cast转换是不是成功,还需要知道具体的类型到底是什么,因此,dynamic_cast在这里不够用。
虚函数返回类型的方式能解决问题,但是不够好,当我们增加新类时容易和以前的重复或者混淆。
多态解决方案的缺陷:

C++的解决方案:



示例程序:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <typeinfo> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 class Base 8 { 9 public: 10 virtual ~Base() 11 { 12 } 13 }; 14 15 class Derived : public Base 16 { 17 public: 18 void printf() 19 { 20 cout << "I'm a Derived." << endl; 21 } 22 }; 23 24 void test(Base* b) 25 { 26 const type_info& tb = typeid(*b); 27 28 cout << tb.name() << endl; 29 } 30 31 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 32 { 33 int i = 0; 34 35 const type_info& tiv = typeid(i); 36 const type_info& tii = typeid(int); 37 38 cout << (tiv == tii) << endl; 39 40 Base b; 41 Derived d; 42 43 test(&b); 44 test(&d); 45 46 return 0; 47 }
typeid返回的是对象,这个对象的类型在typeinfo库中。
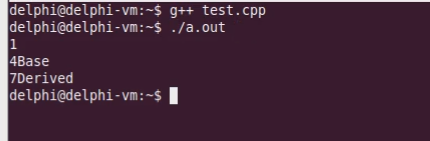
BCC中的输出如下:

可见,typeid在不同系统中的实现时不一样的,我们不能假设typeid的实现。
小结:
